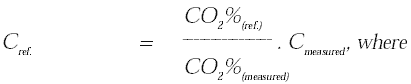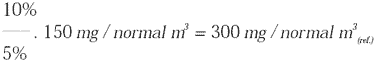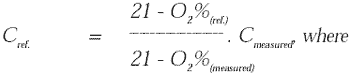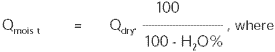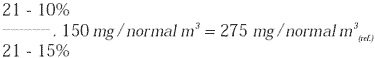| Front page | | Contents | | Previous
| | Next |
Guidelines for Air Emission Regulation
In the following, all percentages are volume % dry gas.
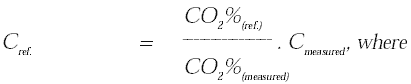
| Cref. |
= |
concentration at reference CO2% [mg
/ normal m3(ref.)] |
| Cmeasured |
= |
measured concentration [mg / normal m3(measured)] |
| CO2%(ref.) |
= |
reference CO2% [Vol%] |
| CO2%(measured) |
= |
measured CO2% [Vol%] |
If the substance is measured at a concentration of 150 mg/normal m3 at 5% CO2,
at 10% CO2 this will correspond to:
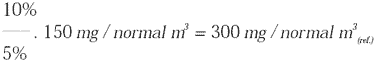
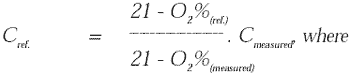
| Cref. |
= |
concentration at reference O2% [mg/normal
m3(ref.)] |
| Cmeasured |
= |
measured concentration [mg/normal m3(measured)] |
| O2%(ref.) |
= |
reference O2% [Vol%] |
| O2%(measured) |
= |
measured O2% [Vol%] |
If the substance is measured at a concentration of 150 mg/normal m3 at 15% O2,
at 10% O2 this will correspond to:
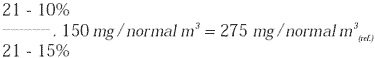
The following values for CO2%(max) can be used (for rough
calculations)
| Wood and straw: |
20% |
| Household waste: |
19% |
| Coal: |
19% |
| Heavy fuel oil: |
16% |
| Light fuel oil: |
15% |
| Natural gas: |
12% |
CO2%(max) gives CO2%, when combustion is without air
surplus.
The definition of moisture percent in the air as used in OML calculations expresses the
proportion of water vapour in relation to the total volume (the volume H2O /
total volume of air (including water vapour))74.
Conversion between the total volume and dry volume is according to the following equation:
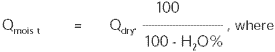
| Qmoist |
= |
the total amount of moist gas [m3,
moist / h]
|
| Qdry |
= |
amount of dry gas [m3, dry / h]
|
| H2O% |
= |
volume percentage of water vapour in relation to the total
amount of moist gas [Vol%] |
|

| Cmoist |
= |
concentration in moist gas [mg / m3,
moist]
|
| Cdry |
= |
concentration in dry gas [mg / m3,
dry]
|
| H2O% |
= |
volume percentage of water vapour in relation to the total
amount of moist gas [Vol%] |
|
 | 1 ppm SO2 |
|
= |
2.93 mg/normal m3 SO2 at 0oC
and 101.3 kPa. |
 | 1 ppm NO |
|
= |
1.34 mg/normal m3 NO at 0oC and 101.3
kPa. |
 | 1 ppm NO2 |
|
= |
2.05 mg/normal m3 NO2 at0oC
and 101.3 kPa. |
 | 1 ppm CO |
|
= |
1.25 mg/normal m3 CO at 0oC and 101.3
kPa. |
 | 1 ppm CO2 |
|
= |
1.98 mg/normal m3 CO2 at 0oC
and 101.3 kPa. |
 | 1 ppm C |
|
= |
1.87 mg/normal m3 C at 0oC and 101.3
kPa. |
 | 1 ppm HCl |
|
= |
1.63 mg/normal m3 HCl at 0oC and 101.3
kPa. |
| 1 J/s |
= |
1 W |
| 1 MJ/s |
= |
0.8598 Gcal/h |
| 1 kJ |
= |
2,778 x 10-4 kWh |
| 1 kWh |
= |
3,600 kJ |
| 1 kWh |
= |
859.8 kcal |
| 1 kcal |
= |
1.163 x 10-3kWh |
| 1 kcal |
= |
4.1868 kJ |
| peta |
(P) |
1015 |
| tera |
(T) |
1012 |
| giga |
(G) |
109 |
| mega |
(M) |
106 |
| kilo |
(k) |
103 |
| milli |
(m) |
10-3 |
| micro |
(µ) |
10-6 |
| nano |
(n) |
10-9 |
| pico |
(p) |
10-12 |
| femto |
(f) |
10-15 |
| atto |
(a) |
10-18 |
| 74 |
Moisture percentages should always be expressed as mentioned above.
Certain methods of measurement (e.g. gravimetric determination of water content) allow the
possibility of stating results as the amount of water vapour in relation to the dry volume
of air. This result should always be converted to Vol% H2O before correction.
Recalculation from "dry" Vol% H2O to Vol% H2O:
Vol% H2O = Vol% H2O(dry) * 100 / (100 + Vol% H2O(dry)). |
| Front page | | Contents | | Previous
| | Next | | Top | |