|
| Front page | | Contents | | Previous | | Next |
Survey of liquid hand soaps, including health and environmental assessments
8 Environmental assessment
8.1 Selection of substances
When selecting substances for assessment of the environmental effects of the use of liquid hand soaps, a preliminary screening of the environmental hazard of the substances was carried out. This screening
has been compared with the frequency with which the substances are contained in the products. In addition, an assessment of the approximate concentrations of the substances in the products has been
carried out based on dispensaries from other consumer products from previous surveys. When combining the hazard of the chemical substances with the frequency with which they are found in the products,
it gives an impression of which substances are expected to cause possible impacts on the aquatic environment.
From an environmental aspect surfactants and preservatives are the most interesting substances. Surfactants are the active substances found in the highest concentrations in the products. The vast majority of
surfactants used in cosmetics are readily biodegradable but are often highly acutely toxic to aquatic organisms. Furthermore, some surfactants are potentially bioaccumulative. Many preservatives are toxic to
aquatic organisms in very low concentrations and are also very difficult to degrade due to their toxic effect on the degrading bacteria.
8.1.1 Surfactants
All surfactants identified in the hand soaps are assessed to be readily biodegradable but the toxicity of the surfactants vary within the different groups of surfactants. As described earlier, particularly two
surfactants are found in the majority of the products. The anionic surfactant Sodium laureth sulfate is found in 39 out of 50 products, and the amphoteric surfactant Cocamidopropyl betaine is found in 31 out
of 50 products. These two substances cannot be characterized as environmentally hazardous but they have been included in the environmental assessment as they occur with the highest frequency and in the
highest concentrations in the products (apart from water).
In addition, Cocamide DEA and Cocamide MEA have been selected as they are found in several of the products (14 and 8 products, respectively). The majority of the remaining surfactants are only found
in a few products and are not estimated to contribute significantly to the overall chemical impact.
8.1.2 Preservatives
Most of the identified preservatives are found to have a low frequency in the products. The most common preservatives are Sodium benzoate (15 of 50 products), Phenoxyethanol (12 of 50 products) and
Dehydroacetic acid (7 of 50 products). None of these three preservatives can be described as critical to the environment. Each of the remaining preservatives are only found in few of the products.
The preservatives with the most critical environmental properties are 2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane-1,3-Diol, Methylchloroisothiazolinone and Methylisothiazolinone (Kathon) (found in common liquid hand
soaps) as well as Chlorhexidine Digluconate, Benzalkonium Chloride and Triclosan (found in anti-bacterial hand soaps). Only limited data are available on DMDM Hydantoin and Imidazolidonyl Urea (found
in common liquid hand soaps). Focus have been concentrated on some of the preservatives in common hand soaps as these make up the largest product volume.
8.1.3 Environmental assessment of selected substances
The following 8 substances have been selected for further environmental assessment (table 8.1):
Table 8.1 Substances selected for environmental assessment
| Type of substance |
Substance |
Estimated concentration in the products* |
Substance found in number of products** |
CAS No. |
| Surfactants |
Sodium laureth sulfate |
5-15% |
39 |
9004-82-4 |
| Cocamidopropyl Betaine |
1-5% |
31 |
61789-40-0 |
| Cocamide DEA |
1-5% |
14 |
68603-42-9 |
| Cocamide MEA |
1-5% |
8 |
68140-00-1 |
| Preservatives |
Methylchloroisothiazolinone |
<0.001- |
4 |
26172-55-4 |
| Methylisothiazolinone |
<0.001 |
4 |
2682-20-44 |
| DMDM Hydantoin |
0.1-0.5% |
4 |
6440-58-0 |
| 2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane-1,3-Diol |
0.01-0.05% |
3 |
52-51-7 |
* Estimated from dispensaries from liquid hand soaps collected in previous projects
** Of the 50 products covered by the survey.
The environmental properties of the selected substances are described according to their biodegradability, acute toxicity to aquatic organisms, and the potential for bioaccumulation according to the
regulations for classification and labelling of chemical substances (33). Below the physical/chemical properties of the substances have been estimated by means of the program EPIWIN v. 3.12 (USEPA,
2004). The water/octanol partition coefficient (log Pow) has been used as a measure for the potential for bioaccumulation of the substances. According to the regulations on classification and labelling of
chemical substances and products (32), a substance is considered potentially bioaccumulative when the log Pow > 3.
8.2 Environmental profiles of the selected substances
8.2.1 Sodium laureth sulfate
Occurrence and use
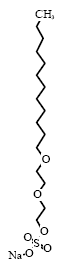
Sodium laureth sulfate is an anionic surfactant (group: alkyl ether sulfate) which is found in 39 of the 50 products in the survey. Typically, Sodium laureth sulphate is used in cosmetics such as liquid hand
soaps, liquid body soaps and shampoos (34).
Identification
Sodium laureth sulfate is composed of an alkyl chain, typically with 12-14 carbon atoms which are combined with a number of ethoxylate (EO) groups via an ester linkage.
| INCI name |
Sodium Laureth Sulfate |
| Synonyms |
Poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl), .alpha.-sulfo-.omega.-(dodecyloxy)-, sodium salt |
| CAS No. |
9004-82-4 |
| EINECS No. |
221-416-0 |
| Molecular
formula |
C16H33O6SNa* |
| Molecular
structure |
 |
Regulations:
Classification
according to
the List of
hazardous
substances
(Danish
Statutory
Order 923 of
28
September
2005) (8)
The list of
unwanted
substances.
Danish
Environmental
Protection
Agency (21)
Cosmetics (1) |
Not classified
Not included on
the list
To be stated by INCI name |
* Generic structure: Sodium laureth sulfate C12, 2EO
Physical-chemical properties *
| Physical state |
Liquid |
| Molecular weight (g/mol) |
376.49 |
| Melting point, °C |
286.89 |
| Boiling point, °CC |
659.05 |
| Evaporation (Pa) |
2.57E-015 |
| Octanol-water dispersion (log Pow) |
1.14 |
| Water-solubility (mg/L) |
451.6 |
Environmental assessment
Sodium laureth sulfate is fully degradable in a 28-day standard test for ready biodegradability. Sodium laureth sulfate is also degradable under anaerobic conditions. The acute effect of Sodium laureth sulfate
to aquatic organisms can be described as toxic to moderately toxic with EC/LC50 values between 1.2-32 mg/l. The lowest EC50 value of 1.2 mg/l is found for daphnia in a 96-hour test. NOEC values < 1
mg/l have been found in chronic tests with daphnia (21 days) and fish (365 days) (34). With an estimated log Pow value of 1.14 the substance is not assessed to bioaccumulate. As the substance is expected
to be fully degraded in waste water treatment plants, Sodium laureth sulfate is assessed not to cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment.
8.2.2 Cocamidopropyl betain
Occurrence and use
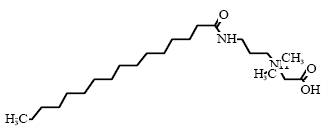
Cocamidopropyl betain is an amphoteric surfactant (group: betains) which is found in 31 of the 50 products in the survey. Cocamidopropylbetain is typically used in products for personal care such as liquid
hand soaps, liquid body soaps, cleansing creams, and shampoos but it is also used in detergents and cleaning materials (34).
Identification
Cocamidopropyl betain is composed of an alkyl chain which is combined with a quaternary nitrogen atom through an amide linkage.
| INCI name |
Cocamidopropyl Betain |
| Synonyms |
1-Propanaminium, 3-amino-N-(carboxymethyl)-N,N-dimethyl-, N-coco acyl derives., hydroxides, inner salts |
| CAS No. |
61789-40-0 |
| EINECS No. |
263-058-8 |
| Molecular
formula |
C23H47N2O3* |
| Molecular
structure |
 |
Regulations:
Classification
according to
the List of
hazardous
substances
(Danish
Statutory
Order 923 of
28
September
2005) (8)
The list of
unwanted
substances.
Danish
Environmental
Protection
Agency (21)
Cosmetics (1) |
Not classified
Not included on the list
To be stated by INCI name |
* Generic structure, C16 alkyl chain
Physical-chemical properties *
| Physical state |
Liquid |
| Molecular weight (g/mol) |
399.64 |
| Melting point, °C |
304.64 |
| Boiling point, °C |
697.05 |
| Evaporation (Pa) |
1.49E-16 |
| Octanol-water dispersion (log Pow) |
2.65 |
| Water-solubility (mg/L) |
16.75 |
* Estimated data for Cocamidopropylbetain, C16 (ref: EPISUITE v. 3.12, USEPA, 2004)
Environmental assessment
Cocamidopropyl betain is fully degradable in a 28-day standard test for ready biodegradability. Cocamidopropyl betain is also degradable under anaerobic conditions. The acute effect of Cocamidopropyl
betain to aquatic organisms can be described as toxic to moderately toxic with EC/LC50 values between 1.8-22 mg/l. The lowest EC50 value of 1.8 mg/l is found for algae in a 72-hour test. There is no
available data on the chronic toxicity of Cocamidopropyl betain (34). With an estimated log Pow value of 2.65 the substance is not assessed to bioaccumulate. As the substance is expected to be fully
degraded in waste water treatment plants, Cocamidopropyl betain is assessed not to cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment.
8.2.3 Cocamide DEA/Cocamide MEA
Occurrence and use
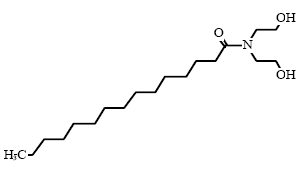
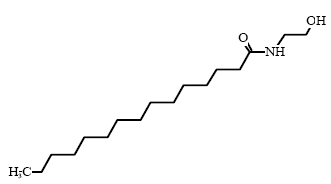
Cocamide DEA and Cocamide MEA are nonionic surfactants (group: fatty acid amides) and they are found in 14 and 8 respectively of the 50 products in this survey. Typically, fatty acid amides are used in
products for personal care such as liquid hand soaps, liquid body soaps, shaving creams, and shampoos (34).
Identification
Cocamide DEA/Cocamide MEA is composed of an alkyl chain which is combined with two or one amide group through an C-N linkage.
| INCI name |
Cocamide DEA |
| Synonyms |
Amides, coco, N,N-bis(hydroxyethyl)- |
| CAS No. |
68603-42-9 |
| EINECS No. |
271-657-0 |
| Molecular
formula |
C19 H39 N O3 |
| Molecular
structure |
 |
Regulations:
Classification
according to
the List of
hazardous
substances
(Danish
Statutory
Order 923 of
28
September
2005) (8)
The list of
unwanted
substances.
Danish
Environmental
Protection
Agency (21)
Cosmetics (1) |
Not classified
Not included on
the list
To be stated by INCI name |
* Generic structure, C15 alkyl chain
Physical-chemical properties *
| Physical state |
Liquid |
| Molecular weight (g/mol) |
329.53 |
| Melting point, °C |
179.84 |
| Boiling point, °C |
465.45 |
| Evaporation (Pa) |
1.81E-11 |
| Octanol-water dispersion (log Pow) |
4.36 |
| Water-solubility (mg/L) |
1.56 |
* Estimated data for Cocamide DEA, C15 (ref: EPISUITE v. 3.12, USEPA, 2004)
| INCI name |
Cocamide MEA |
| Synonyms |
Amides, coco, N-(hydroxyethyl) |
| CAS No. |
68140-00-1 |
| EINECS No. |
2687702 |
| Molecular
formula |
C17H35NO2 |
| Molecular
structure |
 |
Regulations:
Classification
according to
the List of
hazardous
substances
(Danish
Statutory
Order 923 of
28
September
2005) (8)
The list of
unwanted
substances.
Danish
Environmental
Protection
Agency (21)
Cosmetics (1) |
Not classified
Not included on
the list
To be stated by INCI name |
* Generic structure, C15 alkyl chain
Physical-chemical properties *
| Physical state |
Liquid |
| Molecular weight (g/mol) |
285.47 |
| Melting point, °C |
170.82 |
| Boiling point, °C |
439.30 |
| Evaporation (Pa) |
3.95E-10 |
| Octanol-water dispersion (log Pow) |
4.71 |
| Water-solubility (mg/L) |
1.40 |
* Estimated data for Cocamide MEA, C15 (ref: EPISUITE v. 3.12, USEPA, 2004)
Environmental assessment
Both Cocamide DEA and Cocamide MEA are fully degradable in a 28-day standard test for biodegradability and are thus described as readily biodegradable (34). Cocamide MEA is found to be
anaerobically biodegradable (34) whereas Cocamide DEA in a test for anaerobic biodegradability had an inhibiting effect on the degrading bacteria (35). Cocamide DEA and Cocamide MEA can be
described as toxic to moderately toxic to aquatic organisms with EC/LC50 values between 2-6 mg/l for Cocamide DEA and 24->100 mg/l for Cocamide MEA. The lowest EC50 value for Cocamide DEA
of 2.3 mg/l is found for algae in a 96-hour test. Generally, Cocamide MEA is less toxic with the lowest EC50 value of 26 mg/l for algae (34). There is no available data on the chronic toxicity of neither
Cocamide DEA nor Cocamide MEA. With estimated log Pow values >4 for both Cocamide DEA and Cocamide MEA, the substances are assessed to be potentially bioaccumulative. Cocamide DEA will
thus be classified as hazardous to the environment with N; R51/53 (Toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment) because of the acute toxicity of the substance
and its potential for bioaccumulation. However, Cocamide MEA will not be classified as hazardous to the environment as the substance is only moderately toxic (>10 mg/l).
8.2.4 Methylchloroisothiazolinone/Methylisothiazolinone (Kathon)
Occurrence and use
Methylchloroisothiazolinone and Methylisothiazolinone form part of the commercial product Kathon, which is often used as a preservative in cosmetics and cleaning materials. Kathon is found in 4 of the 50
products in this survey.
Identification
Methylchloroisothiazolinone and Methylisothiazolinone are heterocyclic aromatic compounds.
| INCI name |
Methylchloroisothiazolinone |
| Synonyms |
5-Chloro-2-Methyl-4-Isothiazolin-3-One |
| CAS No. |
26172-55-4 |
| EINECS No. |
247-500-7 |
| Molecular formula |
C4H4ClNOS |
| Molecular structure |
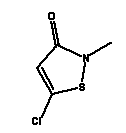 |
Regulations:
Classification according to the
List of hazardous substances (Danish Statutory Order 923 of 28 September 2005)
(8)
The list of unwanted substances. Danish Environmental Protection Agency (21)
Cosmetics
(1) |
Kathon is classified T;R23/24/25 C;R34
R43 N;R50/53
Not included on the list
To be stated by INCI name
The highest permitted concentration of Kathon in cosmetics
is 0.0015% |
Physical-chemical properties *
| Physical state |
No available data |
| Molecular weight (g/mol) |
149.6 |
| Melting point, °C |
68.91 |
| Boiling point, °C |
262.46 |
| Evaporation (Pa) |
0.0054 |
| Octanol-water dispersion (log Pow) |
-0.34 |
| Water-solubility (mg/L) |
Easily soluble |
* Estimated data (ref: EPISUITE v. 3.12, USEPA, 2004)
| INCI name |
Methylisothiazolinone |
| Synonyms |
2-Methyl-4-Isothiazolin-3-one |
| CAS No. |
2682-20-4 |
| EINECS No. |
220-239-6 |
| Molecular formula |
C4H5NOS |
| Molecular structure |
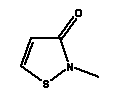 |
Regulations:
Classification according to the
List of hazardous substances (Danish Statutory Order 923 of 28 September 2005)
(8)
The list of unwanted substances. Danish Environmental Protection Agency (21)
Cosmetics
(1) |
Kathon is classified T;R23/24/25 C;R34
R43 N;R50/53
Not included on the list
To be stated by INCI name
The highest permitted concentration of Kathon in cosmetics
is 0.0015% |
Physical-chemical properties *
| Physical state |
No available data |
| Molecular weight (g/mol) |
115.15 |
| Melting point, °C |
47.48 |
| Boiling point, °C |
237.75 |
| Evaporation (Pa) |
0.031 |
| Octanol-water dispersion (log Pow) |
-0.83 |
| Water-solubility (mg/L) |
Easily soluble |
* Estimated data (ref: EPISUITE v. 3.12, USEPA, 2004)
Environmental assessment
Methylisothiazolinene and Methylchloroisothiazolinone are not readily biodegradable and have not been proven to be degradable under anaerobic conditions. Both Methylisothiazolinene and
Methylchloroisothiazolinone have a high acute toxicity and consequently they show inhibiting effects on the degrading bacteria in tests for ready biodegradability. In a modified test for ready biodegradability
in which very low concentrations of 14C labelled Methylisothiazolinene and Methylchloroisothiazolinone were used, a relatively high degree of degradability was observed corresponding to approx. 40-60%
of the added radioactivity (34). Both substances have high acute toxicity to aquatic organisms with EC/LC50 values <1 mg/l. The lowest EC50 value of 0.003 mg/l is found for algae for the commercial
product Kathon. There is no available data on the chronic toxicity of Methylisothiazolinene and Methylchloroisothiazolinone. None of the substances are assessed to be bioaccumulative as the estimated
partition coefficients (log Pow) values are <0. Kathon is classified as hazardous to the environment with N; R50/53 (Very toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic
environment) on the list of unwanted substances.
8.2.5 DMDM Hydantoin
Occurrence and use
DMDM Hydantoin is found in 4 of the 50 products in this survey. DMDM Hydantoin is typically used as a preservative in cosmetics.
Identification
DMDM Hydantoin is a heterocyclic aromatic compound.
| INCI name |
DMDM Hydantoin |
| Synonyms |
1,3-bis (hydroxymethyl)-5,5-dimethyl-2,4-imidazolidinedione |
| CAS No. |
6440-58-0 |
| EINECS No. |
229-222-8 |
| Molecular formula |
C7H12N2O4 |
| Molecular structure |
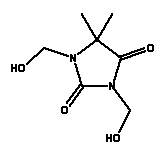 |
Regulations:
Classification according to the
List of hazardous substances (Danish Statutory Order 923 of 28 September 2005)
(8)
The list of unwanted substances. Danish Environmental Protection Agency (21)
Cosmetics
(1) |
Not classified
Not included on the list
To be stated by INCI name
The highest permitted concentration of DMDM Hydantoin
in cosmetics is 0.6%. |
Physical-chemical properties *
| Physical state |
No available data |
| Molecular weight (g/mol) |
188.18 |
| Melting point, °C |
171.27 |
| Boiling point, °C |
411.53 |
| Evaporation (Pa) |
1.06E-09 |
| Octanol-water dispersion (log Pow) |
-2.37 |
| Water-solubility (mg/L) |
Easily soluble |
* Estimated data (ref: EPISUITE v. 3.12, USEPA, 2004)
Environmental assessment
There is no available data neither for the ready biodegradability nor the anaerobic biodegradability of DMDM Hydantoin. QSAR calculations of the biodegradability of DMDM Hydantoin under aerobic
conditions indicate that the substance can be expected to degrade quickly in the environment (EPISUITE v. 3.12, USEPA, 2004). There are few experimental data on the aquatic toxicity of DMDM
Hydantoin. EC50 values of 37 mg/l for daphnia have been found in a 96-hour test, and LC50 values for fish between 173-515 mg/l have been found in a 96-hour test (36). The substance is assessed to be
hazardous to aquatic organisms as the lowest EC50 value is below 100 mg/L. It has not been possible to find data for the chronic toxicity of DMDM Hydantoin. Based on the estimated partition coefficient
(log Pow) value of -2.37, DMDM Hydantoin is not assessed to be bioaccumulative. Provided that DMDM Hydantoin is degraded quickly in the environment, the substance is assessed not to be critical to
the aquatic environment. However, additional data for the biodegradability and for the aquatic toxicity to algae are required to finally assess whether DMDM Hydantoin can be expected to cause adverse
effects in the aquatic environment.
8.2.6 2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane-1,3-Diol (Bronopol)
Occurrence and use
2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane-1,3-Diol is found in 3 of the 50 products in this survey. 2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane-1,3-Diol is used as a preservative in cosmetics and in cleaning materials (34).
Identification
2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane-1,3-Diol is a nitro-substituted compound.
| INCI name |
2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane-1,3-Diol |
| Synonyms |
Bronopol |
| CAS No. |
52-51-7 |
| EINECS No. |
200-143-0 |
| Molecular formula |
C3H6BrNO4 |
| Molecular structure |
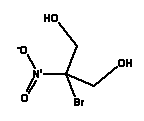 |
Regulations:
Classification according to the
List of hazardous substances (Danish Statutory Order 923 of 28 September 2005)
(8)
The list of unwanted substances. Danish Environmental Protection Agency (21)
Cosmetics
(1) |
Xn;R21/22 Xi;R37/38-41 N;R50
Not included
on the list
To be stated by INCI name
The highest permitted concentration of Bronopol in cosmetics
is 0.1%. |
Physical-chemical properties *
| Physical state |
Crystal |
| Molecular weight (g/mol) |
199.99 |
| Melting point, C |
90.86 |
| Boiling point, C |
300.57 |
| Evaporation (Pa) |
6.06E-06 |
| Octanol-water dispersion (log Pow) |
-0.64 |
| Water-solubility (mg/L) |
Easily soluble |
* Estimated data (ref: EPISUITE v. 3.12, USEPA, 2004)
Environmental assessment
There is no available data for the ready biodegradability of 2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane-1,3-Diol. A standard test for ready biodegradability shows an inhibition of the degrading bacteria as a result of the high
toxicity of 2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane-1,3-Diol (34). 2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane-1,3-Diol is classified with N; R50 (Very toxic to aquatic organisms) on the list of unwanted substances and consequently it is
assumed to be easily biodegradable as it is not classified with R53 (May cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment). 2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane-1,3-Diol has high acute toxicity to aquatic
organisms. The lowest EC50 value of 0.37 is found in a 72-hour test with algae. EC50 values between 1-10 mg/l have been found for crustaceans, while fish are less sensitive to
2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane-1,3-Diol with typical LC50 values between 20-60 mg/L (34). No available data for the chronic toxicity of 2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane-1,3-Diol have been found. With an estimated
partition coefficient (log Pow) value of -0.64, 2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane-1,3-Diol is not assessed to be bioaccumulative.
| Front page | | Contents | | Previous | | Next | | Top |
Version 1.0 June 2006, © Danish Environmental Protection Agency
|