|
|
Toxicological evaluation and limit values for Methyl-tertiary-butyl ether (MTBE), Formaldehyde, Glutaraldehyde, Furfural
1. General description
1.1 Identity
Molecular formula: C5H4O2
Structural formula:
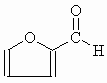
| Molecular weight: | 96.08 |
| CAS-no.: | 98-01-1 |
| Synonyms: | 2-Furaldehyde 2-Furancarboxaldehyde 2-Furfuraldehyde 2-Formylfuran Furfurol |
1.2 Physical / chemical properties
| Description: | Pure furfural is a clear, colourless, oily liquid with a pungent, aromatic odour resembling that of bitter almonds. Turns yellow to brown on exposure to air and light. |
| Purity: | Furfural is available commercially at a purity >98%. |
| Melting point: | -36.5° C |
| Boiling point: | 161.8° C (at 760 mmHg) |
| Density: | 1.1598g/ml (at 20° C) |
| Vapour pressure: | 1 mmHg (133 Pa) at 20° C |
| Concentration of saturated vapours: | 0.13% at 20° C and 760 mmHg |
| Vapour density: | 3.31 (air = 1) |
| Conversion factor: | 1 ppm = 4.0 mg/m3 20° C 1 mg/m3 = 0.25 ppm 1 atm |
| Flash point: | 60° C (closed cup), 68 ° C (open cup) |
| Flammable limits: | 2.1 - 19.3 (v/v% in air) |
| Autoignition temp.: | 392° C |
| Water Solubility: | 83 g/l (at 20° C). Miscible with most of the common organic solvents, only slightly miscible with saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons. |
| logPoctanol/water: | 0.41 |
| Henry’s constant: | - |
| pKa-value: | - |
| Stability: | Furfural is very thermally stable in the absence of oxygen. |
| Incompatibilities: | Can react with oxidising materials. A resinification of almost explosive violence can occur upon contact with strong mineral acids or alkalies. |
| Odour threshold, air: | 0.078 ppm (Amoore & Hautala 1983). |
| Odour threshold, water: | 3.5 mg/l (Amoore & Hautala 1983). |
| References: | Merck Index (1976), ACGIH (1991), HSDB (1995), Brabec (1994), Kirk-Othmer (1985), A&H (1984), IARC (1995), NTP (1990). |
1.3 Production and use
Furfural is prepared industrially from pentosans present in cereal straws and brans by hydrolysis and dehydration with strong inorganic acids (IARC 1995, Brabec 1994, NTP 1990).
Furfural is extensively used in solvent extraction in the petroleum refining industry. It is also used as a solvent (for nitrated cotton, cellulose acetate and gums), to accelerate vulcanisation, as an ingredient of phenolic resins, as an intermediate in the synthesis of furan derivatives, as a weed killer, and as a fungicide. Furfural is also used as a flavouring agent. (IARC 1995, Brabec 1994, ACGIH 1991, NTP 1990, A&H 1984).
1.4 Environmental occurrence
Furfural is a volatile component of a wide range of fruits and vegetables (IARC 1995).
Air
Furfural has been identified as one of the main components of smoke condensates of pine and cottonwood. It was a major constituent of glowing fires of conifer logs. Residential burning of brown-coal briquettes led to emission of furfural, at an emission factor of 1.63 mg/kg. The estimated total amount of furfural emitted in the city of Leipzig was 530 kg/year. Furfural has been measured at a concentration of 0.19 mg/m3 at the foot of Mount Everest in Nepal. (IARC 1995).
Water
No data have been found.
Soil
No data have been found.
Foodstuffs
Furfural is formed during the thermal decomposition of carbohydrates and is thus found in numerous processed food and beverage products. It is also carried over into food from its use as an extraction solvent or as a component of flavour mixtures. The highest reported concentrations were found in wheat bread (0.8-14 mg/kg), cognac (0.6-33 mg/kg), rum (22 mg/kg), malt whisky (10-37 mg/kg), port wine (2-34 mg/kg), and coffee (55-255 mg/kg). The concentrations of furfural in juices were 0.01-4.94 mg/kg. (IARC 1995, JECFA 1993).
1.5 Environmental fate
No data have been found.
1.6 Human exposure
Food additive or processing use provides an intake estimated to be no more than 0.5-1% of the intake from other food sources (JECFA 1993).
No other data concerning human exposure have been found.
|
[Front page] [Contents] [Previous] [Next] [Top] |