|
Environmental Assistance to Eastern Europa - Annual Report 1998
Appendix 1: Selected data on domestic and external environmental finance in CEEC/NIS
Appendix 1: Selected data on domestic and external environmental finance in CEEC/NIS
Appendix 1: Selected data on domestic and external environmental finance in CEEC/NIS
Table 1. Domestic pollution abatement and control investments in selected CEEC/NIS, as a share of GDP, 1990-96 (in per cent)
|
1990 |
1991 |
1992 |
1993 |
1994 |
1995 |
1996 |
|
|
Georgia |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.00 |
0.00 |
|
Hungary |
- |
0.39 |
0.66 |
0.52 |
0.80 |
0.55 |
0.61 |
|
Lithuania |
- |
- |
- |
0.87 |
1.03 |
0.79 |
0.46 |
|
Poland |
0.70 |
1.01 |
1.04 |
0.97 |
1.01 |
1.11 |
- |
|
Russia |
- |
- |
0.28 |
0.34 |
0.39 |
0.39 |
0.36 |
|
Slovenia |
- |
- |
0.16 |
0.30 |
0.61 |
0.44 |
- |
|
Netherlands |
- |
0.55 |
0.62 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
Portugal |
0.48 |
- |
- |
- |
0.40 |
- |
- |
|
Germany |
- |
- |
- |
0.54 |
- |
- |
- |
-
OECD defines pollution abatement and control (PAC) activities as purposeful activities aimed directly at the prevention, reduction and elimination of pollution or nuisances arising as a residual of production processes or the consumption of goods and services. This definition specifically excludes expenditure on natural resource management and activities such as the protection of endangered species (fauna and flora), the establishment of natural parks and green belts and activities to exploit natural resources (such as the supply of drinking water). (OECD, Pollution Abatement and Control Expenditure in OECD Countries, 1998.) This methodology has been used to collect comparable data from the six case study countries, as national definitions of environmental expenditures vary. OECD regularly collects data on Member countries using this methodology.
-
External assistance and finance are, in principle, not included in this table or in figures 1, 2 and 3 which concern domestic finance.
Source: OECD and COWI based on national statistics.
Figure 1. Trends in domestic pollution abatement and control investments, 1990-96. (Index using constant domestic prices, with 1993 = 100)
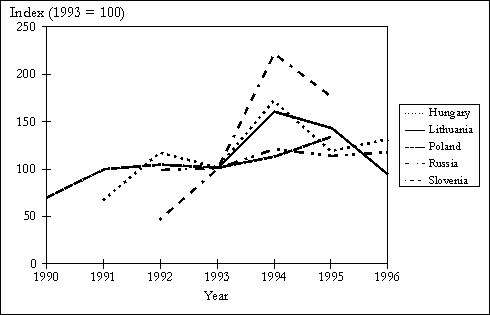
Source: COWI based on official national statistics.
Figure 2. National pollution abatement and control investment per capita, 1996 (in US$, using PPP exchange rates)1
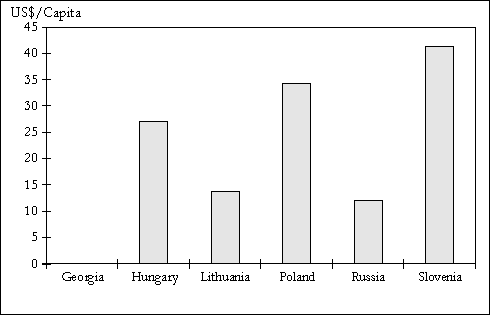
-
1995 data has been used for Poland. Source: COWI based on national statistics.
Figure 3. Share of Environmental Fund spending in total PAC Investments, 1990-96
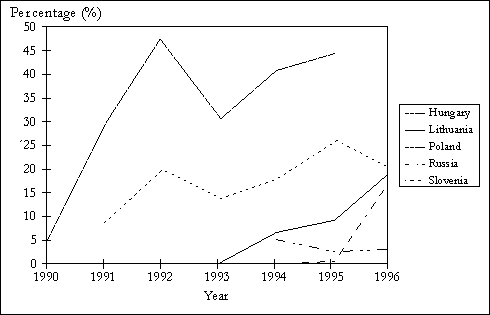
For Slovenia, 1996 data are estimates. Georgia does not have an environmental fund. Sources: COWI.
Table 2. Trends in Donor/IFI Commitments for Environmental Assistance and Finance
|
Typea |
1994 |
1995 |
1996 |
19971 |
Total |
|
|
Bilateral Donors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Austria |
.. |
14.1 |
3.4 |
5.4 |
.. |
22.9 |
|
International Financial |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EBRD env. components |
|
|
|
|
|
..data not available. a) G-grants; L-loans; S-soft loans; E- equity; O-export credits and other forms of assistance.
-
Some responses are incomplete for 1997.
-
1994: 123 mECU loans; 1995: 20.3 mECU export credits.
-
1995 data include grant equivalent of soft loans. Data do not include the Danish environmental investment facility, created in 1995. Through 1996, the facility provided 3.7 mECU in equity and 6.6 mECU in loans.
-
Preliminary data for the Swedish EPA and Swedish International Development Agency only. Includes some energy projects. Due to a change in fiscal year, part of 1995 data are included in 1996; not included in subsequent figures and tables.
-
Data include only technical assistance grants through the Environmental Know How Fund.
-
Preliminary data. May include some double counting.
-
Technical assistance only.
-
EIB signed 555 mECU of projects with significant environmental benefits in 1997, including 425 mECU for flood damage reconstruction. Data on such projects in previous years are not available.
-
World Bank loans to Turkmenistan not included.
-
Values of environmental components only, as calculated by EBRD. 1994 data are not available.
-
Total values of loans with environmental components.
Source: OECD, based on donor and IFI data.
Figure 4. Trends in External Environmental Assistance and Finance to CEECs and NIS a
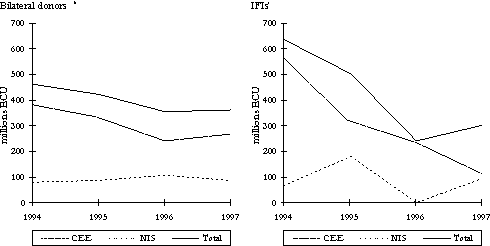
-
Totals are larger than sum of technical assistance and investments, as some donors did not classify commitments.
-
Includes EC. Some responses are incomplete for 1997.
-
Environmental projects only.
Source: OECD, based on donor and IFI data
Table 3. Donor/IFI Commitments for Environmental Investments by Sector (mECU)
|
|
1994 |
1995 |
1996 |
19971 |
|
Air/energy |
488.93 |
384.84 |
53.99 |
94.87 |
|
Water |
143.10 |
133.09 |
198.01 |
177.79 |
|
Waste |
58.76 |
0.43 |
10.04 |
12.96 |
|
Biodiversity |
6.86 |
5.16 |
39.56 |
5.31 |
|
Other2 |
5.65 |
15.08 |
31.86 |
67.49 |
|
Total |
703.30 |
538.60 |
533.46 |
358.42 |
-
Preliminary data
-
Includes commitments to environmental funds
Source: OECD, based on donor and IFI data.
Table 4. Donor/IFI Commitments of Environmental Assistance and Finance to CEECs and NIS3 by Recipient Country (1994-1997)
|
Partner Country |
Technical Co-operation |
Invest- |
Totalb |
Total |
|
|
Policy |
Investment |
||||
|
Albania |
20.7 |
0.9 |
24.9 |
60.5 |
17.9 |
|
Armenia |
0.1 |
0.3 |
0.0 |
0.4 |
0.1 |
|
Region CEE +
NIS |
11.6 |
2.2 |
0.0 |
13.7 |
|
-
Preliminary data.
-
Totals are larger than sum of technical assistance and investments, as some donors did not classify commitments.
-
Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia.
Source: OECD, based on donor and IFI data.
Table 5. Foreign Direct Investment to CEEC/NIS:
The five main recipient countries
|
FDI inflows 1996 |
FDI inflows per capita 1996 |
Cumulative |
|
|
Czech Republic |
1.264 |
123 |
7.120 |
|
Hungary |
1.986 |
195 |
13.260 |
|
Poland |
2.741 |
71 |
5.398 |
|
Kazakhstan |
1.100 |
67 |
3.067 |
|
Russia |
2.040 |
14 |
5.843 |
|
Total - 5 main reciept. |
|
|
|
|
Total for all CEEC/NIS |
12.330 |
31 |
43.888 |
Source: EBRD
[Front page] [Contents] [Previous] [Next] [Top] |