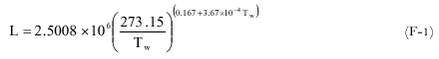Dry deposition and spray drift of pesticides to nearby water bodies
Appendix F. Parameters necessary to calculate the drop temperature and the ventilation coefficient for water vapourLatent heat of evaporation of waterDiffusivity of water vapour in air Thermal conductivity of air Saturation pressure of water vapour References Latent heat of evaporation of waterThe latent heat of evaporation of water L (J kg-1)between –40° C and 40° C (J kg-1) is given by:
where Tw is the water temperature (K). Diffusivity of water vapour in airThe diffusivity of water vapour in air Dwa (m2 s-1) is given by (Pruppacher and Klett, 1997):
where: Tw = water temperature (K) Thermal conductivity of airThe thermal conductivity of moist air ka (J m-1 s-1 K-1) is almost the same as the thermal conductivity of dry air. The thermal conductivity of dry air (J m-1 s-1 K-1) is given by (Pruppacher and Klett, 1997):
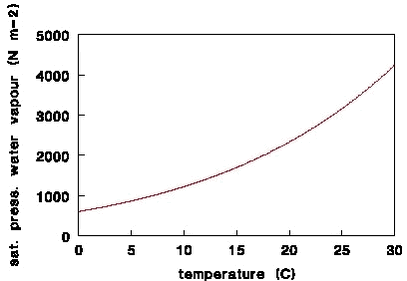
where ta is the air temperature (C). Saturation pressure of water vapourThe saturation pressure of water vapour above liquid water psat (N m-2) between - 50 ° C and 50° C is given by (Pruppacher and Klett, 1997):
where:
Figure F-1. Saturation pressure of water vapour as a function of temperature. ReferencesPruppacher, H.R., Klett, J.D. (1997) Microphysics of clouds and precipitation. Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands. |