Working Report No. 1, 2009
Survey on planning and development of new cities and areas in China
Contents
1 Procedures of a new city planning project
- 2.1 Outline mapping and location
- 2.1.1 Bejing
- 2.1.2 Tianjin
- 2.1.3 Hebei Province
- 2.1.4 Henan Province
- 2.1.5 Shanxi Province
- 2.1.6 Liaoning Province
- 2.1.7 Jiangxi Province
- 2.1.8 Shandong Province
- 2.1.9 Inner Mongolia
- 2.1.10 Anhui Province
- 2.1.11 Shanghai
- 2.1.12 Zhejiang Province
- 2.1.13 Jiangsu Province
- 2.1.14 Chongqing
- 2.1.15 Guangdong Province
- 2.1.16 Hainan Province
3 More in depth description of 11 projects
-
- 3.1.1 Beijing Shunyi New City
- 3.1.2 Beijing Tongzhou New City
- 3.1.3 Beijing Yizhuang New City
- 3.1.4 Shenfu City
- 3.1.5 Sino-Singapore Tianjin Eco-city
- 3.1.6 Tangshan Caofeidian International Ecological Town China (CFD)
- 3.1.7 Diao Yu Zui Peninsula Project
- 3.1.8 Lingang New City
- 3.1.9 Qianjiang Century City/Qianjiang Century Central Business District
- 3.1.10 Qianjiang New City
- 3.1.11 Zhenhai New City
4 List of key Chinese individuals and major foreign involvements
5 A list of key reference documents
- 5.1 Appendix 1: Urban and Rural Planning Law of the People’s Republic of China
- 5.2 Appendix 2: Real Estate Management Law
- 5.3 Appendix 3: Construction Law
- 5.4 Appendix 4: Environmental Protection Law of the People’s Republic of China
- 5.5 Appendix 5: Land Administration Law of the People‘s Republic of China
Forord
Undersøgelse af såkaldte nye byer i Kina, hvordan skabes plads til yderligere 350 mio. mennesker i byerne indenfor de næste 15 år?
Verdenshistoriens største urbaniseringsproces, en styrkelse af den kinesisk miljøpolitik samt stigende velstand giver betydelige muligheder for salg af danske ressourcebesparende kvalitets løsninger og udstyr.
Nærværende rapport ”Survey on planning and development of new cities and urban areas in China” kortlægger planlægningsprocedurer og beskriver de vigtigste nybygningsprojekter.
Sammenfatning og konklusioner
Baggrund og formål
Kina gennemgår verdenshistoriens største urbanisering og der er ingen tegn på at det vil stoppe i de kommende år. Fortsatte produktivitetsforbedringer i det kinesiske landbrug kombineret med den kraftige vækst og højere levestand i byerne vil fortsat betyde et stort pres på de urbane områder i den østlige del af landet i årene fremover. Antallet af kinesere der bor i byer forventes således i år 2020 at overstige 900 mio., hvilket vil være 350 mio. flere end i 2005. Denne situation nødvendiggør massive investeringer i urban infrastruktur og nybyggeri i Kina i en skala ikke tidligere set i verdenshistorien. Samtidigt skal miljøet indtænkes i alle projekter, lige som en række Økoby-projekter er under planlægning. Denne unikke situation er motivationen bag følgende to danske initiativer: Danish Water Partnership, Bright Green City China og Green China.
Intiativet Water Partnership fokuserer på at positionere danske virksomheder inden for planlægning og gennemførelse af store projekter inden for vand/spildevand mv. Den primære interesse er at komme i kontakt med projektudviklere på et meget tidligt stadie, for derigennem at kunne demonstrere vigtigheden af en grundig og professionel planlægningsproces.
Det andet initiativ går under navnet Bright Green City China og er et konsortiumsamarbejde med DI som sekretariat. Målet for dette initiativ er at etablere et udstillingsvindue for dansk teknologi og kompetencer. Udvælgelsen af placeringen af dette udstillingsvindue sker i samarbejde med det tredje initiativ ”Green China”.
Det tredje initiativ ”Green China” koordineres af den danske ambassade i Beijing og Kina-ledelsen af pt. 12 danske virksomheder indenfor ressource-effektivisering. Gennem dette initiativ arbejdes der på at skabe en markedsmæssig succes i 6 udvalgte provinser gennem en langsigtet relationsombygning og forståelse af behov og afhjælpning af udfordringer i provinserne. ”Green China” optræder som en samlet værktøjskasse og partner for de ansvarlige i provinserne.
Nærværende rapport har således til formål at understøtte ovennævnte initiativer ved at give en dybere forståelse af byplanlægningen i Kina og frembringe detaljerede informationer om konkrete projekter af relevans for de danske virksomheder og øvrige beslutningstagere.
Undersøgelsen
Denmarks Eksportråd’s Energi og Miljø Team i Kina) udarbejdet nærværende rapport. Trade Council of Denmark in China (TCD-C) er placeret i Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Chonqqing og Hong Kong.
Undersøgelsen er blevet til ved
- indsamling af relevante lovtekster, forordninger, kinesisk og international faglitteratur på området mv.
- møder med centrale myndigheder på centralt hold og i en række provinser; møder med relevante internationale organisationer samt kinesiske og internationale virksomheder, der deltager i byplanlægningsprojekter og/eller projekter relateret til vandressourceforvaltning mv.
- kvalitative interviews med nøglepersoner i 11 nybygningsprojekter (udvalgt i samarbejde med Water Partnership/BGCC).
Efter indledningsvist at have identificeret kerneaktørerne har TCD-C’s medarbejdere i hele Kina foretaget screening af en lang række byudviklingsprojekter. En del af disse projekter er blevet udvalgt til en kort bekrivelse i kapitel 3 (”long list”). Ud af disse projekter har TCD-C i samarbejde med Water Partnership/BGCC udvalgt 11 projekter, der i særligt grad syntes interessante for de danske virkosmheder. Disse 11 projekter er efterfølgende blevet beskrevet med udgangspunkt i et spørgeskema stillet til rådighed af Water Partnership (kapitel 4)
Hovedkonklusioner/Projektresultater
Rapporten har bekræftet, at der er et betydeligt antal byudviklingsprojekter under planlægning over hele Kina og at økologi/bæredygtighed er et element i den måde projekterne præsenteres på. Projektets parter har således identificeret en række interessante projekter, hvis videre projektmodning ville have stor gavn af dansk ekspertise. Der blev i forbindelse med vores kvalitative interviews udtrykt stor interesse for de danske kompetencer og det er således TCD-Cs opfattelse, at der er mange muligheder for de danske virksomheder.
Det er dog samtidigt klart, at flere af de beskrevne projekter risikerer at lide skibbrud på grund af manglende finansiering, ændrede prioriteter fra lokale myndigheder, fx når ændringen i betaling for vand/energi har sociale konsekvenser. Det står heller ikke altid klart, hvad definitionen af en ECO City er og hvorvidt de lovende hensigter om kan fastholdes. Det forekommer desværre i Kina, at miljøhensyn kommer under pres, når projekter når til implementeringsfasen.
TCD-China har bl.a. via arbejdet med denne rapport udarbejdet tætte kontakter til nøglepersoner fra de skitserede projekter og bistår gerne med at etablere kontakt mellem disse nøglepersoner og myndigheder og de danske virksomheder.
Andre kilder
Der henvises til rapportens appendiks.
1 Procedures of a new city planning project
- Process of Planning at the central level
- The general decision-making process in China for spatial planning and new city developments through the various stages of planning including responsibilities of the key authorities at central level
- Process of Planning at the provincial level and big cities (mainly province capitals)
- The general decision-making process in China for spatial planning and new city developments through the various stages of planning including responsibilities of the key authorities at provincial and municipal level
1.1 At the central level
At central level in China, 20 years is a time circle for making a new master plan, now it is at the third circle period (2000 – 2020). New city planning and development is based on below approval procedures. Be aware that it is generic and applied for normal building projects. The illustrated procedures can be varied from region to region slightly.
Procedure 1: Map the master plan.Planning department at central level takes the lead and organizes different functions to conduct the master plan (National Development and Reform Commission)
![]()
Procedure 2: Write out the plan.In general, the local municipal government will be responsible for organizing editing work of the master. The local Urban Planning Bureau/Commission will be entrusted for practical work. A leading group will be established and experts from relevant parties will be involved and give their comments to this master plan, such as
- Local Water Affairs Bureau
- Local Environmental Protection Bureau
- Local Land Resources Bureau
- Local Construction Bureau
- Local Development & Reform Commission
- Local Transportation Bureau
- Local Agriculture Bureau
- Local Health Bureau
- Local Culture Bureau
- Local Statistic Bureau
- Local Tourism Bureau
- Local City Administration Management Bureau
- Local Telecommunication Bureau
- Local Power Corporation
- Local Finance Bureau
- Local Public Security Bureau
- Etc.
![]()
Procedure 3: Approval from State Council.Submit the master plan to the State Council for approval, for those provincial cities and cities directly under the central government (86 cities in total)
![]()
Procedure 4: Approval from National People’s Congress.After the approval of State Council, submit the master plan to the National People’s Congress (NPC)
![]()
Procedure 5: Clarify details of the Plan. Based on master plan or district plan, the regulatory plan will define the land use nature, road and pipeline location and space environment control, etc. normally the plan is in accordance with a reasonable construction cycle. The local planning department will host a joint meeting for detail planning. Relevant parties are design institute, municipal engineering company, water affairs department, environment bureau, etc. They will give comments and provide relevant data to regulatory planning.
![]()
Procedure 6: Land preparation and developing. The land development project must be in accordance with local government’s social development plan, general urban planning, master planning of land use, yearly land use planning, yearly land supply planning, etc...
Normally, the local government will establish their own investment company or construction company to do land development. Land development includes keeping the joint connection to traffic, electricity, water, drainage, telecommunication, cable TV, coal gas, and natural land consolidation. Through a serious of procedures, the land developer moves industries, villages and people, deals with old buildings, infrastructure and pollution. Then a new infrastructure e.g. water and energy should be implemented. After finishing all the developing procedures, the developed land should be put into land bank which is administrated by local government.
![]()
Procedure 7: Developer selection.Licensed registered real estate development companies participate in the open bidding for the planned project and the winning company shall be eligible to carry out development of the planned project.
![]()
Procedure 8: Purchase developed land.The developer shall pay fee to local government for developed land use (in China all lands are state-own) and afterwards obtain permit of land use from local government.
![]()
Procedure 9: Apply for building permission. The real estate developer can apply for building permit from local construction administration with construction plan and so on.
![]()
Procedure 10: Construct the buildings. All needed permits and contracts (with designing institute, contractor, auditor, etc.) are in place, the construction can start. In China, there are a few real new cities construction. The most popular projects are city enlargement, industry park projects, tourism area construction, university town projects, or development zone construction.
The local municipal government or administration commissions are mainly responsible for coordinating the detail work. A joint meeting will be carried out and representatives from relevant parties will participate so as to ensure project implementation. See following parties:
- Local Development & Reform Commission
- Local Construction Commission
- Local Urban Planning Commission
- Local Environmental Protection Bureau
- Local Water Affairs Bureau
- Local Power Supply Corporation
- Local Municipal Administration Management Commission
- Local Transportation Bureau
- Local Greening & Landscape Bureau
- Local Tourism Bureau
- Local Real Estate Management Bureau
- Local Land Resources Bureau
- Local Fire Control Bureau
- Local Civil Defence Bureau
- Local Statistic Bureau
- Local Subway Company
- Local Road Agency
- Etc.
![]()
Procedure 11: Acceptance. After the construction finished, local administration will inspect the buildings according to codes and signed contracts and issue certificates if qualified.
1.2 At the provincial level
For cities not in the list of the provincial cities and cities directly under the central government, the approval procedures are as below. The illustrated procedures can be varied from city to city slightly. This is often smaller scale projects compared to the projects above (1.1) and therefore the following process does not include the development of the land.
Procedure 1: Map and Write out the master plan.In cooperation with local planning, land, environment protection and house/real estate administrations, a local (city or town) annual real estate development plan will be mapped out by local construction administration according to local overall land plan, yearly land plan for construction, local urban planning and the demand and supply of house market and subsequently submitted to local government for approval.
![]()
Procedure 2: Clarify details of the plan. Having been consulted with relevant administrations, local construction administration will come up with an ‘opinion-notice’ on a planned real estate project with following information:
- Function (for commercial or living), size and time/period
- Design requests based on local urban overall plan
- Construction requirements on infrastructure and public facilities
- Building lines and the boundary of land
- Ownership of the planned project
- Requirement on demolition
- Construction quality request (Grade)
- Taxes
![]()
Procedure 3: Developer selection.Licensed registered real estate development companies participate in the open bidding for the planned project and the winning company shall be eligible to carry out development of the planned project.
![]()
Procedure 4: Land preparation.The developer shall pay fee to local government for land use (in China all lands are state-own) and afterwards obtain permit of land use from local government.
![]()
Procedure 5: Design and architect preparation.Design and architect will start based on national codes and both concept and final drawing shall be approved by local urban planning administration.
![]()
Procedure 6: Apply for building permission.With obtaining all above requested permits or approves, the developer shall apply for building permit from local construction administration with construction plan and so on.
![]()
Procedure 7: Construct the buildings.All needed permits and contracts (with designing institute, contractor, auditor, etc.) are in place, the construction can start.
![]()
Procedure 8: Acceptance.After the construction finished, local administration will inspect the buildings according to codes and signed contracts and issue certificates if qualified.
For purchase of building materials or suppliers selection, according to relevant laws, the public funded projects shall go through the open bidding process and now the private developers also quite often to use bidding mechanism in order to ensuring ‘value for money’.
2 Specific projects
- 2.1 Outline mapping and location
- 2.1.1 Bejing
- 2.1.2 Tianjin
- 2.1.3 Hebei Province
- 2.1.4 Henan Province
- 2.1.5 Shanxi Province
- 2.1.6 Liaoning Province
- 2.1.7 Jiangxi Province
- 2.1.8 Shandong Province
- 2.1.9 Inner Mongolia
- 2.1.10 Anhui Province
- 2.1.11 Shanghai
- 2.1.12 Zhejiang Province
- 2.1.13 Jiangsu Province
- 2.1.14 Chongqing
- 2.1.15 Guangdong Province
- 2.1.16 Hainan Province
2.1 Outline mapping and location
This chapter outlines mapping and location of major new city development projects in China being planned within the next twenty years describing overall vision, guiding strategies and key features of the individual initiatives and involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies. It is worth noting that our interest and the purpose of it has been well received by project owners, several of which have expressed a great interest for Danish environmental technologies.
The below long list is not an all-embracing list of all major city development projects in China but an attempt to describe the most important projects taking into account Danish strongholds in the environmental field.
The long list has been compiled based on:
- Review of relevant literature, web pages, legal documents etc in Chinese and English language.
- Meetings with key central and provincial authorities, international organisations and Chinese and international companies involved in urban planning, water resource management etc.
- Interviews with the management/secretariat of the below listed new city development projects
2.1.1 Bejing
2.1.1.1 Hai Dian New Area, Beijing
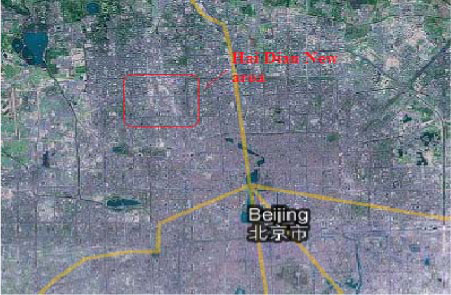
| Location | Northern part of Hai Dian District, Beijing |
| Description | 226 km2, with a population of about 190,000. Restructuring towns and villages, and new construction. The Western and Southern part of this area will be for development of an ecological sector. The middle part of this area will be for development of high-tech industries. The Eastern and Northern part will be for green land. |
| Overall vision |
|
| Guiding strategies |
|
| Key features of the initiative |
|
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies |
Hai Dian District Administrative Committee |
2.1.1.2 Eleven New Cities in Beijing
| Location | Beijing |
| Description | The ambitious 11 new cities plan was put forward by Beijing Urban Planning Committee at the end of 2007 as a mean to ensure a gradual and environmentally sustainable expansion of Beijing. The project time frame is from 2008 – 2020. Of the 11 new cities, Shun Yi new city, Tong Zhou new city and Yi Zhuang new city will be the most important projects. |
| Key features of the initiative | Planned area:
|
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Urban Planning Committee of Beijing |
2.1.2 Tianjin
2.1.2.1 Tianjin Sino-Singapore Eco-city, Tianjin
| Location | Tianjin Sino-Singapore Eco-city is located in the central part of the Circum-Bohai region and the Eastern seaboard of Tianjin |
| Description | With a planned area of 31,23 km2, and a resident population of 350,000. This is amongst the most ambitious new city projects in China |
| Overall vision | “Three harmonies” and“Three ables”: Three Harmonies: harmony between individuals, between individual and environment, between individual and economy Three Ables:replicable, durble, inspiring |
| Guiding strategies | Advanced manufacturing and R&D center for China and the world |
| Key features of the initiative | Ecological, Environmental, Efficient, Natural, Livable, Harmonious |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | TEDA Holding Ltd National Development Bank Tianjin Real Estate Co. Ltd Keppel Group. Ltd Other Singapore Companies |
2.1.3 Hebei Province
2.1.3.1 Cao Fei Dian Bin Hai New City, Tangshan, Hebei
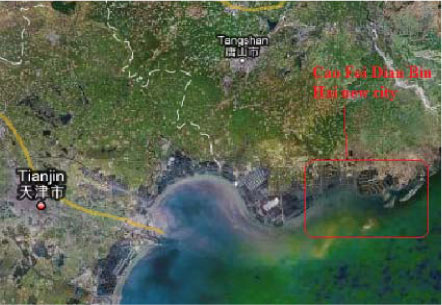
| Location | The southern part of Tangshan city |
| Description | Total area for this project will be 30 km2, with population of 400,000 to 500,000, to form a eco and international costal city The first phase runs from 2008 to 2010. This phase focuses on water, electricity, infrastructure, telecom and urban areas; 5 km2; The second phase (2011-2013), area size is about 10 km2, aims at further developing the recreational areas and at the same time to build up public institutions such as schools, hospitals, shopping malls, star hotels, entertainment centers etc; The final phase (2013-2016) aims at developing a financial centre, R&D center, information center, cultural centre etc, and further develop the eco-environment in the area In April 2008 a letter of intent was signed between the Tangshan Mayor and Swedish Prime Minister, Fredrik Reinfeldt’s. So far, Swedish consultancy Sweco signed a consultancy contract with Tangshan totaling SEK10 million. |
| Overall vision | A world-class eco city, a harbor city, a coastal city, a pilot city, an international city |
| Guiding strategies | Ecological and recycled materials will be the main technologies used in the new city construction |
| Key features of the initiative | Ecological Recycling |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Beijing Tsing Hua City Planning & Design Institute Italy ArchA Design Co. Ltd Sweco Sweden China City Planning and Design Institute |
2.1.3.2 Wan Zhuang Eco-city, Hebei
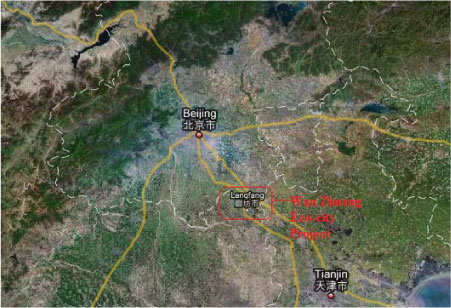
| Location | Lang Fang city, Hebei province |
| Description | Construction started Sep 2008. The project is expected to be completed 2016-2018. Size: 80 km2. Population 300,000 |
| Overall vision | Sustainable development |
| Guiding strategies | Utilization of renewable energy in construction, eco-friendly building materials. Service industry will be the main industry in the city, no or limited petrol involved e.g. walking, bicycle and public transportation will be the main means of transportation |
| Key features of the initiative |
|
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Shanghai Dongtan Investment Management Consulting Co. Ltd Shanghai Industrial Investment (Holding) Co. Ltd |
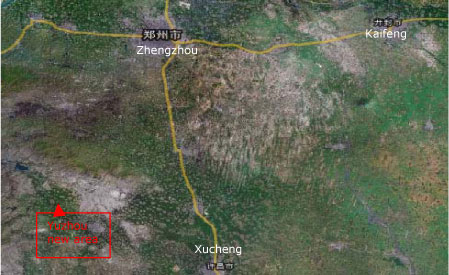
2.1.4 Henan Province
2.1.4.1 Zhengdong New Area, Zhengzhou, Henan
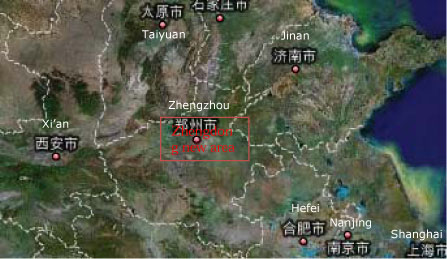
| Location | Zhengdong New Area, Zhengzhou |
| Description | 2003 – 2007 is the first phase of this project construction. 2008 – 2012 is the second phase. Total area is 150 km2 with a population of 800,000 in 2010. |
| Overall vision | A livable new city, harmonious relations between nature and individual |
| Guiding strategies | Sustainable development is the guiding strategy; high standard planning, high standard design, high standard construction and high standard management |
| Key features of the initiative |
|
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Japan Kisho Kurokawa Co. Ltd Shanghai Tong Ji University New area administrative committee Other companies |
2.1.4.2 Luoyang New Area, Luoyang, Henan
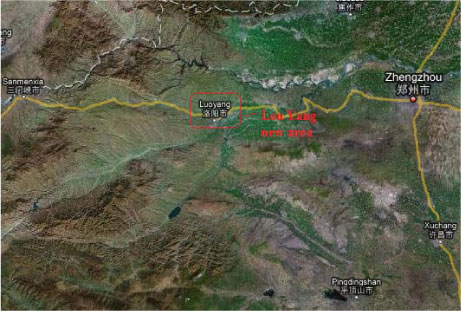
| Location | Southern part of Luo Yang city |
| Description | The total area is 71.3 km2, with a population of 500,000. This project was started in 2003, so far focusing on basic infrastructure. |
| Overall vision | Assisting Luo Yang to develop into a combination of an international tourism city and a modern industrial city |
| Guiding strategies | A green new area, an eco city, combination of traditional and modern buildings |
| Key features of the initiative | Old Town 22.1km2, this land is not for construction Bin He Park 4.9km2 Guan Lin District10.8km2 Luo Nan Centre District 11.19km2 University Town and Stadium 8.5km2 Hi tech development zone 13.9km2 |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Luo Yang city new area development and construction office |
2.1.4.3 Yang Shan New Area, Xin Yang City, Henan
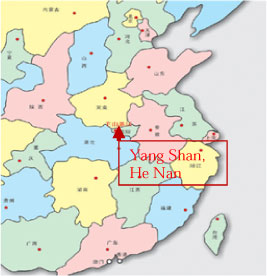
| Location | Xin Yang city |
| Description | The area is is expected to become the new city centre of Xin Yang, with a total size of 76 km2 |
| Overall vision | Green Yangshan |
| Guiding strategies | To build a modern ecological city and a city with distinct character. First phase (2080-2013) will focus on basic infrastructure development. |
| Key features of the initiative | Modern and sustainable |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | China City Planning and Design Institute |
2.1.4.4 Cheng Dong New Area, Yu Zhou, Henan
| Location | The project is located at the eastern part of the city, Yu Zhou, He Nan |
| Description | The total size of the area is 76 km2. It is a planned as a new building project with gradual development of commercial and living area as well as high-tech educational facilities The plan was drafted in 2003. |
| Overall vision | Urbanization |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | He Nan City and Town Planning and Design Institute Shanghai Tongji University Design Institute of Zhengzhou University Shenzhen Guang Zhu Design Institute Chengdong New Area Administrative Committee |
2.1.5 Shanxi Province
2.1.5.1 Tongchuan New Area, Tongchuan city, Shanxi
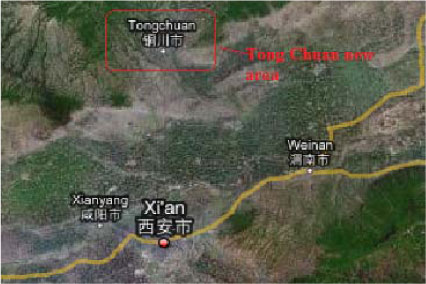
| Location | 25km from the old downtown area of Tong Chuan. Tong Chuan is 70 km North of Xi An |
| Description | It is a combined project on administrative restructuring and new construction work. Size 35.8 km2, estimated population after completion 350,000 people 1993 – 2005 is the project phase 1 2005 – 2015 is the second half of the project |
| Overall vision | Modernization, with special characters within building construction; a green city |
| Guiding strategies | Develop into a world-class green city |
| Key features of the initiative | Good geographic location: only 70 km to Xi’an Favourable government policy Low cost for manufacturing |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | New area administrative committee |
2.1.6 Liaoning Province
2.1.6.1 Shen Bei New Area, Shenyang, Liaoning
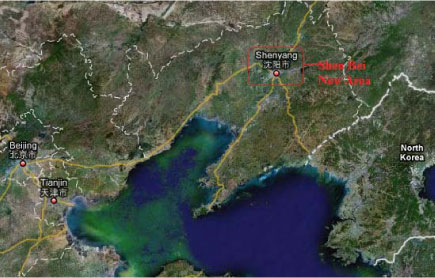
| Location | The project is at the Northern part of Shenyang city, Shenyang |
| Description | Established Oct 2006, the fourth new area is officially approved by the State Council. The new city is a combination of existing houses (administrative restructuring) and new construction work. Total area is 300 km2, population as of 1,000,000, with a greenery rate of 50% in 2020 |
| Overall vision | An innovative city An eco city A cultural city A livable city |
| Guiding strategies | Urbanization, gradual development into an eco-city |
| Key features of the initiative |
|
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Shen Yang Dong Chun Science Development Co. Ltd |
2.1.6.2 Shen Fu (Shen Yang and Fu Shun) Eco-city, Liaoning
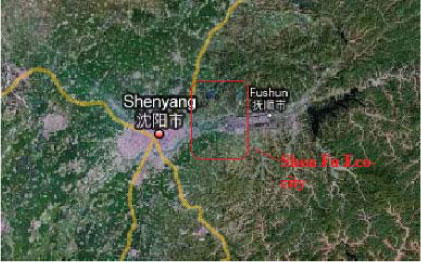
| Location | Along the Hui river, the border between Shenyang city (Eastern part) and Fushun city (Western part) |
| Description | Size: 30 km2 Population: 100,000. It is expected to develop into a pilot eco-city The project was initiated in 2007 2008-2010 is the development phase (master plan of eco area, basic infrastructur 2011-2015 Further development of Fushun, linking Shenyang and Shenfu together |
| Overall vision | A livable, commercialized, industrialized eco city |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Pan-China Construction Group Hong Kong Infrastructure Construction Investment Co. Ltd Shanghai Industrial Holding Co. Ltd |
2.1.7 Jiangxi Province
2.1.7.1 Yang Tian Gang New City, Xin Yu City, Jiangxi
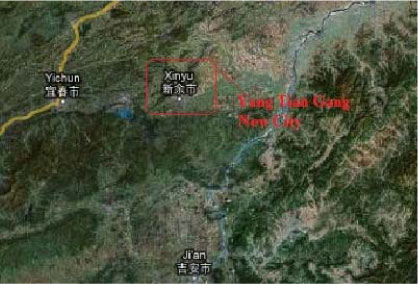
| Location | Yang Tian Gang, Xin Yu City, the central part of Jiangxi Province |
| Description | Under guidance of ecological environment-protect, Yang Tian Gang New City will be one large-scaled scenery area with distinguished features and foreign dialogue platform among science, culture and art. In conclusion, a new eco-city with nice scenery, prosperous industries, harmonious environment and developed economy. Size is 86 km2 |
| Overall vision | A city that embodies nature |
| Guiding strategies | Based on the nature ecological environment, to build up an eco new city |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Xin Yu Yang Tian Gang Investment Development Co. Ltd Xin Tian Investment Development Co. Ltd Sai Wei Group Nan Chang Public Holding Co. Ltd |
2.1.8 Shandong Province
2.1.8.1 Chang Qing New City, Ji Nan, Shandong
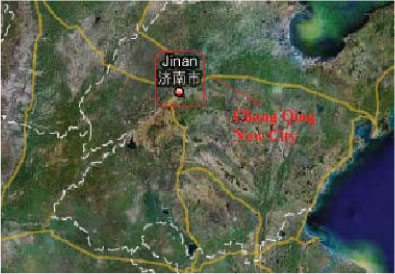
| Location | Chang Qing, Ji Nan City, Shan Dong Province |
| Description | A new city combined with ecological, tourism, high education and research. Total area is 1178km2, population of 0.68 million. |
| Overall vision | An eco-city surrounded by nature |
| Guiding strategies | Ecological and environmental protection, harmony and sustainable development |
| Key features of the initiative | Five featured areas: Ji Nan Economic Development Zone, University Science & Technology Park, Political & Commercial Area, Wu Feng Mountain Tourist Resort, Agricultural Belt |
2.1.9 Inner Mongolia
2.1.9.1 Hu He Hao Te New City, Hu He Hao Te, Inner Mongolia
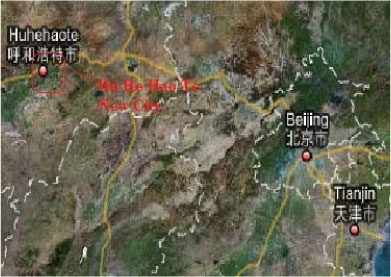
| Name | Hu He Hao Te New City |
| Location | In the northern part of Hu He Hao Te, covering 12.88 km2 |
| Description | An energetic and habitant-friendly modern eco-city combined by modern logistics, living style and timberland |
| Overall vision | By 2010, a comprehensive modern eco-city, combined by commercial, manufacturing, modern service, living and timberland, will be functionally oriented, equipped with affiliated equipments, surrounded by fine scenery and steadily developing in economics. Short term plan: from 2005 – 2010, form the framework Long term plan: from 2010 – 2020, to improve and complete |
| Guiding strategies | Construction guideline is “one axis, one center, two areas and three belts”. “One axis”: runs through the ChengJiSiHan Scenic Street from east to west, links up the industrial zone, commercial region and residential area. “One center”: in the heart of new city – key commercial region “Two areas”: industrial zone and residential area “Three belts”: Hongshankou Gully, Bakouzi Gully, Wusutu Gully – three green passages |
2.1.10 Anhui Province
2.1.10.1 Hefei New Civil and Cultural District, Hefei, Anhui
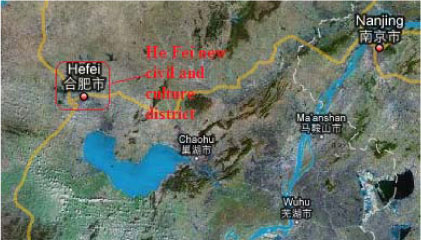
| Location | Hefei City |
| Description | This project plan was firstly initiated in 2001. |
| Overall vision | Ecological and sustainable development |
| Guiding strategies | A ecological city with, sustainable development and a greenery city |
| Key features of the initiative | Focus on natural building, culture building and scenery building, to create more chances for the individual to be connected with the nature |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | USA RTKL International Co. Ltd Jin Xin Planning Construction Studio Hefei New Civil and Cultural District Investment Co. Ltd |
2.1.11 Shanghai
2.1.11.1 Dong Tan Eco-city Project, Shanghai
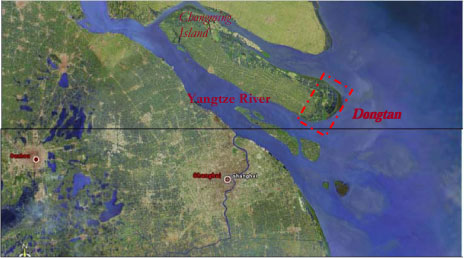
| Location | Dongtan Eco City, Chongming Island, Shanghai |
| Description | Dongtan will be built as the world’s first eco city. Shanghai plans to build the demonstration eco-city, which will ultimately house 500,000 people, designed by the UK engineering consultancy firm Arup. The project has received great support from both Chinese and British government but is presently delayed due to uncertainties in relation to financing of the ambitious plans. |
| Overall vision | Dongtan's designers hope to build an eco city to demonstrate how cities could support, rather than destroy, the environment. Its two major goals are to generate zero carbon emissions and cut average energy demands by two thirds via a unique city layout, energy infrastructure and building design. |
| Guiding strategies | The key principles of the sustainability framework of Dongtan project are:
|
| Key features of the initiative | By 2010 (the first phase), 1 km2 will be developed to accommodate up to 10,000 people; By 2020 (the second phase), the 6.5 km2 start-up area will be developed to accommodate up to 80,000 people; By 2050 around 30 km2 will be developed with 500,000 people accommodated there. |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Shanghai Industrial Investment (Holdings) Co., Ltd. (SIIC), |
2.1.11.2 Lingang New City, Nanhui District, Shanghai

| Location | Lingang New City, Nanhui District, Shanghai |
| Description | Lingang New City is the biggest development plan for Shanghai since Pudong New Area. It will be built as the largest satellite city in Shanghai. |
| Overall vision | Linggang New City is planned to be built as:
|
| Guiding strategies |
|
| Key features of the initiative |
|
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Lingang Group |
2.1.11.3 Chongming Three Islands Development, Shanghai
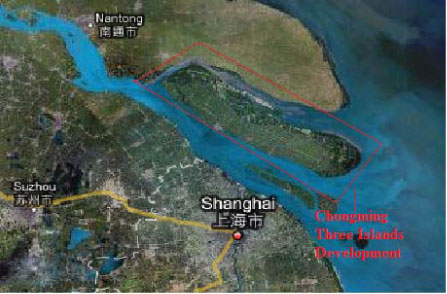
| Location | Chongming Island, Shanghai |
| Description | The Chongming three islands, consisting of Chongming, Changxing and Hengsha, provide strategic space for sustainable development of Shanghai in the 21st century. The State Council officially approved Shanghai Master Plan 1999-2020 in May of 2001. On May 18, 2005, the State Council formally approved Changxing and Hengsha islands under the jurisdiction of Chongming County; evidently, the development plan for three islands is particularly essential for future development of Shanghai. |
| Overall vision | Chongming islands shall be constructed into world-class eco-island, mainly consisting of the following six portions:
|
| Guiding strategies | The development of Chongming islands shall adopt a scientific outlook, focus on the construction of modern eco-island pursuant to requirements of harmonious society, implement science and education strategy, and realize the interaction between functions, industries, population and infrastructures on the three islands. The three islands will be respectively constructed into comprehensive eco-island, marine equipment island and eco-friendly relaxation island. Based on Sci-Tech innovations, further attempts will be made to promote cyclic economy, develop eco-agriculture, and build Chongming into a modern eco-island featuring a beautiful and harmonious environment, the thrifty use of natural resources, and the coordinated social and economic development. |
| Key features of the initiative | Population: According to the plan, total population on three islands will be controlled within 0.8 million by 2020, with an increase of about 0.1 million. Among which, total population on Chongming Island will be controlled within 0.68 million, about 0.1 million on Changxing, and less than 20,000 on Hengsha. Towns: The 3-level system of “new city - new township - central township” will be established in accordance with requirement of “coordinated and balanced development of between urban and rural”. |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | SOM (U.S), Shanghai Urban Planning Administration Bureau, Chongming County Government |
2.1.11.4 Ju Yuan New Area, Shanghai
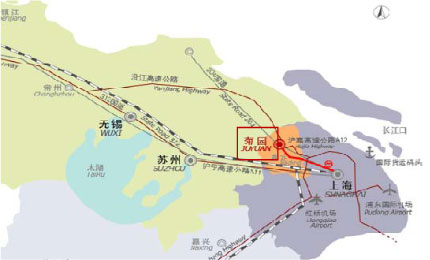
| Location | It is located at the north western part of Jia Ding district. 25 km to Shanghai Hong Qiao Airport |
| Description | 18.6 km2, with a population of 42,000 |
| Overall vision | A new area with blue sky, green water, liveable area and prosperous industries. |
| Guiding strategies | Develop into a high tech and multi-functional area |
| Key features of the initiative | Greenery and water is the key feature for this new area; high quality with ecological, functional and comfortable A wireless city A complete public facilities A rich education resources A liveable environment |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Shanghai Wu He International Design & Consultancy Co. Ltd German ASP design Co. Ltd |
2.1.12 Zhejiang Province
2.1.12.1 Ten New Cities along Qianjiang River, Hangzhou, Zhejiang
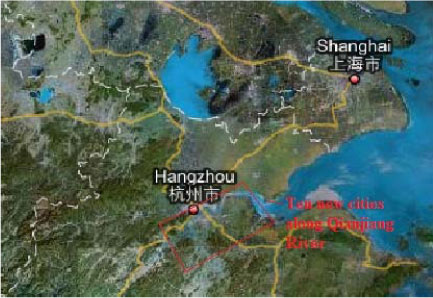
| Location | Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province, China |
| Description | The development pace of the areas along and across Qianjiang River is speeding up. It was reported in early June 2008 that a series of important projects along both sides of Qiantang River are being prepared and implemented. Hangzhou will construct 10 new cities along Qianjiang River from upper to lower reaches, namely, Qianjiang New City, Binjiang New City, Xiasha New City, Konggang New City, Zhijiang New City, Chengdong New City, Linjiang New City, Qianjiang Century New City, Jiangdong New City, and Linpu New City. It will take up to 30 years to construct these 10 new cities as initially planned. Among the ten new cities, Qianjiang New City is under construction. Binjiang New City and Xiasha New city were originally planned as development zones and are now planed and constructed towards as “city”. Kongkang New City will be built as a wholly new city based on Hangzhou Xiaoshan International Airport. |
| Overall vision | The ten new cities project will be along Qiantang River in Hangzhou and to be built as modern cities with high buildings to accommodate approximately 4 million people. |
| Guiding strategies | Hangzhou’s urban planning is shifting from the West Lake to Qianjiang River. The old development concept of establishing industrial zones is replaced by the idea of building new cities. |
| Key features of the initiative | Population: 1 million (now), aim for more than 4 million in the future Planned area:
|
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Urban Planning Administration Bureau of Hangzhou |
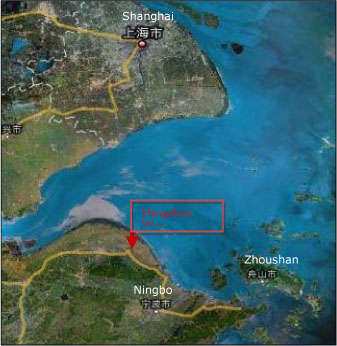
2.1.12.2 Zhenhai New City, Ningbo, Zhejiang
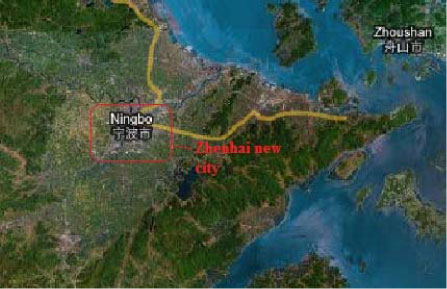
| Location | Zhenhai New City, Ningbo, Zhejiang Province |
| Description | Ningbo City Government has made a strategic development plan for the Period of Eleventh Five-year Plan (2006-2010), one of which is to further develop the central area of Ningbo. Zhenhai is one of the central districts of Ningbo city and the aim is to build “two centres, one base” in this area. The project aims at building a business and commercial centre in the Northern central area of Ningbo city based on Zhenhai New City, to build production-oriented harbor logistic centre based on Zhenhai old town and the National-level Petrochemical Industry Base based on Ningbo Chemical Zone. |
| Overall vision | The Zhenhai New City will be built as a comprehensive new city with business, commerce, education and research, office and residential area, which will not only show the modern business district outlook but also represent the water town characteristics of east China. |
| Guiding strategies | Zhenhai New City will be built as the sub-CBD of the central city of Ningbo, the northern business and trade centre, the core education area as well as the scientific and technological base in Ningbo city. |
| Key features of the initiative | Planned area: 46 km2 with population: 400,000 – 450,000 Since the start up of the project in 2001, a total of 8 billion RMB has been invested. The road of 40 kilometers has been completed. There are more than 40 construction projects for institutions, such as Ningbo Institute of Material Technology & Engineering, CAS, Ningbo University, Ningbo Engineering Institute, The 5th Hospital of Ningbo, and etc have already kicked off. |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Ningbo Zhenhai District Zhenhai New Town Management Administration Committee |
2.1.12.3 Hang Zhou Wan New Area, Ningbo, Zhejiang
| Location | Ci Xi city, Ningbo |
| Description | The new city will be built on tidal flat, with size 145 km2, for population more than 500,000. Target is to have a new coastal city in 12 years along the Hang Zhou Wan bridge Wind power is one of the shinning points for this project. Total amount for project phase 1 of wind power is RMB566 million, it is expected to be finished at 2009. |
| Overall vision | A Green, ecological, livable and modernized new city |
| Guiding strategies | Green and ecological |
| Key features of the initiative |
|
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | GEF – the Global Environment Facility Hangzhou City Construction and Design Institute Co. Ltd DTZ real estate consultant Co. Ltd Zhe Jiang Ci Xi export processing Zone (an economic development zone) administrative committee Hangzhou Bay bridge administrative bureau USA Edaw Tongji University? Ningbo Planning and Design Research Institute Ci Xi Chang Jiang Wind Power Co. Ltd (jointly established by China Chang Jiang Three Gorgers Engineering Co. Ltd and Ci Xi Wind Power Co. Ltd) Zhe Jiang Provincial Environmental Protection Sciences and Design Institute |
2.1.13 Jiangsu Province
2.1.13.1 Taihu New City, Wuxi, Jiangsu
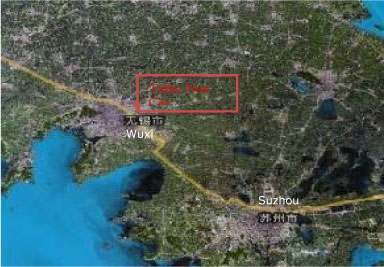
| Location | Tiahu New City, Wuxi City, Jiangsu Province |
| Description | Wuxi is one of the important cities in the Yangtze River Delta with regard to its economic development. Wuxi city government has decided in 2007 to develop the area around South Tai Lake (Tai Hu) to build Taihu New City. Taihu New City will make the most of its geological advantage so as to attract more companies. Wuxi was in a critical moment of economic and social development and the local government realizes it is important to further develope Wuxi city in connection with water treatment program, Shanghai 2010 Expo and the construction of Shanghai-Beijing Express Railway and Shanghai-Nanjing Railway in order to enhance Wuxi’s overall competitiveness in Yangtze River Delta. |
| Overall vision | The Taihu New City covers an area of 150 km², and will be divided into 3 functional areas, which are Eastern Zone, Central Zone and Western Zone. The Eastern Zone will be built as a science & technology park of 23 km². The Western Zone is focused on innovative and tourism industries with a total area of 72 km². The Central Zone will be built as financial, commercial and residential centre. As Wuxi’s new city centre, it would become a wonderful place with high living standards. |
| Guiding strategies | The Taihu New City is planned to be built as an administration, commercial, science, technology and leisure centre. The government plans to spend ten years to turn this area into Wuxi’s new city centre. |
| Key features of the initiative | Permanent residence: 1 Million Land for construction: 99.8 kilometres² Land for ecological reservation: 50.2² Currently, the Civil Centre is already under construction and is to be completed by the end of 2009. Exhibition centre started construction in June 2008 and is planned to be finished before end of 2009. Financial and Commercial 1st Street will be finished before the opening of Expo 2010. In 2008 a total area of 1.8 million square meters housing is to be expected to be completed for the relocation of farmers. |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Urban Planning Administration Bureau of Wuxi |
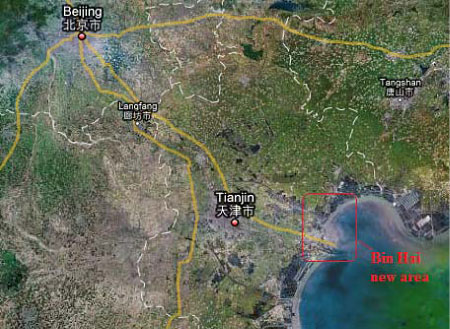
2.1.13.2 Bin Hai New City, Lian Yun Gang, Jiangsu
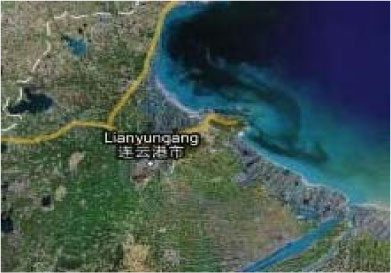
| Location | Lian Yun Gang City, Jiang Su province |
| Description | The size for this new city is about 54 km2, aim to have a population of 640,000. Built on a tidal flat. The construction was started in 2006 |
| Overall vision | An international coastal city, a modernized harbour city and a well known tourism city |
| Guiding strategies | An international coastal city, modernized harbour city and a well known tourism city |
| Key features of the initiative | Education area e.g. for schools Area for relaxation and holidays Commercial and living area Coastal area Cultural area e.g. museum, library etc Parks |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Lian Yun Gang City Planning Bureau Jiang Su Jin Hai Investment Co. Ltd Jin Hai An Development and Construction Co. Ltd Arup, the UK planning, engineering and consultancy firm USA Edaw Shenzhen Planning Institute USA HOK International Co. Ltd German AS&P Co. Ltd Hong Kong Aedas USA RTKL Co. Ltd China Transportation and Construction Investment Co. Ltd |
2.1.13.3 Shu Gang Eco-city, Yangzhou City, Jiangsu
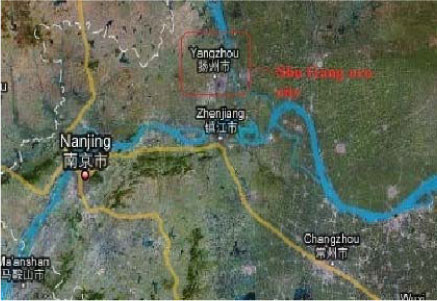
| Location | Shu Gang, Yangzhou City, Jiangsu Province |
| Description | Size: app. 13 km2 80000 – 100000 people |
| Overall vision | Make good use of the eco-environment; Directed by “habitant-friendly theme”, Shu Gang will focus on harmonious ecology, profound culture, complete functions and distinguished character. |
| Guiding strategies | Tourism serves as the thread of the plan and the engine to boost itself. Innovatively industrial zone serves as a platform assembling “green” “youthful” new industries. Based on developed areas and affiliated service, they aim to build a place which is best for living. |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Wei Yang Investment Development Co. Ltd |
2.1.14 Chongqing
2.1.14.1 Diao Yu Zui, Chongqing
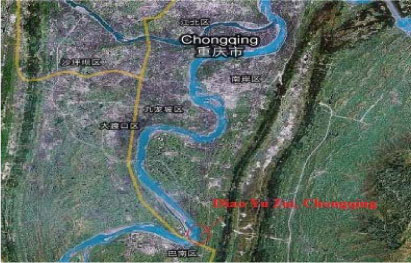
| Location | Diao Yu Zui, Da Du Kou District |
| Description | Planned investment is about 44 billion. Close to Yangtze River, with size of 6,400,032 m² |
| Guiding strategies | It is an overall planning and construction project |
| Key features of the initiative | CRBD Central recreation centre Central business centre Ecological park Residential area |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | China Shi Dai Holdings Co. Ltd |
2.1.14.2 Hua Long Qiao of Yu Zhong, Chongqing
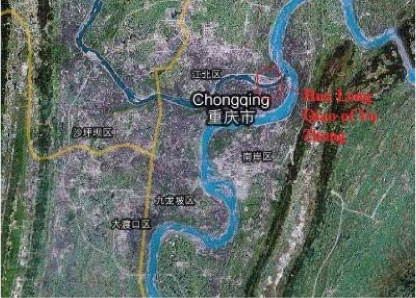
| Location | Hua Long Qiao, Yu Zhong District, Chong Qing |
| Description | It is located at the river side of Jia Ling River. Size 1,300,000 m² |
| Overall vision | Restructuring of old urban area |
| Guiding strategies | Restructuring of old urban area |
| Key features of the initiative | Real estate Residential area Shopping area Recreation area |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Hong Kong Sui On Group |
2.1.15 Guangdong Province
2.1.15.1 Shenzhen Guang Ming New City, Shenzhen, Guangdong
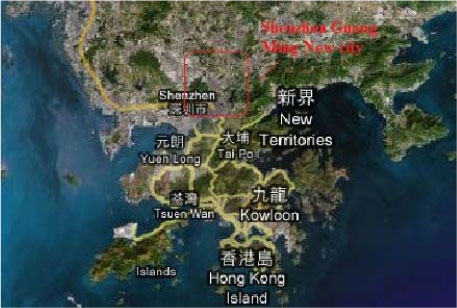
| Location | Located at the north western part of Shenzhen city |
| Description | Size: 28.2 km2. Construction started May 2008. |
| Overall vision | Concentrated, efficiency, harmony and ecological |
| Guiding strategies | Green and harmony city |
| Key features of the initiative | Hi-tech industry and modernized manufacturing, an ecological and relaxed city. Planned zone: Secondary development zone in Long Hua Olympic sports new city Guangming new city Large industrial zone |
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | Singapore Bang Cheng Planning Consultant Co. Ltd (cooperating with China on the Tianjian Binhai project) Tsing Hua University Etc |
2.1.16 Hainan Province
2.1.16.1 Crabapple Bay International New Town, Sanya, Hainan
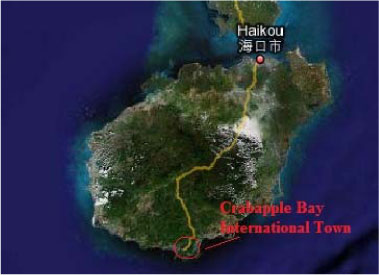
| Location | It is located to the east of the city of Sanya in the island province of Hainan. |
| Description | Size is 98.78 km2. for 250,000 population |
| Overall vision | Aims to develop into the ultimate holiday haven-cum-sustainable new town in China. i.e.: The Only Tropical Beach-Resort City in China The City with the Best Air Quality in China The Most Livable City in China |
| Guiding strategies | Primarily focused on tourism-based and residential development |
| Key features of the initiative | Crabapple Bay, together with YaLong Bay, DaDong Bay and SanYa Bay have been labeled as "The Four Most Beautiful Beaches in Sanya Hainan", totalling 40 km of foreshore. Crabapple Bay enjoys the best location among them. It is Sanya's last remaining "Golden Coast" ripe for development.
|
| Involved Chinese and foreign institutions and companies | China Newtown Group (H.K.) USA HOK Shanghai Tongji University China city planning and design institute Crabapple Bay Administrative Committee Crabapple Development and Construction Co. Ltd |
3 More in depth description of 11 projects
- 3.1.1 Beijing Shunyi New City
- 3.1.2 Beijing Tongzhou New City
- 3.1.3 Beijing Yizhuang New City
- 3.1.4 Shenfu City
- 3.1.5 Sino-Singapore Tianjin Eco-city
- 3.1.6 Tangshan Caofeidian International Ecological Town China (CFD)
- 3.1.7 Diao Yu Zui Peninsula Project
- 3.1.8 Lingang New City
- 3.1.9 Qianjiang Century City/Qianjiang Century Central Business District
- 3.1.10 Qianjiang New City
- 3.1.11 Zhenhai New City
The above outline mapping (3.a) was sent to DEPA, Water Partnership and Sustainable City China Mid July 2008. After consultations with the parties a total of 11 projects were selected for in-depth description. The projects were selected taking into account their relevance in relation to the Danish resource base and competencies in relation to eco-friendly materials and water technology. Another important criteria was the availability of information, likelihood for implementation, availability of financing etc. (i.e. Dongtan project in Shanghai was excluded due to significant delays in project implementation and uncertainties in relation to the Shanghai Government’s continued commitment to the project)
3.1.1 Beijing Shunyi New City
The questions below are not all relevant for the intended interviews. Part A relates to concrete/planned urban development projects that (some of) the interviewed have or are participating in, part B is general as well as concrete projects, while C and D test the feasibility/demand for our concept and possible services.
| Country: China Organisation: Beijing Embassy Contact person: Nathalie Chen |
Date: August - September Interviewer: Mr Wang, Ms Zhao Jianjie. Organisation: Construction & Management Division, Beijing Water Affairs Bureau Shunyi Branch & Planning Division, Beijing Urban Planning Commission Shunyi Branch |
| A. Information on the new city project | |
| 1. Name | Beijing Shunyi New City |
| 2. Location | Shunyi District is located north-east of Beijing. It is 30 km from downtown Beijing and is 1,020 square kilometres wide. |
| 3. Visions of the project | In the aspect of city development, Shunyi New City will mainly undertake functions to lead the development of modern manufactures, air logistics, exhibitions, international communication, sports recreation and liveable city. According to these functions, Shunyi district sets up the plan of Shunyi New City and confirms the urban space layout of “one airport, two rivers, three zones, and four towns”, identifies the development target of “modern international airport, engine of regional industries, and green and liveable new city”, as well as “riverside, ecological, international, vigorous, and liveable”. |
| 4. Size (area, people, investment) | It is expected that until 2020, the population of Shunyi New City will be controlled to be below 900.000, the planned construction land will be controlled to be within 162 square kilometers, and the urbanization rate above 86 %. |
| 5. Responsible authority | People’s Government of Shunyi District |
| 6. Developer | Shunyi New City Real Estate Development Company |
| 7. Financing body/institution, mechanism | |
| 8. Architects | The urban planning of Shunyi new city was worked out by Beijing Municipal Institute of City Planning and Design. Regarding the individual project, the owner or developer will decide architects. |
| 9. Project status and plans | The government is now focused on first-class land development, such as moving and relocation. |
| 10. How is the informant involved in the project? | The interviewee is mainly responsible for editing the city planning. |
| B. The role of integrated water infrastructure | |
| 1. Do water reliability and the quality of the water environment have a special focus in development of new cities/the concrete project? | Yes. The Water Affairs Bureau of Shunyi district works out water industry planning for Shunyi new city. |
| 2. Is integrated water infrastructure a part of the vision for the project? | Yes. As for the water system, Shunyi District has built 9 large-scale water plants, and water pipeline stretching 750 kilometres, with the ability to provide 150.000 tons per day. At the same time, there is a sewage treatment plant, which is capable of treating 80.000 tons of sewage waste per day. |
| 3. Is it necessary that integrated water infrastructure is part of developing the project concept for development of new cities/the concrete projects? | Yes. The district has thoroughly applied the “Beijing General City Planning (2004-2020)”, expedited the application of the “Shunyi New City Planning”, |
| 4. Will the role of water in its broadest sense be included in the concept development for new cities/the concrete project? | Yes. According to the new city planning, ‘one airport, two rivers, three regions and four towns’ will become the core for the development of Shunyi district. |
| 5. Which part of water infrastructure has highest focus and priority | Water infrastructure along Wenyu river and Chaobai river. |
| C. The key stakeholders and decision maker on water infrastructure | |
| 1. Who are the public authorities that shall approve the water infrastructure? | Beijing Municipal Commission of Urban Planning |
| 2. Who are the planners who decide if water infrastructure shall have a prominent role in concept development? | The People’s Government of Shunyi District |
| 3. Are there other decision makers, who have a decisive say in prioritising water infrastructure? | The Shunyi District Government will invite relevant organizations to review the urban planning, and then report to the Beijing Municipal Commission of Urban Planning. |
| D. Presentation of business concept | |
|
|
| E. Which technologies are the key ones to this particular city project? The Ministry of Construction has released relevant notice to promote energy savings in all new buildings. The idea is to promote water saving, material saving, land saving and energy saving. The listed item is of important to the new city project. But different projects will involve different technologies. |
|
|
E.g.
Are there any plans to construct a new city or to renovate existing structures - or a combination – elaborate Are there plans to involve a "showcase" element in this project - allowing other Chinese players to learn from this project? Are there plans to link up to local knowledge institutions within research, standardization etc. to document and disseminate environmental results of the project and feed into the national Chinese standard setting? |
In the Shunyi new city project, there are renovation projects to the old town of Shunyi. Most of the projects in airport area have been built recently. Not clear at the moment. No plan. |
3.1.2 Beijing Tongzhou New City
The questions below are not all relevant for the intended interviews. Part A relates to concrete/planned urban development projects that (some of) the interviewed have or are participating in, part B is general as well as concrete projects, while C and D test the feasibility/demand for our concept and possible services.
| Country: China Organisation: Beijing Embassy Contact person: Nathalie Chen |
Date: August Interviewer: Mr Li Wei Organisation: Beijing Urban Planning Commission Tongzhou Branch |
| A. Information on the new city project | |
| 1. Name | Beijing Tongzhou New City |
| 2. Location |
Tongzhou, located in southeast Beijing, is considered to be the capital's eastern gate. It is located at the north end of the Grand Canal and the east end of Chang'an Avenue. Tongzhou is 37 km wide from east to west and 48 km from north to south, covering an area of 906.27 square kilometres which accounts for 5.55% of Beijing's total territory and 14.3% of Beijing's plain. Tongzhou is neighbored by Tianjin and Hebei province, at the core of Bo Sea Economic Circle. It is new to CBD, 13 km from the International Trade Center, 20 km from the Tian'anmen Square, 16 km from the Capital International Airport, and 110 km from Tianjin New Harbor. |
| 3. Visions of the project | Tongzhou new city is one of the three new key cities of Beijing. In the aspect of city development, Tongzhou New City will mainly undertake functions as comprehensive service zone, culture industry base and liveable city. |
| 4. Size (area, people, investment) | It is expected that until 2020, the population of Tongzhou New City will be controlled to be below 1.19 mil., the planned construction land will be controlled to be within 155 square kilometres. |
| 5. Responsible authority | The People’s Government of Tongzhou District |
| 6. Developer | Beijing Xincheng Jiye Investment & Development Co. Ltd. It is a national first class land developer affiliated directly to Tongzhou District Government. |
| 7. Financing body/institution, mechanism | Bank loan, government investment, etc. |
| 8. Architects | |
| 9. Project status and plans | The master plan of Tongzhou new city has been approved by the municipal government. The detailed planning is now undertaken by Beijing Institute of Urban Planning & Design. |
| 10. How is the informant involved in the project? | |
| B. The role of integrated water infrastructure | |
| 1. Do water reliability and the quality of the water environment have a special focus in development of new cities/the concrete project? | Tongzhou abounds in water resources. There are altogether 13 rivers, big or small, including the Grant Canal, River Tonghui, River Wenyu, River Liangshui, and River Chaobai, with a total length of 245 km. The forestation coverage of Tongzhou is 46%. Tongzhou Urban Planning Commission made a special study on water resources in Tongzhou. They have also invited Hong Kong Chinese University and Tsinghua University to make a special study on water quality, river channels, environment, etc. |
| 2. Is integrated water infrastructure a part of the vision for the project? | Yes. The detailed arrangements will be implemented in the project detail planning, such as waste water treatment plant, grey water treatment plant, etc. |
| 3. Is it necessary that integrated water infrastructure is part of developing the project concept for development of new cities/the concrete projects? | Yes. The project concept planning focuses on Area development of the Grand Canal. |
| 4. Will the role of water in its broadest sense be included in the concept development for new cities/the concrete project? | Yes. The construction of water systems has close relations with the construction of Tongzhou new city since the water system is designed for the whole developing area. |
| 5. Which part of water infrastructure has highest focus and priority | Waste water treatment and water quality |
| C. The key stakeholders and decision maker on water infrastructure | |
| 1. Who are the public authorities that shall approve the water infrastructure? |
|
| 2. Who are the planners who decide if water infrastructure shall have a prominent role in concept development? | Beijing Municipal Commission of Urban Planning |
| 3. Are there other decision makers, who have a decisive say in prioritising water infrastructure? |
|
| D. Presentation of business concept | |
|
|
| E. Which technologies are the key ones to this particular city project? | |
E.g.
Are there any plans to construct a new city or to renovate existing structures - or a combination – elaborate Are there plans to involve a "showcase" element in this project - allowing other Chinese players to learn from this project? Are there plans to link up to local knowledge institutions within research, standardisation etc. to document and disseminate environmental results of the project and feed into the national Chinese standard setting? |
The project is now in the process of rational planning. At a later stage, some technical factors will be considered. Energy saving, environmental friendly, green technologies are general principles to the development of the project. It will be a combination. There are projects relating the renovation of the old downtown but it also has some new development projects, such as construction of a cultural exchange center, an international ecological district, and a residential area. Some projects along the Grant Canal, Tonghui river and Wenyu river, such as residential projects, business projects and office buildings are considered to be a pilot project. Still in progress. |
3.1.3 Beijing Yizhuang New City
The questions below are not all relevant for the intended interviews. Part A relates to concrete/planned urban development projects that (some of) the interviewed have or are participating in, part B is general as well as concrete projects, while C and D test the feasibility/demand for our concept and possible services.
Country: China Organisation: Beijing Embassy Contact person: Nathalie Chen |
Date: August Interviewer: Mr Caili, Mr Zhang Yong Organisation: Water Affairs Bureau, Beijing Development Zone & Planning Bureau, Beijing Development Zone |
| A. Information on the new city project | |
| 1. Name | Beijing Yizhuang New City |
| 2. Location | The Beijing Economic-Technological Development Area (BDA), originally built on 15.8 square kilometres, is located at e-Town (Yizhuang) in Southeast Beijing. The BDA is located only 16.5 km from Tiananmen Square, 30 km from the Beijing Capital International Airport, 10 km from the Beijing Railway Freight Station, five km from a road freight station, one km from an international logistics centre, and 140 km from the Tianjin New Port. |
| 3. Visions of the project |
|
| 4. Size (area, people, investment) | As of 2010, the population of e-Town New City will be about 300,000 people, who will reside on 55 square km of land. By 2020, the population will increase to about 700,000 on 100 square km of land. |
| 5. Responsible authority | Beijing Municipal Commission of Urban Planning responsible for editing the master planning. The municipal government of Beijing attaches importance to Yizhuang new city. Mr Jilin, Vice Mayor of Beijing, will be the lead of the working group. Another two vice mayors will provide support to Yizhuang’s work. The Beijing Municipal Commission of Development and Reform will be responsible for detail implementation and coordination of Yizhuang new city project. |
| 6. Developer | Not yet decided. |
| 7. Financing body/institution, mechanism | Not yet decided. |
| 8. Architects | Beijing Municipal Institute of Urban Planning and other foreign design companies are to be involved in the work of master planning. |
| 9. Project status and plans | The master plan was approved in January 2007. The detailed planning is still in the process of approval. |
| 10. How is the informant involved in the project? | BDA Planning Bureau has taken the task of planning management. Beijing Water Affairs Bureau BDA Branch involved water system planning. |
| B. The role of integrated water infrastructure | |
| 1. Do water reliability and the quality of the water environment have a special focus in development of new cities/the concrete project? | According to the Beijing water environment standard, the BDA water affairs bureau has set up water function standards to each sector of river. Rivers in BDA are located in the lower reaches of the river, thus it is difficult to have a high quality water environment. Now it can meet the basic requirement of industrial development and landscape. With the present technologies, wastewater in industrial zone can reach a treatment of 100%. BDA have also set up a new water treatment plant this year with the capacity 20,000 m³. Furthermore, they have introduced recycled water in BDA. |
| 2. Is integrated water infrastructure a part of the vision for the project? | According to the 11 infrastructure plans of Beijing, 5 items has relation to water infrastructure. That is flood prevention, rain water treatment, waste water treatment, water supply and recycle water. After the publishing of the macro planning, the detail planning for the above-mentioned item will be worked out in the end of this year. |
| 3. Is it necessary that integrated water infrastructure is part of developing the project concept for development of new cities/the concrete projects? | Yes. The new city planning is only a conceptual plan. The detail planning, such as water quality, water flow, etc., will be presented in the water industry planning. |
| 4. Will the role of water in its broadest sense be included in the concept development for new cities/the concrete project? | Yes. In the concept development for the new city, the role of river channel and flood prevention has been considered. |
| 5. Which part of water infrastructure has highest focus and priority | First, water-related infrastructure should meet flood prevention standard. The government has focused intensively on combining water system and land development. The reason for this focus is that an environmental improvement will increase the land value. |
| C. The key stakeholders and decision maker on water infrastructure | |
| 1. Who are the public authorities that shall approve the water infrastructure? | Beijing Municipal Commission of Urban Planning. |
| 2. Who are the planners who decide if water infrastructure shall have a prominent role in concept development? | The BDA Water Affairs Branch will give their comments to Beijing Municipal Commission of Urban Planning. |
| 3. Are there other decision makers, who have a decisive say in prioritising water infrastructure? | Other organizations will give critical comments to these projects. For example, Water Affairs Bureau and Water Affairs Bureau at the municipal level and at the district level. |
| D. Presentation of business concept | |
|
|
| E. Which technologies are the key ones to this particular city project? | |
E.g.
Are there any plans to construct a new city or to renovate existing structures - or a combination – elaborate Are there plans to involve a "showcase" element in this project - allowing other Chinese players to learn from this project? Are there plans to link up to local knowledge institutions within research, standardisation etc. to document and disseminate environmental results of the project and feed into the national Chinese standard setting? |
The listed technologies will be used in the project development but Yizhuang new city will follow up the national basic policy of energy efficiency and pollution reduction. In this aspect, they have detailed work arrangements including the promotion of the utilization of water resource heating pumps; promote the use of clean technology; set up CCHP according to the requirement of micro-electricity enterprises. Its strict environmental standards won the BDA title of “National Environmental Protection Model Area.” By the end of 2007, the BDA had developed 665 hectares of green lands with a 36 percent forestation rate. Among all the development zones in China, the economic gross scale of BDA is the fifth highest. But the unit consumption of water, electricity and energy is ranked in first place. Thus BDA has the experience of developing recycling economy. Its infrastructure planning has the character of advanced and modern. Regarding Yizhong new city, all projects are newly built. |
3.1.4 Shenfu City
The questions below are not all relevant for the intended interviews. Part A relates to concrete/planned urban development projects that (some of) the interviewed have or are participating in, part B is general as well as concrete projects, while C and D test the feasibility/demand for our concept and possible services.
Country: China Organisation: Beijing Embassy Contact person: Nathalie Chen |
Date: August - September Interviewer: Mr Cao Jun, Division Chief of Planning Organisation: Liangning Provincial Development & Reform Commission |
| A. Information on the new city project | |
| 1. Name, | Shenfu City |
| 2. Location, | The Shenfu project is located in the area between the two cities of Shenyang and Fushun in north-eastern China. |
| 3. Visions of the project | To be built as a first class eco-city |
| 4. Size (area, people, investment), | The total development area is 605 square kilometres, in which 335.54square kilometres is for Shenyang city, 250.8 square kilometres is for Fushun city and 11square kilometres is for the Hunhe river area. By 2020, the population will be 700,000. |
| 5. Responsible authority, | Liaoning provincial government has set up working group responsible for the work of Liaoning middle part cities. The detailed implementation will be carried out by the municipal governments of Shenyang and Liaoning. In Shenyang, the Municipal Development and Reform Commission establish economic zone office will be responsible for the project. In Fushun, the Municipal Development and Reform Commission established City Integration Office will be responsible for the project. The master planning was organized by Liaoning Provincial Development and Reform Commission. |
| 6. Developer, | Not yet decided. Some factors need to be concerned, such as the administrative system, economic advantages, etc. The two cities have joint activities within coordination and investment. Each city is responsible for the implementation of projects in their area. |
| 7. Financing body/institution, mechanism/, | Multiple channels. |
| 8. Architects | |
| 9. Project status and plans | The conceptual planning has been approved. Some project areas have already been included in the original city master planning. Now they are working on the beginning part of master plan. |
| 10. How is the informant involved in the project? | The informant responsible for organizing urban planning. |
| B. The role of integrated water infrastructure | |
| 1. Do water reliability and the quality of the water environment have a special focus in development of new cities/the concrete project? | According to the concept plan, the project will focus on water treatment to Hunhe river and the river bank. Fushun city has published a detailed water environment improvement standard and a list of detailed projects, such as waste water treatment and renovation projects. In a word, Fushun has a package plan in water sector. |
| 2. Is integrated water infrastructure a part of the vision for the project? | Yes. It is mainly considered for the sight-seeing propose and its style should be in consistence with the surrounding buildings. Visions for anti-flood, water-supply and discharge have already been worked out, based on existing plans of the two cities. |
| 3. Is it necessary that integrated water infrastructure is part of developing the project concept for development of new cities/the concrete projects? | No. The new water infrastructure is mainly based on the previous hydraulic projects. The plans are not detailed enough. Only general direction is provided, such as improving the flood control standard, it is not concerned with detailed design. |
| 4. Will the role of water in its broadest sense be included in the concept development for new cities/the concrete project? | Some parts are included, such as water supply and discharge, the use of water, park, wastewater treatment but they are not detailed enough. And it is considered at the general industry level. |
| 5. Which part of water infrastructure has highest focus and priority | For the landscape the most important part is how to ensure the water quality and how to make good use of the water so that the environment in Hunhe river area can be improved |
| C. The key stakeholders and decision maker on water infrastructure | |
| 1. Who are the public authorities that shall approve the water infrastructure? | For the dam construction the water resource departments and flood control departments are involved. For wastewater treatment the environmental-protection department is involved. |
| 2. Who are the planners who decide if water infrastructure shall have a prominent role in concept development? | Safety should be considered in the master plan, and the water resource departments must guarantee the stability of the dam for flood control. Water conservancy data needs to be considered when writing out the master plan and detailed deployment should be mapped by plan departments. |
| 3. Are there other decision makers, who have a decisive say in prioritising water infrastructure? | No other departments except the water resource department and the environmental protection department are directly involved in the decision-making process. |
| D. Presentation of business concept | |
|
|
| E. Which technologies are the key ones to this particular city project? | |
E.g.
Are there any plans to construct a new city or to renovate existing structures - or a combination – elaborate Are there plans to involve a "showcase" element in this project - allowing other Chinese players to learn from this project? Are there plans to link up to local knowledge institutions within research, standardisation etc. to document and disseminate environmental results of the project and feed into the national Chinese standard setting? |
Technologies relating to ecological civilization, cycle economy, eco-environment and construction are important. This project is planned to use of the existing infrastructure to expand the scale of development. Regarding the showcase no details are yet available. |
3.1.5 Sino-Singapore Tianjin Eco-city
The questions below are not all relevant for the intended interviews. Part A relates to concrete/planned urban development projects that (some of) the interviewed have or are participating in, part B is general as well as concrete projects, while C and D test the feasibility/demand for our concept and possible services.
Country: China Organisation: Beijing Embassy Contact person: Nathalie Chen |
Date: August Interviewer: Mr Liu Zhenjiang and Mr Liu Wenchuang Organisation: Environment Bureau and Construction Bureau |
| A. Information on the new city project | |
| 1. Name, | Sino-Singapore Tianjin Eco-city |
| 2. Location, | Sino-Singapore Tianjin Eco-city is formally specified in the Coastal Leisure and Tourism Zone in the TBNA, along the northern side of Beijing-Tianjin urban development axis, at the core area of Circum-Bohai region and in east China. It is 15km away from the core area of the Tianjin Binhai New Area (TBNA), 45km from the Tianjin proper, 150km from Beijing and 50km from Tangshan. Its scope is as follows: east to Hanbei Highway — planned Central Avenue, west to the Ji River, south to the estuary of Yongdingxin River and north to planned Jinhan Expressway, covering an area of 30km2. The site selected is adjacent to industrial functional zones in the TBNA, endowed with favourable communicate and infrastructure conditions capable of providing infrastructure guarantee for the eco-city including water, gas, electricity, heating and communication etc. and favourable for the eco-city to make development achievements in a short time. |
| 3. Visions of the project | The TBNA is a pilot zone of China's comprehensive supporting reforms and plays a significant role in reform and opening up as well as independent innovations in the whole country. As an important component of the TBNA, the urban function of Sino-Singapore Tianjin Eco-city must be linked up to the TBNA's orientation. It not only takes the ecologically inhabitable function as one major goal of development, but also implements the concept of ecological economy through policies and measures such as establishing a new-type cooperative mechanism in international technology, economy and trade and founding a financing system to adapt to the development of ecological industries and led by science - technology innovations, to build a high-level industrial structure, to build a world-leading ecological industrial system and a system of modern service industry so as to become an original place and headquarters for technologies of ecological improvement and environmental protection in the world and become a model area of sustainable development, to improve the service capability, boost up its comprehensive strength and international competitiveness, complement and link up closely with each industrial functional zone, promote the development and opening up of the TBNA and provide guarantee for the reform and opening up as well as independent innovation. |
| 4. Size (area, people, investment), | It is expected that until 2020, the population of the Eco-city will be controlled within 350 thousand, the planned construction lands will be controlled within 34.2 square kilometers. |
| 5. Responsible authority, | Sino-Singapore Tianjin Eco-City Administrative Committee |
| 6. Developer, | Sino-Singapore Tianjin Eco-City Investment Development Co. Ltd. |
| 7. Financing body/institution, mechanism/, | Sino-Singapore Tianjin Eco-City Investment Development Co. Ltd. will be responsible for financing issues from multiple channels. |
| 8. Architects | No starting date yet. |
| 9. Project status and plans | The master plan has been sent to Tianjin Municipal Planning Commission and expected to be approved soon. Singapore Urban Planning Institute, China Urban Planning Institute and Tianjin Urban Planning Institute are all involved in this work. At present, the 3 km-new service center building has been finished by the end of August 2008 and relevant departments have already been moved into new office. |
| 10. How is the informant involved in the project? | The Construction Bureau and The Environment Bureau have important responsibilities in relation to the eco-city’s planning, approval, housing, land, environment standard, etc. |
| B. The role of integrated water infrastructure | |
| 1. Do water reliability and the quality of the water environment have a special focus in development of new cities/the concrete project? | Yes. Ambitions for water quality standards are high and should reach specifics standards in the China- Singapore agreement. |
| 2. Is integrated water infrastructure a part of the vision for the project? | Yes. The integrated water infrastructure is an important element of the eco-city. This includes three key measures:
Now all the three projects have been started at the same time. The project of waste water reservoir is collecting plans and will be finished the end of September 2008. |
| 3. Is it necessary that integrated water infrastructure is part of developing the project concept for development of new cities/the concrete projects? | Yes. Water projects are an important part of developing the project concept. |
| 4. Will the role of water in its broadest sense be included in the concept development for new cities/the concrete project? | Yes. The water system has been considered in concept development for the eco-city. |
| 5. Which part of water infrastructure has highest focus and priority | For the eco-city project, the main focus is the treatment to the reservoir and three rivers in this area. |
| C. The key stakeholders and decision maker on water infrastructure | |
| 1. Who are the public authorities that shall approve the water infrastructure? | The Environmental Bureau responsible for the relevant project approval. |
| 2. Who are the planners who decide if water infrastructure shall have a prominent role in concept development? | The Sino-Singapore Tianjin Eco-City Administrative Committee is in charge of overall planning and decision-making. |
| 3. Are there other decision makers, who have a decisive say in prioritising water infrastructure? | Yes. For example, the work of treatment to Ji river is on-going. Tianjin municipal government will be responsible for the coordination work. Because Ji river is also in the area of Tianjin city. |
| D. Presentation of business concept | |
|
|
| E. Which technologies are the key ones to this particular city project? | |
E.g.
Are there any plans to construct a new city or to renovate existing structures - or a combination – elaborate Are there plans to involve a "showcase" element in this project - allowing other Chinese players to learn from this project? Are there plans to link up to local knowledge institutions within research, standardisation etc. to document and disseminate environmental results of the project and feed into the national Chinese standard setting? |
The project is trying to make use of the best available advanced technologies. This is a complete new city project. There are no plans for now for systematic partnerships with knowledge institutions, but project implementation expected to be monitored at the national level (dissemination of best practice etc). |
3.1.6 Tangshan Caofeidian International Ecological Town China (CFD)
The questions below are not all relevant for the intended interviews. Part A relates to concrete/planned urban development projects that (some of) the interviewed have or are participating in, part B is general as well as concrete projects, while C and D test the feasibility/demand for our concept and possible services.
Country: Organisation: Beijing Embassy Contact person: |
Date: Interviewer: Li Yang, Investment Section Organisation: Caofeidian Construction Office of International Ecological Town |
| A. Information on the new city project | |
| 1. Name, | Tangshan Caofeidian International Ecological Town China (CFD) |
| 2. Location, | Situated at northeast part of CFD Industrial Zone. |
| 3. Visions of the project | CFD international ecological town is going to be built into ’a first-rate international ecological city, a coastal city with harbor and a pilot city’. |
| 4. Size (area, people, investment), | The planned starting area will be 30skm. The construction land of the ecological town will be 80sq. km in the near future and will be 150sq. km at a non-specified future date. By 2020, the population will be 500,000. The estimated investment by now is about 45 billion. The following planned investment will be 150billion yuan. |
| 5. Responsible authority, | Caofeidian Construction Office of International Ecological Town |
| 6. Developer, | Caofeidian International Ecological City Investment & Development Co. Ltd. (pending registration) |
| 7. Financing body/institution, mechanism/, | Multiple channels. |
| 8. Architects | |
| 9. Project status and plans | The concept planning of 30skm starting area will be approved in September 2008. The involving parties include domestic and overseas companies. The construction will be started in September. The main task for this year will be urban greening and planting. |
| 10. How is the informant involved in the project? | |
| B. The role of integrated water infrastructure | |
| 1. Do water reliability and the quality of the water environment have a special focus in development of new cities/the concrete project? | Yes. The project is situated in an area with limited water resources. Therefore water management is particularly important. |
| 2. Is integrated water infrastructure a part of the vision for the project? | Yes. According to the 30 km planning zone, there is a special planning zone the water system construction. |
| 3. Is it necessary that integrated water infrastructure is part of developing the project concept for development of new cities/the concrete projects? | Yes. CFD plans to work out special planning of water resources, underground pipeline network etc. |
| 4. Will the role of water in its broadest sense be included in the concept development for new cities/the concrete project? | There are plans to build up an energy center dealing with waste water, solid waste, etc for the whole city. |
| 5. Which part of water infrastructure has highest focus and priority | Sea water desalination and waste water treatment |
| C. The key stakeholders and decision maker on water infrastructure | |
| 1. Who are the public authorities that shall approve the water infrastructure? | The Caofeidian Construction Office of International Ecological Town has only been in existence for one year. Division of tasks between various entities not clear yet. Important to stay in contact with Construction Office. |
| 2. Who are the planners who decide if water infrastructure shall have a prominent role in concept development? | The local water affairs bureau will provide comments to the planners. |
| 3. Are there other decision makers, who have a decisive say in prioritising water infrastructure? | The CFD Construction Office will invite high level experts to participate in evaluation meeting on water-related projects. |
| D. Presentation of business concept | |
|
|
| E. Which technologies are the key ones to this particular city project? | |
E.g.
Are there any plans to construct a new city or to renovate existing structures - or a combination – elaborate |
New clean tech and the use of renewable energy are key technologies to this city project. This is a completely new city construction project. It is expected that the development of CFD international ecological town will be a pilot project in China showing the use of advanced technology in the fields of architecture, water treatment, building, energy, etc. There are no plans now to document and disseminate environmental results of the project. |
3.1.7 Diao Yu Zui Peninsula Project
The questions below are not all relevant for the intended interviews. Part A relates to concrete/planned urban development projects that (some of) the interviewed have or are participating in, part B is general as well as concrete projects, while C and D test the feasibility/demand for our concept and possible services.
Country: China Organisation: TCD-Chongqing Contact person: Annie Tang |
Date: August 21, 2008 Interviewer: Hao Qiao Organisation: chief commercial representative from the central relaxation zone, Diao Yu Zui Government office. |
| A. Information on the new city project | |
| 1. Name, | Diao Yu Zui Peninsula Project |
| 2. Location, | Da Du Kou District, Chongqing, China |
| 3. Visions of the project | Central Recreation and Business District (CRBD) in Chongqing City Planning (2005-2020) |
| 4. Size (area, people, investment), | 6,400,032 m², 44 billion RMB |
| 5. Responsible authority, |
|
| 6. Developer, | Pending |
| 7. Financing body/institution, mechanism/, |
|
| 8. Architects | Hotel, conference centre, commercial centre, shopping centre, entertainment, residence, parks, golf club, boat club |
| 9. Project status and plans | The planning and designing will be completed by the end of 2008. |
| 10. How is the informant involved in the project? | Chief Representative of CRBD, Foreign Trade & Economic Relation Commission of Da Du Kou District, Chongqing. A promoter and co-ordinator of the project |
| B. The role of integrated water infrastructure | |
| 1. Do water reliability and the quality of the water environment have a special focus in development of new cities/the concrete project? | Yes |
| 2. Is integrated water infrastructure a part of the vision for the project? | Yes |
| 3. Is it necessary that integrated water infrastructure is part of developing the project concept for development of new cities/the concrete projects? | Yes |
| 4. Will the role of water in its broadest sense be included in the concept development for new cities/the concrete project? | Yes |
| 5. Which part of water infrastructure has highest focus and priority | Waste water treatment |
| C. The key stakeholders and decision maker on water infrastructure | |
| 1. Who are the public authorities that shall approve the water infrastructure? | Chongqing Development and Reform Committee |
| 2. Who are the planners who decide if water infrastructure shall have a prominent role in concept development? |
|
| 3. Are there other decision makers, who have a decisive say in prioritising water infrastructure? | Chongqing Environment Protection Bureau |
| D. Presentation of business concept | |
|
|
| E. Which technologies are the key ones to this particular city project? | |
E.g.
Are there any plans to construct a new city or to renovate existing structures - or a combination – elaborate Are there plans to involve a "showcase" element in this project - allowing other Chinese players to learn from this project? Are there plans to link up to local knowledge institutions within research, standardisation etc. to document and disseminate environmental results of the project and feed into the national Chinese standard setting? |
Waste handling, new clean tech, general urban planning The plan is to construct a new city from a current farming land. Yes, at least a model in Chongqing |
3.1.8 Lingang New City
The questions below are not all relevant for the intended interviews. Part A relates to concrete/planned urban development projects that (some of) the interviewed have or are participating in, part B is general as well as concrete projects, while C and D test the feasibility/demand for our concept and possible services.
Country: China Organisation: Consulate General of Denmark, Shanghai Contact person: Jessie Ji |
Date: 15 Aug and 18 Aug Interviewer: Mr. James Huang, Ms. Sun Tiantian, Ms. Zhou Yuqin Organisation: Lingang Administrative Committee |
|
| A. Information on the new city project | ||
| 1. Name, | Lingang New City | |
| 2. Location, | Nanhui District, Shanghai | |
| 3. Visions of the project | Linggang New City is planned to be built as
The Lingang Industrial Zone is a state level heavy industry area. |
|
| 4. Size (area, people, investment), |
Multi function area with Finance, Trade, Business, Residential, Tourism, Education & Research facilities. |
|
| 5. Responsible authority, | Lingang New City Administrative Committee | |
| 6. Developer, | Shanghai Lingang Economic Development (Group) Co., Ltd (Lingang Group) Shanghai Harbour City Development (Group) Co., Ltd Lingang Group has a registered capital of RMB 3 Billion and is a state-owned investment enterprise. Lingang Group has subsidiary companies including Shanghai Caohejing New Technology Development Corporation, Shanghai Lingang International Logistics Development Co., Ltd, Shanghai Lingang Real Estate Co., Ltd, Shanghai Lingang Economic Development Group Investment Management Co., Ltd. and four sub-district development companies that Lingang Group has established together with local government. |
|
| 7. Financing body/institution, mechanism/, | Shanghai Lingang Economic Development Group Investment Management Co., Ltd is the wholly owned subsidiary enterprise under Lingang Group. It undertakes and represents Lingang Group for strategic study, investment, capital management and capital operation. It covers a broad area including the internal operating assets and possible investment in the future. | |
| 8. Architects | German GMP Architectural Design Institute | |
| 9. Project status and plans | 2003 – 2010 Turn Lingang into a modern city with modern equipment manufacturing and harbour industry as the major industry and a city with beautiful environment, convenient transportation, and fine design. Population size is to increase from 150,000 to 400,000. 2011 – 2020 Turn Lingang into a most dynamic and attractive mid-sized new city with population of 600,000. After 2020 Turn Lingang into the subsidiary city of Shanghai. |
|
| 10. How is the informant involved in the project? | The informant is from the Lingang New City Administrative Committee, the organization that is responsible for the overall development and planning of Lingang New city. | |
| B. The role of integrated water infrastructure | ||
| 1. Do water reliability and the quality of the water environment have a special focus in development of new cities/the concrete project? | Yes, water reliability and the quality of the water environment have a special focus in development of Lingang New City. The Central Living Area of Lingang City lies at the gathering point of Yangtze River and Hangzhou Bay. It is adjacent to East China Sea in the east, the industrial area of Lingang City in the north, and Chengsi Island, Da Yangshan and Xiao Yangshan Islands in the south. Dishui Lake (also known as Waterdrop Lake) is the core of this area. The Lake is around 2.5 kilometres in diameter and about 5 square kilometres large and will be the landscape and ecological epicentre of the Central Living area of Lingang City. The location of Lingang, rich water resources and the Dishui Lake has decided the importance of the quality of the water environment in the development of Lingang’s city. |
|
| 2. Is integrated water infrastructure a part of the vision for the project? | Yes, the integrated water infrastructure is part of the vision for the project. The Lingang city will be built as the largest satellite city in Shanghai with an estimated population of 500,000 to 800,000. Integrated water infrastructure will be one of the important factors for Lingang’s overall development. |
|
| 3. Is it necessary that integrated water infrastructure is part of developing the project concept for development of new cities/the concrete projects? | Yes. | |
| 4. Will the role of water in its broadest sense be included in the concept development for new cities/the concrete project? | Yes. Lingang City project has included the internal river system, water supply, waste water treatment, and water landscape as part of the development plan. | |
| 5. Which part of water infrastructure has highest focus and priority | Water supply and waste water treatment | |
| C. The key stakeholders and decision maker on water infrastructure | ||
| 1. Who are the public authorities that shall approve the water infrastructure? | Shanghai Water Authority | |
| 2. Who are the planners who decide if water infrastructure shall have a prominent role in concept development? | Shanghai Urban Plan Administration Bureau | |
| 3. Are there other decision makers, who have a decisive say in prioritising water infrastructure? | Water supplier , Shanghai Environmental Protection Bureau |
|
| D. Presentation of business concept | ||
|
|
|
| E. Which technologies are the key ones to this particular city project? | ||
E.g.
Are there any plans to construct a new city or to renovate existing structures - or a combination – elaborate Are there plans to involve a "showcase" element in this project - allowing other Chinese players to learn from this project? Are there plans to link up to local knowledge institutions within research, standardisation etc. to document and disseminate environmental results of the project and feed into the national Chinese standard setting? |
All the technologies listed are the key ones to Lingang New City project. It is a combination of both. Lingang New City is mainly to construct a new city and the renovation of existing towns/counties is of much smaller scale. Other project developers are welcome to study from our experience. The project currently follows the national criteria and regulations. So far there is no plan on the cooperation with local institutions within research and standardization on environmental issues. |
|
3.1.9 Qianjiang Century City/Qianjiang Century Central Business District
The questions below are not all relevant for the intended interviews. Part A relates to concrete/planned urban development projects that (some of) the interviewed have or are participating in, part B is general as well as concrete projects, while C and D test the feasibility/demand for our concept and possible services.
Remarks:
In early June 2008 the development of ten new cities along both sides of Qiantang River is announced.
Hangzhou will construct 10 new cities along Qianjiang River from upper to lower reaches, namely, Qianjiang New City, Binjiang New City, Xiasha New City, Konggang New City, Zhijiang New City, Chengdong New City, Linjiang New City, Qianjiang Century City, Jiangdong New City, and Linpu New City. It'll take 30 years to construct these 10 new cities as initially planned.
Among the ten new cities, Qianjiang New City and Qianjiang Century City are the most representative ones and will be built as the central administrative and business area, and therefore, the analysis of these two cities are conducted as below.
Country: China Organisation: Consulate General of Denmark, Shanghai Contact person: Jessie Ji |
Date:27 - 28 Aug, 2008 Interviewer: Mr. Zhou Jianming, Mr. Yao and Mr. Li Organisation: Qianjiang Century City Administrative Committee |
|
| A. Information on the new city project | ||
| 1. Name, | Qianjiang Century City/Qianjiang Century Central Business District | |
| 2. Location, | Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province | |
| 3. Visions of the project | Background: Qianjiang New City and Qianjiang Century City are two new cities projects in Hangzhou. The two areas are separated by Qiantang River. Qianjiang New City will be more of a government and administrative centre while Qianjiang Century City will be more of a business ad commerce centre.
|
|
| 4. Size (area, people, investment), | Planed area: 22.74 km² Estimated population: 144,000 Investment: When “33811” project started in March 2008, the total investment has so far reached RMB 15.57 billion. |
|
| 5. Responsible authority, | Qianjiang Century City Administrative Committee | |
| 6. Developer, | The developers who have been confirmed and for the development of residential areas are mainly companies from Zhejiang Province including Sunrise Estate, Shun Fa Estate, and Hangzhou Real Estate Development Group. | |
| 7. Financing body/institution, mechanism/, | The financing is from both the local government and social investment. | |
| 8. Architects | Zhejiang Chengxiang Architectural Design Institute NIKKEN SEKKEI Design Firm (Japan) – for conceptual design only. |
|
| 9. Project status and plans | The project is still at the early stages. The initial project “33811” has just started on 19 March 2008. “33811” project includes the construction of 3 compound for relocated residence, the relocation of 3 towns, 8 infrastructure facilities and 11 social-invested projects.
|
|
| 10. How is the informant involved in the project? | The informant is from the Planning and Construction Division of Qianjiang Century City Administrative Committee and is directly involved with the development and planning of the area. | |
| B. The role of integrated water infrastructure | ||
| 1. Do water reliability and the quality of the water environment have a special focus in development of new cities/the concrete project? | Yes, the water reliability and quality of the water environment has a special focus in development of Qiantang Century City. | |
| 2. Is integrated water infrastructure a part of the vision for the project | Yes. Integrated water infrastructure is a part of the vision for the project. Qiantang Century City has made a water plan for the integrated water infrastructure of the area, including inner water system, lake and river rehabilitation, and plan on bank reparation and water transportation. | |
| 3. Is it necessary that integrated water infrastructure is part of developing the project concept for development of new cities/the concrete projects? | Yes. It is necessary. The area has rich water resources and the extensive inner water system requires an integrated water infrastructure plan. Apart from the water system itself, the establishment of international exhibition centre and other multi-function buildings will be built close to the water, which also put requirement on the water plan as such constructions, are defined as landscape building. |
|
| 4. Will the role of water in its broadest sense be included in the concept development for new cities/the concrete project? | Yes. The water plan for the Qianjiang Century City includes water supply, the re-arrangement of the inner river networks, waste water discharge, flood control and flood release. | |
| 5. Which part of water infrastructure has highest focus and priority | The re-arrangement of inner water networks, flood control and flood release. | |
| C. The key stakeholders and decision maker on water infrastructure | ||
| 1. Who are the public authorities that shall approve the water infrastructure? | The Administration Bureau of Qiantang River, Bureau of Water Resource of Zhejiang Province, Bureau of Water Resource and Agriculture Infrastructure, Xiaoshan, Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province | |
| 2. Who are the planners who decide if water infrastructure shall have a prominent role in concept development? | Hangzhou City Government Zhejiang Development and Reform Commission |
|
| 3. Are there other decision makers, who have a decisive say in prioritising water infrastructure? | Hangzhou Construction Commission Hangzhou Bureau of Environment Protection |
|
| D. Presentation of business concept | ||
|
|
|
| E. Which technologies are the key ones to this particular city project? | ||
E.g.
Are there any plans to construct a new city or to renovate existing structures - or a combination – elaborate Are there plans to involve a "showcase" element in this project - allowing other Chinese players to learn from this project? Are there plans to link up to local knowledge institutions within research, standardisation etc. to document and disseminate environmental results of the project and feed into the national Chinese standard setting? |
The key technologies are:
The Qiantang Century City is mainly a project of constructing a new city. The renovation of existing small towns only accounts for a small part. Not at the moment. |
|
3.1.10 Qianjiang New City
The questions below are not all relevant for the intended interviews. Part A relates to concrete/planned urban development projects that (some of) the interviewed have or are participating in, part B is general as well as concrete projects, while C and D test the feasibility/demand for our concept and possible services.
Country: China Organisation: Consulate General of Denmark, Shanghai Contact person: Jessie Ji |
Date:2 September, 2008 Interviewer: Ms. Chen, Deputy Director of Planning Dept. Organisation: Qianjiang Construction and Administrative Committee |
|
| A. Information on the new city project | ||
| 1. Name, | Qianjiang New City | |
| 2. Location, | Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province | |
| 3. Visions of the project | The Qianjiang New City will be the central business and commerce center of Hangzhou city as well as Zhejiang Province. It will be built as a garden city with modern outlook, characteristics of Hangzhou city and Qiantang river, and the touch of high tech and cultural legacy. With the completion of Qianjiang New City, the majority of government bodies, authorities will be moved to Qianjing New City to make it an administrative centre of Hangzhou and Zhejiang Province. |
|
| 4. Size (area, people, investment), | Planned area: 15.8 Square Kilometres (Phase 1) 2.86 Square Kilometres (Phase 2). In total: 18.86 Square Kilometres. Estimated population: 300,000 Investment: RMB 50 billion |
|
| 5. Responsible authority, | Qianjiang New City Construction and Administrative Committee | |
| 6. Developer, | So far the big developers who get involved in the real estate project include Huarun Group and Sun Hung Kai Properties. Negotiation with big real estate developers, such as Hutchison Whampoa Properties and Hang Lung Properties are still on-going and have yet to be finalized. | |
| 7. Financing body/institution, mechanism/, | The financing is from both the local government and social investment. | |
| 8. Architects | Shanghai Urban Planning and Design Institute, Hangzhou Plan and Design Institute, OBERMEYER Design Consulting Co., Ltd. | |
| 9. Project status and plans | Currently the Qianjiang New City Project has completed the first phase infrastructure of eight square kilometres. Large scale project, such as Hangzhou Grand Theatre, has been completed. Other government invested projects, such as Civil Centre, International Convention Centre, Culture Centre and etc has been gradually finished and put into use. Qingchun Tunnel Project going through Qiantang River started in June 2006. The infrastructure of metro lines is under construction. A landscape green area project covering an area of 1.3 million square meters have been completed with the completion of two parks, namely Forest Park and Century Park. Qianjiang New City has attracted foreign investment with a contracted capital of RMB 16 billion. More than 30 domestic and international enterprises will have offices in Qianjiang New City. 47 building projects for corporate headquarters, business buildings, hotels, shopping malls and high end residential compound will be constructed. |
|
| 10. How is the informant involved in the project? | The informant is from the Planning Division of Qianjiang New City Construction and Administrative Committee and is involved with the overall plan of the area. | |
| B. The role of integrated water infrastructure | ||
| 1. Do water reliability and the quality of the water environment have a special focus in development of new cities/the concrete project? | Yes. Water reliability and the quality of the water environment have a special focus in the development of Qiantang New City. The planned area of Qianjiang New City is to the east of Qiantang River. The inner river system includes Xin Tang River and Xin Kai River. The water resources of the area has required a good plan on the water environment to be incorporated into the overall construction and planning of the area. The quality of the water environment is monitored according to the standard of Hangzhou City. |
|
| 2. Is integrated water infrastructure a part of the vision for the project? | Yes. Integrated water infrastructure is a part of the vision of the project. The vision for Qianjiang New City is to plan the construction in harmony with the natural resources, green area and Qiantang River to create a harmonious landscape. | |
| 3. Is it necessary that integrated water infrastructure is part of developing the project concept for development of new cities/the concrete projects? | Yes. It is necessary that integrated water infrastructure is part of the developing the project concept for development of Qianjiang New city. The location of Hangzhou city and its rich water resources has decided the integrated water infrastructure need to be taken into consideration while making the development plan. | |
| 4. Will the role of water in its broadest sense be included in the concept development for new cities/the concrete project? | The development of Qianjiang New City includes water and water related infrastructure in: landscape planning, water supply, waste water discharge, flood control, flood release, and water transportation. | |
| 5. Which part of water infrastructure has highest focus and priority | All aspects of water infrastructure are considered to be very important to the local government. In the near future, how to utilize the water from Qiantang River for irrigation purpose will be the major focus. | |
| C. The key stakeholders and decision maker on water infrastructure | ||
| 1. Who are the public authorities that shall approve the water infrastructure? | Hangzhou City Government Hangzhou Construction Commission Administration Bureau of Qiantang River Hangzhou Environment Protection Bureau |
|
| 2. Who are the planners who decide if water infrastructure shall have a prominent role in concept development? | Hangzhou Urban Planning Bureau The Administration Bureau of Qiantang River Hangzhou Construction Commission |
|
| 3. Are there other decision makers, who have a decisive say in prioritising water infrastructure? | Consultant and expert invited by the government authorities. | |
| D. Presentation of business concept | ||
|
|
|
| E. Which technologies are the key ones to this particular city project? | ||
E.g.
Are there any plans to construct a new city or to renovate existing structures - or a combination – elaborate Are there plans to involve a "showcase" element in this project - allowing other Chinese players to learn from this project? Are there plans to link up to local knowledge institutions within research, standardisation etc. to document and disseminate environmental results of the project and feed into the national Chinese standard setting? |
The key technologies to Qianjiang New City Project are:
Qianjiang New City is to construct a new city which used to be farming land and warehouse. Yes. Qianjiang New City Construction and Administrative Committee hopes to build Qianjiang New City as a showcase project. So far there is no such plan. |
|
3.1.11 Zhenhai New City
The questions below are not all relevant for the intended interviews. Part A relates to concrete/planned urban development projects that (some of) the interviewed have or are participating in, part B is general as well as concrete projects, while C and D test the feasibility/demand for our concept and possible services.
Country: China Organisation: Consulate General of Denmark, Shanghai Contact person: Jessie Ji |
Date:27 - 28 Aug, 2008 Interviewer: Ms. Jessie Li Organisation: Zhenhai New City Administrative Committee |
|
| A. Information on the new city project | ||
| 1. Name, | Zhenhai New City | |
| 2. Location, | Ningbo, Zhejiang Province, China | |
| 3. Visions of the project | The Zhenhai New City will be built as a comprehensive new city with business, commerce, education and research, office and residential area, which will not only show the modern business district outlook but also represent the water town characteristics of east China. | |
| 4. Size (area, people, investment), | Planned area: 46 square kilometeres Estimated population: 400,000 – 450,000 Investment: RMB 10 billion |
|
| 5. Responsible authority, | Zhenhai New City Administrative Committee | |
| 6. Developer, | Ningbo Yinyi Real Estate Development Co., Ltd, Wanda Group, Zhejiang Greentown Real Estate Development Co., Ltd. | |
| 7. Financing body/institution, mechanism/, | Local financial revenue and social financing. | |
| 8. Architects | EDAW (Shanghai) Consulting Co., Ltd. Zhenhai Institute of Design, Survey and Plan |
|
| 9. Project status and plans | Currently the first phase of a living compound covering an area of 550,000 square meters is completed. The 5th Hospital of Ningbo is at the stage of interior decoration and facility installation. The construction of Ningbo Museum with a total investment of RMB 160 Million and Zhenhai High School is on-going. There are more than ten big scale commercial and public projects that are under construction. The Zhenhai Administrative Committee hopes to complete the core area of 1 square kilometer within next three years. By October 2008. The detailed plan, key architectural project and the design plan for underground space will be completed. The Yinyi – Haishang Plaza covering an area of 144 mu (1 mu = 666.67 square meters) with a total investment of RMB 1 billion will start end of this year. So far the road of 40 kilometers has been completed. There are more than 40 construction projects for institutions, such as Ningbo Institute of Material Technology & Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo Engineering Institute, The 5th Hospital of Ningbo, and etc have already started. |
|
| 10. How is the informant involved in the project? | The informant is from the Zhenhai New City Administrative Committee which is directly involved with the overall development of this area. | |
| B. The role of integrated water infrastructure | ||
| 1. Do water reliability and the quality of the water environment have a special focus in development of new cities/the concrete project? | Yes. | |
| 2. Is integrated water infrastructure a part of the vision for the project? | Yes. | |
| 3. Is it necessary that integrated water infrastructure is part of developing the project concept for development of new cities/the concrete projects? | Yes. | |
| 4. Will the role of water in its broadest sense be included in the concept development for new cities/the concrete project? | Yes. The water and water related infrastructure is included in the development of Zhenhai New City plan. Water infrastructure, such as,
Are included in the development plan. |
|
| 5. Which part of water infrastructure has highest focus and priority |
|
|
| C. The key stakeholders and decision maker on water infrastructure | ||
| 1. Who are the public authorities that shall approve the water infrastructure? | Zhenhai Water Resource Bureau | |
| 2. Who are the planners who decide if water infrastructure shall have a prominent role in concept development? | Zhenhai Division, Ningbo Urban Planning Bureau | |
| 3. Are there other decision makers, who have a decisive say in prioritising water infrastructure? | Ningbo Water Resource Bureau | |
| D. Presentation of business concept | ||
|
Will be the major areas to be considered. In a long run, the improvement of water environment will be the focus.
|
|
| E. Which technologies are the key ones to this particular city project? | ||
E.g.
Are there any plans to construct a new city or to renovate existing structures - or a combination – elaborate Are there plans to involve a "showcase" element in this project - allowing other Chinese players to learn from this project? Are there plans to link up to local knowledge institutions within research, standardisation etc. to document and disseminate environmental results of the project and feed into the national Chinese standard setting? |
The key technologies to Zhenhai New City are:
Zhenhai New City project is to construct a new city. Yes. The Zhenhai New City has been considered to be built as a showcase project. Yes. There is such plan. |
|
4 List of key Chinese individuals and major foreign involvements
4.1 List of key Chinese individuals
Click here to see the table "List of key Chinese individuals".
4.2 List of major foreign involvements
| Company Name | Website | Contact Information | Contact Person |
| Arup, the UK planning, engineering and consultancy firm | http://www.arup.com/ | 39/F-41/F Huai Hai Plaza, 1045 Huai Hai Road (M) (near FenYang Road) Shanghai 200031 China Tel: +86-21-6126 2888 Fax: +86-21-6126 2882 |
Michael Kwok |
| GEF – the Global Environment Facility | http://www.gefweb.org/ | Address: 1818 H Street, NW, MSN G6-602,Washington, DC 20433 USA Tel: (202) 473-0508 Fax: (202) 522-3240/3245 |
|
| German AS&P Co. Ltd | http://www.as-p.de/ content/e3-projects/e_3-2-urban_planning.php |
AS&P Architecture Consulting (Shanghai) Co.Ltd. 841 Yan An Road (M) Room 1505, 200040 Shanghai, China Tel: +86-21-62791451 or +86-21-62790914 Fax:+86-21-62791547 Email: as-p.china@163.com |
Dipl.Ing. Lili Yang (General Manager) Tel: +86.21.62 791451- 101 or +86.21.62 790914-101 Mail: I.yang@as -p.de |
| Japan Kisho Kurokawa Co. Ltd | http://www.kisho.co.jp/ index.php |
ARK MORI BLDG.13F. |
|
| Keppel Corporation Limited | http://www.kepcorp.com/ home/ |
1 HarbourFront Avenue #18-01 Keppel Bay Tower Singapore Postcode: 098632 Fax:+65 64136452 Tel:+65 62706666 Email: keppelgroup@kepcorp.com |
|
| SOM (U.S) | http://www.som.com/ content.cfm/www_home |
Address: Suite 201, Block 7, No 8 Jian Guo Zhong Road,Shanghai 200025, PRC Tel:+ 86-21-54666888 Fax: +86-21-54657536 |
|
| Sweco Sweden | http://www.sweco.se/ sv/Sweden/ |
Sweco AB (publ) Gjörwellsgatan 22 Box 34044 100 26 STOCKHOLM Tel: 08-695 6000 Fax 08-695 60 10 |
|
| USA Edaw | http://www.edaw.com/ | 30F Shanghai Times Square, No.93 Huaihai Zhong Road, Shanghai, China 200021 Tel:+86-21-6391 0303 Fax:+86-21-6391 8123 |
|
| USA HOK | http://www.hok.com/ | Address: Suite 3705 A, Ciro's Plaza, 388 Nanjing West Road, Shanghai Postcode:200003 Tel:+86-21-63346181 Email:shanghai@hok.com |
|
| USA RTKL International Co. Ltd | http://www.rtkl.com | Address:RTKL International Ltd. Suite 2106 Platinum, 233 Taicang Road,Shanghai 200020 China Tel:+86-2161227922 Fax:+86-21-61227912 |
Scott Kilbourn (Vice President, General Manager) |
5 A list of key reference documents
- 5.1 Appendix 1: Urban and Rural Planning Law of the People’s Republic of China
- 5.2 Appendix 2: Real Estate Management Law
- 5.3 Appendix 3: Construction Law
- 5.4 Appendix 4: Environmental Protection Law of the People’s Republic of China
- 5.5 Appendix 5: Land Administration Law of the People‘s Republic of China
5.1 Appendix 1: Urban and Rural Planning Law of the People’s Republic of China
| Promulgation date: | 10-28-2007 |
| Effective date: | 01-01-2008 |
Urban and Rural Planning Law of the People’s Republic of China
(Adopted at the 30th meeting of the Standing Committee of the Tenth National People’s Congress of the People’s Republic of China on October 28th, 2007)
Contents
Chapter I General Provisions
Chapter II Establishment of Urban and Rural Planning
Chapter III Implementati on of Urban and Rural Planning
Chapter IV Modification of Urban and Rural Planning
Chapter V Supervision and Inspection
Chapter VI Legal Liability
Chapter VII Supplementary Provisions
Article 1 This Law is formulated for the purpose of strengthening urban and rural planning administration, harmonizing urban and rural spatial layout, improving people’s living environment and promoting the integrated, harmonious and sustainable development of urban and rural society and economy.
Article 2 Making and implementing urban and rural planning as well as conducting construction activities in planning areas shall be governed by this Law.
The term “urban and rural planning” as mentioned in this Law includes urban system planning, city planning, town planning, township planning and village planning. City or town planning includes overall planning and detailed planning. Detailed planning includes regulatory detailed planning and site detailed planning.
The term “planning area” as mentioned in this Law refers to the built-up areas of cities, towns and villages as well as areas that must be under planning control for urban and rural construction and development. The specific scope of a planning area shall be defined by the related people’s government, in light of the urban and rural economic and social development level and the needs for the overall development of urban and rural areas, in organizing the establishment of the overall planning of a city or town, a township planning or a village planning.
Article 3 Cities and towns shall work out city planning and town planning in accordance with this Law. Construction activities within a city or town planning area shall be conducted in accordance with the planning requirements.
The local people’s government at or above the county level shall, in light of the local rural economic and social development level and in accordance with the principles of adjusting measures to local conditions and feasibility, determine regions required to establish township or village planning. The townships and villages inside the regions shall work out their respective planning in accordance with this Law. The township and village construction within the planning areas shall be in line with the planning requirements.
The local people’s government at or above the county level shall encourage and guide the townships and villages outside the regions to work out and implement township and village planning.
Article 4 Urban and rural planning shall be worked out and implemented by following the principles of planning the urban and rural areas as a whole, reasonable layout, saving the land, intensive growth and planning before constructing so as to improve ecological environment, enhance the conservation and comprehensive utilization of resources and energy, protect farmland and other natural resource as well as cultural heritages, maintain local features, ethnic features and traditions, prevent pollution and other public nuisance, and satisfy the needs of regional population development, national defense construction, disaster prevention and alleviation, public health and public safety.
Construction activities in the planning area shall be conducted by observing laws and regulations governing land management, natural resources and environmental protection, etc.
The local people’s government at or above the county level shall, in light of the local social and economic development level, reasonably determine the development scale, steps and construction standards of a city or town in the overall planning of the city or town.
Article 5 The establishment of the overall planning of a city or town, a township planning or a village planning shall be based on the national economic and social development planning as well as the overall planning on land use.
Article 6 The people’s governments at various levels shall bring the expenses necessary for the establishment and administration of urban and rural planning into the fiscal budget at the corresponding level.
Article 7 An urban and rural planning which has been approved according to law shall be a basis for urban and rural construction as well as planning administration, and may not be altered without going through the legal procedure.
Article 8 Organs organizing the establishment of urban and rural planning shall publicize legally approved urban and rural planning in a timely manner, except for contents which shall not be disclosed as required by laws or administrative regulations.
Article 9 All entities and individuals shall abide by urban and rural planning which have been legally approved and disclosed, be submit to the administration of such planning, and have the right to inquiry of the competent department of urban and rural planning about whether a construction activity affecting their interests is in compliance with the planning requirements.
Any entity or individual shall have the right to report or accuse of any act in violation of any urban and rural planning to the competent department of urban and rural planning or other related department. Such department shall promptly accept the report or accusation and organize manpower to investigate and handle it.
Article 10 The state encourages adopting advanced scientific technologies to make urban and rural planning more scientific and to improve the efficiency of the implementation, supervision and administration of urban and rural planning.
Article 11 The competent department of urban and rural planning under the State Council shall take charge of the urban and rural planning administration of the whole nation.
The local people’s governments at or above the county level shall take charge of the urban and rural planning administration work of their respective administrative region.
Chapter II Establishment of Urban and Rural Planning
Article 12 The competent department of urban and rural planning under the State Council shall, together with other relevant departments under the State Council, organize the establishment of the national urban system planning, which shall be used to guide the establishment of provincial urban system planning and overall planning of cities.
The national urban system planning shall be filed by the competent department of urban and rural planning under the State Council with the State Council for examination and approval.
Article 13 The people’s government of a province or autonomous region shall organize the establishment of its provincial urban system planning and file it with the State Council for examination and approval.
A provincial urban system planning shall include: spatial layout of cities and towns and scale control, layout of significant infrastructures and areas which shall be under strict control for the purpose of protecting ecological environment and resources.
Article 14 The people’s government of a city shall organize the establishment of the overall planning of the city.
The overall planning of a municipality directly under the Central Government shall be filed by the people’s government of the municipality with the State Council for examination and approval. The overall planning of a city where the provincial or autonomous region people’s government is located or which is specified by the State Council shall be filed with the State Council for examination and approval after it is examined and approved by the provincial or autonomous region people’s government. The overall planning of any other city shall be filed by the people’s government of the city with the provincial or autonomous region people’s government for examination and approval.
Article 15 The county people’s government shall organize the establishment of the overall planning of the town where the county people’s government is located, and shall file the planning with the people’s government at the next higher level for examination and approval. The overall planning of any other town shall be established by the people’s government of the town and filed with the people’s government at the next higher level for examination and approval.
Article 16 The provincial urban system planning established by the people’s government of a province or an autonomous region or the overall planning established by the people’s government of a municipality or county shall, before it is submitted to the people’s government at the next higher level for examination and approval, be deliberated by the standing committee of the people’s congress at the same level, and the deliberation opinions of the members of the standing committee shall be submitted to the people’s government at the same level for consideration.
The overall planning of a town established by the people’s government of the town shall, before it is submitted to the people’s government at the next higher level for examination and approval, be firstly deliberated by the people’s congress of the town, and the deliberation opinions of the deputies shall be submitted to the people’s government at the same level for consideration.
When filing a provincial urban system planning, a city overall planning or a town overall planning for examination and approval, the organ establishing the planning shall file the deliberation opinions of the members of the standing committee of the people’s congress at the same level or the deputies to the people’s congress of the town as well as the changes in the planning made in accordance with the opinions together.
Article 17 The overall planning of a city or town shall include: the overall arrangement for the development of the city or town, functional zones, land use layout, comprehensive traffic system, regions prohibited, restricted from or appropriate for construction and various kinds of special planning, etc.
The following contents shall be included in the overall planning of a city or town as mandatory contents: coverage of the planning area, scale of the land used for the construction of the planning area, land used for infrastructure and public service facilities, water head sites and water system, basic farmland, and land used for afforestation, environmental protection, protection of natural and historical cultural heritages, and disaster prevention and alleviation, etc.
The planning period of the overall planning of a city or town is usually 20 years. The overall planning of a city shall forecast the long-term development trend of the city and make corresponding arrangements.
Article 18 A township or village planning shall proceed from the actual situation of the rural district, respect the will of the villagers and embody local and rural features.
A township or village planning shall include: the coverage of the planning area, the layout of the land used and the construction requirements for dwelling houses, roads, water supply, drainage, power supply, garbage collection, livestock and poultry feeding plants, service facilities for the production and livelihood in rural areas, and public welfare establishments, and the specific arrangements on protecting farmland as well as other natural resources and historical cultural heritages and preventing and alleviating disasters, etc. A village planning shall also include the overall arrangement for the development of all villages within this administrative region.
Article 19 The competent department of urban and rural planning of a city people’s government shall, in accordance with the requirements of the overall planning of the city, organize the establishment of a regulatory detailed planning, and file the planning with the standing committee of the people’s congress at the same level and the people’s government at the next higher level for archival purpose upon the approval of the people’s government at the same level.
Article 20 A town people’s government shall, in accordance with the requirements of the overall planning of the town, organize the establishment of a regulatory detailed planning and file the planning with the people’s government at the next higher level for examination and approval. The regulatory detailed planning of the town where the county people’s government is located shall be established by the competent department of urban and rural planning under the county people’s government in accordance with the overall planning of the town, and be filed with the standing committee of the people’s congress at the same level and the people’s government at the next higher level for archival purpose upon the approval of the county people’s government.
Article 21 The competent department under the people’s government of a city or county or the people’s government of a town may organize the establishment of a site detailed planning for important land blocks. The site detained planning shall be in conformity with the regulatory detained planning.
Article 22 The people’s government of a township or town shall take charge of establishing the township or village planning, and shall file such planning with the people’s government at the next higher level for examination and approval. A village planning shall be consented to by the villagers’ meeting or the villagers’ representative meeting before it is filed for examination and approval.
Article 23 The overall planning or detailed planning of the capital shall take the layout of land used by central state organs as well as their spatial arrangements into full consideration.
Article 24 Organs organizing the establishment of urban and rural planning shall authorize entities with corresponding qualification grades to undertake the specific establishment work.
An entity may undertake urban and rural planning establishment work within the scope authorized by its qualification grade after satisfying the following requirements, passing the examination conducted by the competent department of urban and rural planning under the State Council or under the people’s government of the concerned province, autonomous region or municipality directly under the Central Government, and obtaining the qualification certificate of the corresponding grade:
- having the corporate capacity;
- having the prescribed number of planners who have been legally registered at the competent department of urban and rural planning under the State Council;
- having the prescribed number of related technical personnel;
- having corresponding technical equipment; and
- having a sound technique management system, a sound quality management system and a sound financial management system.
The administrative measures for the practicing qualification of planners shall be formulated by the competent department of urban and rural planning under the State Council together with the personnel administrative department under the State Council.
The relevant state standards shall be observed when establishing urban and rural planning.
Article 25 When establishing urban and rural planning, the basic materials about prospecting, mapping, weather, seism, hydrology and environment as required by the state must be in hand.
The local competent departments under the local people’s government at or above the county level shall, in light of the needs for urban and rural planning, provide the relevant basic materials in a timely manner.
Article 26 Before filing an urban or rural planning for examination and approval, the organ establishing it shall announce the draft of the planning and collect opinions from experts and the general public by way of argumentation, hearing or other. The draft shall be announced for at least 30 days.
The organ establishing the planning shall fully consider the opinions of experts and the general public, and attach an explanation on the adoption of the relevant opinions and an explanation to the materials filed for examination and approval.
Article 27 Before approving a provincial urban system planning, a city overall planning or a town overall planning, the examining and approving organ shall organize experts and the related departments to conduct an examination.
Chapter III Implementation of Urban and Rural Planning
Article 28 The local people’s governments at various levels shall, in light of the local economic and social development level, and according to their abilities, respect the willingness of the general public and organize the implementation of urban and rural planning in a planned and step-by-step manner.
Article 29 As for the construction and development of urban areas, priority shall be given to the construction of infrastructure and public service facilities, the relation between the development of new zones and the reconstruction of old zones shall be properly handled, and overall consideration shall be given to the livelihood of persons migrating to urban areas to work, surrounding rural economic and social development and villagers’ production and livelihood needs.
The construction and development of towns shall be based on rural economic and social development as well as industrial restructuring, and priority shall be given to the construction of infrastructure of water supply, water drainage, power supply, gas supply, road, telecommunication, broadcasting and TV as well as public service facilities including schools, hospitals, cultural stations, kindergartens and welfare institutions so as to provide services for surrounding rural areas.
As for the construction and development of townships and villages, it is necessary to make adjusts according to local conditions, use land in an effective way, give play to villagers’ autonomous organizations and guide villagers to make reasonable constructions so as to improve the production and livelihood conditions in rural areas.
Article 30 As for the development and construction of newly developed zones in urban areas, it is necessary to reasonably determine the construction scale and time sequence, fully use the existing infrastructure and public service facilities, vigorously protect natural resources and ecological environment and materialize local characteristics.
Beyond the scope of land used for construction as determined in a city or town overall planning, no development zone or new urban developed zone may be established.
Article 31 As for the reconstruction of old urban areas, it is necessary to protect historical and cultural heritage and traditional style, reasonably determine the demolition and construction scale, and reconstruct the places where there are many dilapidated houses and the infrastructure is relatively backward.
The protection of famous historical and cultural cities as well as the preservation and use of protected structures shall be conducted in accordance with the related laws, administrative regulations and the provisions of the State Council.
Article 32 As for the construction and development of urban and rural areas, it is necessary to legally protect and reasonably use famous scenery resources, make overall arrangements on the construction of famous scenic sites as well as surrounding townships, towns and villages.
The planning, construction and management of famous scenic sites shall be proceeded in accordance with the related laws, administrative regulations and the provisions of the State Council.
Article 33 The development and utilization of urban underground space shall be conducted according to the economic and technical development level, the principles of overall arrangement, comprehensive development and reasonable utilization shall be followed, and the needs for disaster prevention and reduction, civil air defense and communication shall be taken into full consideration. It shall also be in line with the city planning, and the examining and approving formalities must be handled.
Article 34 The people’s government of a city, county or town shall, in accordance with the city/town overall planning, overall planning on land use, annual plan as well as the national economic and social development planning, work out a near-term construction planning and submit the planning to the overall planning examining and approving organ for archival purpose.
The near-term construction planning shall lay stress on the construction of important infrastructure, public service facilities and residential houses for mid and low income residents as well as the protection of ecological environment, specify the sequence, development direction and spatial layout. The period of a near-term construction planning shall be five years.
Article 35 As for the land used for railway, highway, port, airport, road, greenbelt, electricity transmission and distribution facilities, electricity transmission lines, communication facilities, broadcasting & TV facilities, pipeline facilities, water courses, reservoirs, water head sites, natural reserves, flood prevention passages, fire fighting accesses, nuclear power plants, garbage landfills and incineration sites, sewage disposal plants and public service facilities, as well as other land whose use is under the protection of law as specified in urban and rural planning, it is forbidden to change their purpose without approval.
Article 36 As for a construction project which is subject to the approval or verification of the related department as required by the state provisions, if the right to use state-owned land is appropriated, the construction entity shall, before filing the project with the related department for approval, apply to the competent department of urban and rural planning for issuing a written proposal of location.
Written proposal of location is not required for other construction projects.
Article 37 If the right to use state-owned land for a construction project within a city or town planning area is appropriated, upon the approval or verification of the related department, or putting-on-archive of the project, the construction entity shall apply to the competent department of urban and rural planning under the people’s government of the city or town for permitting the land use for construction, and the department shall issue a construction land use permit after checking and verifying the location and area of the land used for construction as well as the scope of areas where construction is permitted in accordance with the regulatory detailed planning.
The construction entity may only apply to the competent department of land under the local people’s government at or above the county level for land use after obtaining the land use permit. The competent department of land may appropriate land to it upon the approval of the people’s government at or above the county level.
Article 38 If the right to use state-owned land within a city or town planning area is assigned, the competent department of urban and rural planning under the people’s government of the city or county shall, before the assignment, raise such planning requirements as the location of the land to be assigned, nature of its use and development intensity as a component of the contract for assignment of the right to use start-owned land on the basis of regulatory detailed planning. As for any state-owned land, if the planning requirements are not specified yet, the right to use it may not be assigned.
If the right to use state-owned land for a construction project is obtained by assignment, the construction entity shall, after concluding the contract for assignment of the right to use start-owned land, obtain the land use permit from the competent department of urban and rural planning of the people’s government of the city or county upon the strength of the approval, or verification or archive-filing documents of the project as well as the contract for assignment of the right to use start-owned land.
The competent department of urban and rural planning of the people’s government of the city or county may not change the planning requirements which constitute a component of the contract for assignment of the right to use start-owned land in the land use permit without approval.
Article 39 If the planning requirements are not incorporated into a contract for assignment of the right to use start-owned land, this contract is invalid. Where a construction entity without the land use permit is approved to use land, the people’s government at or above the county level shall cancel the approval document, if any land has been occupied, such land shall be returned promptly, and if any damage has been caused to a party concerned, compensations shall be made according to law.
Article 40 To build any structure, fixture, road, pipeline or other engineering project within a city or town planning area, the construction entity or individual shall apply to the competent department of urban and rural planning under the people’s government of the city or county or the town people’s government specified by the people’s government of the province, autonomous region or municipality directly under the Central Government for a planning permit on construction project.
To apply for a planning permit on construction project, the relevant documentary evidence on land use, the engineering design plan of the project as well as other related documents shall be submitted. If the project requires a site detailed planning, such planning shall also be submitted. If the project satisfies the regulatory detailed planning and the planning requirements, the competent department of urban and rural planning under the people’s government of the city or county or the town people’s government specified by the people’s government of the province, autonomous region or municipality directly under the Central Government shall issue a planning permit on construction project.
The competent department of urban and rural planning under the people’s government of the city or county or the town people’s government specified by the people’s government of the province, autonomous region or municipality directly under the Central Government shall publicize the general site layout of the site detailed planning and the engineering design plan which have been deliberated and adopted according to law.
Article 41 To build facilities needed by township and village enterprises, village public utilities or public welfare establishments within a township or village planning area, the construction entity or individual shall file an application with the people’s government of the township or town, which shall submit the application to the competent department of urban and rural planning of the people’s government of the city or county for issuing a planning permit for rural construction.
The planning administrative measures for building villagers’ residential houses in the original house sites within a township or village planning area shall be formulated by each province, autonomous region or municipality directly under the Central Government on its own.
When building premises needed by township and village enterprises, rural common facilities or public welfare establishments within a township or village planning area, no farm land may be used therefor. Where it is really necessary to use farm land, the competent department of urban and rural planning under the people’s government of the city or county may issue the planning permit for rural construction after the construction entity or individual handles the examining and approving formalities for changing the purpose of farm land in accordance with the relevant provisions of the Land Administration Law of the People’s Republic of China.
The construction entity or individual may not handle the examining and approving formalities for land use until he obtains the planning permit for rural construction.
Article 42 The competent departments of urban and rural planning may not grant any planning permit beyond the scope of land used for building as specified in urban and rural planning.
Article 43 A construction entity shall proceed the construction in accordance with the planning requirements; in the case of any change, it must file an application therefor with the competent department of urban and rural planning under the people’s government of the city or county. If the change violates the regulatory detailed planning, the competent department may not approve the change. The competent department of urban and rural planning under the people’s government of the city or county shall notify the competent department of land at the same level of the changed planning requirements and publicize them.
The construction entity shall file the changed planning requirements with the competent department of land of the related people’s government for archival purpose.
Article 44 Any temporary construction within a city or town planning area must be subject to the approval of the competent department of urban and rural planning under the people’s government of the city or town. If the temporary construction impedes the implementation of the near-term construction planning, the regulatory detailed planning, traffic, townscape or safety, it shall be disapproved.
A temporary construction must be dismantled before the expiration of the approved time limit.
The specific measures for the administration of temporary construction and land use planning shall be formulated by the people’s government of each province, each autonomous region and each municipality directly under the Central Government.
Article 45 The competent department of urban and rural planning under the local people’s government at or above the county level shall check and verify whether a construction project satisfies the planning requirements in accordance with the provisions of the State Council. Without such check or without passing the check, the construction entity may not organize the completion check and acceptance of the project.
A construction entity shall, within 6 months after the completion check and acceptance, file the relevant materials about the completion check and acceptance with the competent department of urban and rural planning.
Chapter IV Modification of Urban and Rural Planning
Article 46 The organ establishing a provincial urban system planning, a city overall planning or a town overall planning shall organize the related departments and experts to evaluate the implementation of the planning on a regular basis and collect public opinions by argumentation, hearing or other ways. The organ shall submit an evaluation report attached with the collected opinions to the standing committee of the people’s congress at the same level, the people’s congress of the town and the organ examining and approving the planning.
Article 47 Under any of the following circumstances, the organ establishing the planning may modify the provincial urban system planning, the city overall planning or the town overall planning within its power limits and in accordance with the prescribed procedure:
- changes in the urban and rural planning established by the people’s government at a higher level require to modify the planning;
- adjustment of administrative divisions requires to modify the planning;
- a significant construction project approved by the State Council requires to modify the planning;
- the modification is necessary upon evaluation; and
- other circumstances under which the modification is necessary as deemed by the organ examining and approving the urban and rural planning.
Before modifying the provincial urban system planning, the city overall planning or the town overall planning, the organ establishing it shall summarize the implementation of the planning and report the situation to the organ examining and approving the planning. If the modification involves the mandatory content of the city or town overall planning, the organ establishing it shall submit a special report to the organ examining and approving the planning, and shall set about to prepare the modification plan after obtaining the consent of the organ examining and approving the planning.
The modified provincial urban system planning, city overall planning or town overall planning shall be filed for approval in accordance with the examining and approving procedures prescribed in Articles 13 through 16 of this Law.
Article 48 To modify a regulatory detailed planning, the organ establishing it shall demonstrate the necessity of the modification, take counsel with the interested persons within the planning area, submit a special report to the organ examining and approving it, and set about to prepare the modification plan after obtaining the consent of the organ examining and approving the planning. The modified regulatory detailed planning shall be filed for approval in accordance with the examining and approving procedures as prescribed in Article 19 and Article 20 of this Law. If the modification involves the mandatory content of the city or town overall planning, the overall planning shall be modified first.
The modification of a township or village planning shall be filed for approval in accordance with the examining and approving procedure prescribed in Article 22 of this Law.
Article 49 The modified version of the near-term construction planning modified by the people’s government of a city, county or town shall be filed with the organ examining and approving overall planning for archival purpose.
Article 50 Where, after the written proposal of location, the land use permit, the planning permit on construction project or the planning permit for rural construction is issued to a licensee, the licensee’s legitimate rights and interests are damaged as a result of the legal modification of urban and rural planning, compensations shall be made according to law.
The general site layout of a site detailed planning or an engineering design plan approved according to law may not be modified without approval. If it is really necessary to modify it, the competent department of urban and rural planning shall hear the opinions of the interested parties in the form of hearing, etc. If the legitimate rights and interests of any interested party are damaged because of such modification, compensations shall be made according to law.
Chapter V Supervision and Inspection
Article 51 The people’s governments at or above the county level and the competent departments of urban and rural planning under them shall make more efforts in supervising and inspecting the establishment, examination and approval, implementation and modification of urban and rural planning.
Article 52 A local people’s government shall report the implementation situation of urban and rural planning to the standing committing of the people’s congress at the same level or the people’s congress of the township or town, and shall be subject to the latter’s supervision.
Article 53 The competent department of urban and rural planning of the people’s government at or above the county level shall supervise and inspect the implementation situation of urban and rural planning, and has the right to take the following measures:
- requesting the related entity or personnel to provide documents and materials related to issues under supervision, and copying them;
- requesting the related entity or personnel to make explanations on issues under supervision, and entering the field to carry on an investigation when necessary; and
- ordering the related entity or personnel to stop the act violating the relevant laws and regulations on urban and rural planning.
The working personnel of the competent department of urban and rural planning shall produce their certificates when performing the aforesaid supervision and inspection duties. Entities and personnel under supervision shall cooperate with them, and may not impede or obstruct the supervision and inspection activities conducted according to law.
Article 54 Supervision and inspection situation as well as handling results shall be opened according to law for the general public to refer to and supervise.
Article 55 Where a competent department of urban and rural planning finds out, when investigating acts violating this Law, that a state functionary deserves an administrative penalty, it shall propose a penalty suggestion to the organ with the right to appoint and dismiss him or the supervisory body.
Article 56 Where a competent department of urban and rural planning must give an administrative penalty as required by this Law but fails to do so, the competent department of urban and rural planning of the people’s government at a higher level has the right to order it to make a decision on giving the administrative penalty or suggest the related people’s government to impose an administrative penalty upon it.
Article 57 Where a competent department of urban and rural planning grants an administrative license by violating this Law, the competent department of urban and rural planning of the people’s government at a higher level has the right to either order it to cancel or directly cancel the administrative license. If the cancellation damages the legitimate rights and interests of the party concerned, compensations shall be made according to law.
Chapter VI Legal Liability
Article 58 If any organ is required by law to establish urban and rural planning but fails to do so, or fails to establish, examine and approve or modify urban and rural planning in accordance with the prescribed procedure, the higher level people’s government shall order it to correct, circulate a notice of criticism and impose punishments on the principal of the related people’s government as well as other directly liable personnel.
Article 59 If an organ establishing urban and rural planning entrusts an unqualified entity to establish urban and rural planning, the higher level people’s government shall order it to correct, circulate a notice of criticism and impose punishments on the principal of the related people’s government as well as other directly liable personnel.
Article 60 Where the people’s government of a town or the competent department of urban and rural planning of the people’s government at or above the county level commits any of the following behaviors, the people’s government at the same level, the competent department of urban and rural planning of the higher level people’s government or the supervisory organ shall, within the authorized power limits, order it to correct, circulate a notice of criticism and impose punishments on the directly liable person in charge and other directly liable persons according to law:
- failing to organize the establishment of the regulatory detailed planning of the city or the town where the county people’s government is located;
- issuing the written proposal of location, the land use permit, the planning permit on construction project or the planning permit for rural construction to an applicant by exceeding its power limits, or to an applicant not satisfying the prescribed requirements;
- failing to issue within the legal time limit the written proposal of location, the land use permit, planning permit on construction project or the planning permit for rural construction to an applicant satisfying the prescribed requirements;
- failing to publicize the general site layout of an approved site detailed planning or engineering design plan;
- failing to hear the opinions of the interested parties in the form of hearing or other form before approving the modification of the general site layout of a site detailed planning or engineering design plan; or
- failing to investigate and punish a behavior of constructing within a planning area without obtaining the planning permit or by going beyond the planning permit after finding out the behavior, or failing to handle it according to law after being informed of the behavior.
Article 61 If the related department of the people’s government at or above the county level commits any of the following acts, the people’s government at the same level or the related department of the higher level people’s government shall order it to correct, circulate a notice of criticism, and impose punishments upon the directly liable person in charge and other directly liable persons:
- issuing an approval document to a construction project for which the written proposal of location hasn’t been obtained according to law;
- failing to specify the planning requirements in the contract for the assignment of the right to use state-owned land, or changing the planning requirements legally determined in the contract for the assignment of the right to use state-owned land; or
- appropriating the right to use state-owned land to a construction entity which fails to obtain the land use permit according to law.
Article 62 If an organ establishing urban and rural planning commits any of the following acts, the competent department of urban and rural planning of the people’s government of the city or county where it is located shall order it to correct within a certain time limit and impose a fine of not less than the planned planning expenses as stipulated in the contract but not more than double that amount. If the circumstances are serious, it shall be ordered to stop business for rectification, and the license-issuing organ shall degrade its qualification or revoke its qualification certificate. In the case of losses, it shall make compensation according to law:
- undertaking urban and rural planning establishing work beyond the scope authorized by its qualification grade; or
- establishing urban and rural planning by going against the relevant state standards.
If any organ undertakes urban and rural planning establishing work without obtaining the required qualification certificate according to law, the competent department of urban and rural planning of the local people’s government at or above the county level shall order it to stop the illegal act, and impose a fine in accordance with the preceding paragraphs. In the case of losses, it shall make compensation according to law.
If any organ undertakes urban and rural planning establishing work with a defrauded qualification certificate, the license-issuing organ shall revoke its certificate, and impose a fine in accordance with the preceding paragraphs. In the case of losses, it shall make compensation according to law.
Article 63 If, after obtaining the qualification certificate, an organ establishing urban and rural planning no longer satisfies the corresponding requirements, the license-issuing organ shall order it to correct within a certain time limit, and, if it fails to do so, degrade its qualification or revoke its certificate.
Article 64 If a construction project is proceeded without obtaining the planning permit on construction project or by violating the provisions of the planning permit on construction project, the competent department of urban and rural planning of the local people’s government at or above the county level shall order it to stop construction. If it is still possible for the construction entity or individual to take measures to eliminate the impact on the implementation of urban and rural planning, the department shall order it or him to correct within a certain time limit and impose a fine of not less than 5% the construction cost but not more than 10% the cost; if it is impossible to take measures to eliminate the impact, the department shall order the construction entity or individual to dismantle the building or structure within a certain time limit and confiscate the real objects or the illegal gain, and may also impose a fine not more than 10% the construction cost.
Article 65 Where a construction project is proceeded within a township or village planning area without obtaining the planning permit for rural construction or by violating the provisions of the planning permit for rural construction, the people’s government of the township or town shall order the construction entity or individual to stop construction, make correction within a certain time limit, and, if the entity or individual fails to do so within the time limit, dismantle the building or structure.
Article 66 Where a construction entity or individual commits any of the following behaviors, the competent department of urban and rural planning of the people’s government of the city or county where it is located shall order it to dismantle the building within a certain time limit, and may impose a fine not more than the cost of the temporary construction project:
- making temporary construction without approval;
- making temporary construction beyond the approved content; or
- failing to dismantle the temporary building or structure after the approved time limit expires.
Article 67 If a construction entity fails to file the materials about the completion check and acceptance of the project with the competent department of urban and rural planning within 6 months after the completion check and acceptance of the project, the competent department of urban and rural planning of the people’s government of the city or county where it is located shall order it to make a supplementary report within a certain time limit, and impose a fine of not less than 10,000 yuan but not more than 50,000 yuan if it fails to do so.
Article 68 If, after the competent department of urban and rural planning orders to stop building or dismantle the building or structure within a certain time limit, the party concerned refuses to stop building or fails to dismantle within the time limit, the local people’s government at or above the county level of the place where the construction project is located may order the related department to take measures such as closing down the construction site and mandatory dismantling.
Article 69 Where any entity or individual violates this Law and constitutes a crime, it/he shall be subject to criminal liability.
Chapter VII Supplementary Provisions
Article 70 This Law shall come into force as of January 1st, 2008. The City Planning Law of the People’s Republic of China shall be abolished simultaneously.
5.2 Appendix 2: Real Estate Management Law
(Adopted at the Eighth Meeting of the Standing Committee of the Eighth National People's Congress on July 5, 1994, promulgated by Order No. 29 of the President of the People's Republic of China on July 5, 1994, and effective as of January 1, 1995)
Contents
Chapter I General Provisions
Chapter II Land Used for Development of Real Estate
Section 1 Granting of the Land-use Right
Section 2 Allocation of the Land-use Right
Chapter III Development of Real Estate
Chapter IV Transaction of Real Estate
Section 1 General Conditions
Section 2 Transfer of Real Estate
Section 3 Mortgage of Real Estate
Section 4 Lease of Houses
Section 5 Intermediary Service Agencies
Chapter V Administration of Real Estate Ownership Registration
Chapter VI Legal Liability
Chapter VII Supplementary Provisions
Chapter I General Provisions
Article 1 This Law is formulated in order to strengthen administration of the urban real estate, maintain the order of real estate market, protect the legitimate rights and interests of real estate obligees and promote the healthy development of real estate business.
Article 2 Obtaining the land-use right for development of real estate, engaging in development of real estate and transaction of real estate, and exercising administration of real estate in the State-owned land within a planned urban district in the People's Republic of China (hereinafter referred to as the State-owned land) shall comply with this Law.
“Houses” as used in this Law means buildings and structures such as houses on the land.
“Development of real estate” as used in this Law means acts of building infrastructure and houses on the State-owned land, the land-use right for which has been obtained in accordance with this Law.
“Transaction of real estate” as used in this Law includes transfer of real estate, mortgage of real estate and lease of houses.
Article 3 The State shall practise a compensatory and terminable system for the use of State-owned land in accordance with the law, however, allocation of the land-use right by the State under this Law shall be excepted.
Article 4 The State shall, based on the social and economic development, support the development of construction of residential houses so as to gradually improve the housing conditions of the residents.
Article 5 Obligees of real estate shall abide by the laws, administrative rules and regulations and pay taxes according to law. The legitimate rights and interests of the obligees of real estate shall be protected by the law and shall not be infringed by any units or individuals.
Article 6 The department of construction administration and the department of land administration under the State Council shall, in accordance with the division of functions and powers prescribed by the State Council, attend to their own duties, act in close coordination and manage the work concerning real estate of the whole country.
Institutional structures, and functions and powers of the departments of housing administration and land administration under the people's governments at or above the county level shall be determined by the people's governments of provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government.
Chapter II Land Used for Development of Real Estate
Section 1 Granting of the Land-use Right
Article 7 Granting of the land-use right refers to acts that the State grants land users the right to use the State-owned land(hereinafter referred to as the land-use right) for a certain number of years and the users shall pay the State a granting fee for the land-use right.
Article 8 The land-use right for the collective-owned land within a planned urban district may be granted with payment only after it is requisitioned in accordance with the law and turned into State-owned land.
Article 9 Granting of the land-use right must conform to the overall planning for land utilization, urban planning and the annual plan for land to be used for construction.
Article 10 Where the local people's governments at or above the county level grant land-use right for development of real estate, they must, based on the quota set by the people's governments at or above the provincial level, draw up plans for the total area for annual granting of the land-use right, which shall, according to the provisions of the State Council, be reported to the State Council or the provincial people's government for approval.
Article 11 Granting of the land-use right shall be carried out by the people's governments of the cities or counties in a planned and step-by-step way. With regard to each lot granted, plans for its purposes, term of use, and other conditions shall be worked out by the departments of land administration under the people's governments of the cities and counties in conjunction with the competent departments of urban planning, construction and housing administration. Such plans shall, according to the provisions of the State Council, be implemented by the departments of land administration under the people's governments of the cities or counties after their submission to and approval by the people's governments with due authority for approval.
Limits of authority as provided in the preceding paragraph for the people's governments and their departments concerned of the counties of the municipalities directly under the Central Government shall be prescribed by the people's governments of the municipalities directly under the Central Government.
Article 12 The land-use right may be granted in mode of auction, bidding or agreement between the two parties.
For Land used for commercial, tourism, recreation and luxury housing purposes, where conditions permit, the mode of auction or bidding shall be adopted; where conditions do not permit and it is impossible to adopt the mode of auction or bidding, the mode of agreement between the two parties may be adopted.
Fees for granting the land-use right in the mode of agreement between the two parties shall not be lower than the lowest price as determined in accordance with the provisions of the State.
Article 13 The maximum term for the granting of the land-use right shall be prescribed by the State Council.
Article 14 Granting of the land-use right shall be conducted through concluding a written granting contract.
The contract for granting the land-use right shall be concluded between the departments of land administration under the people's governments of the cities or counties and the land users.
Article 15 A land user must pay the fees for the granting of the land-use right as agreed upon in the granting contract. Where fees are not paid as agreed upon in the granting contract, the department of land administration shall have the power to rescind the contract and may demand compensation for the breach of contract.
Article 16 Where a land user has paid the fees for the granting of the land-use right as agreed upon in the granting contract, the department of land administration under the people's government of the city or county must provide the land granted as agreed upon in the granting contract; where the land granted is not provided as agreed upon in the granting contract, the land user shall have the right to cancel the contract, the fees for granting the land-use right shall be returned by the department of land administration, and the land user may demand compensation for the breach of contract.
Article 17 Where a land user who needs to modify the land-use purpose agreed upon in the contract for granting the land-use right, he must obtain the consent of the granting party and the competent administrative department for urban planning under the people's government of the city or county, conclude an agreement on the modification of the granting contract or conclude a new contract for granting the land-use right and the fees for granting the land-use right shall be accordingly readjusted.
Article 18 All the fees for granting the land-use right shall be turned over to the State Treasury and incorporated into the budget so as to be used for the construction of urban infrastructure and land development. Specific measures for the turning over and use of the fees for granting the land-use right shall be formulated by the State Council.
Article 19 Before the term for the use of land as agreed upon in the contract for granting the land-use right expires, the State is not to recover the land-use right obtained by the land user in accordance with the law. Under special circumstances as required by public interests, the State may, in accordance with legal procedures, recover the land-use right before the expiration of the term and shall make appropriate compensation based on the number of years of utilization and the actual development of the land by the land user.
Article 20 The land-use right shall be terminated with loss of the land.
Article 21 Where the term for the use of land as agreed upon in the contract for granting the land-use right expires, and the land user needs to continue the use of the land, the land user shall apply for an extension of the term no later than one year ahead of the expiration. Such an application shall be approved except for the land to be reclaimed as required by public interests. Upon approval of the extension, the land user shall enter into a new contract for the granting of the land-use right and pay fees for the granting in accordance with the relevant provisions.
Where the term for the use of land as agreed upon in the contract for granting the land-use right expires, and the land user does not apply for an extension of the term or his application therefor is not approved in accordance with the provisions in the preceding paragraph, the land-use right shall be reclaimed by the State without compensation.
Section 2 Allocation of the Land-use Right
Article 22 Allocation of the land-use right refers to acts that the people's government at or above the county level approves in accordance with the law to allocate the land to a land user after the latter has paid compensation and expenses for resettlement, etc. for the allocated land, or gratuitously allocates the land-use right to the land user.
Where the land-use right is obtained by mode of allocation in accordance with the provisions of this Law, except as otherwise provided by the laws, administrative rules and regulations, there shall be no restriction with respect to the term of use.
Article 23 The land-use right for the following land used for construction may, if really necessary, be allocated upon approval by the people's government at or above the county level in accordance with the law:
- land used for State organs or military purposes;
- land used for urban infrastructure or public facilities;
- land used for projects of energy, communications or water conservancy, etc. which are selectively supported by the State; and
- land used for other purposes as provided by the laws, administrative rules and regulations.
Chapter III Development of Real Estate
Article 24 The development of real estate must be strictly subjected to the urban planning and carried out in a manner of overall planning, rational distribution, comprehensive development and construction with supporting facilities, in line with the principle of combining the economic, social and environmental benefits.
Article 25 Where the land-use right is obtained by mode of granting for development of real estate, the land must be developed according to the land-use purpose and the time limit for starting the development as agreed upon in the contract for granting the land-use right. Where one year has elapsed from the date for starting the development as agreed upon in the granting contract and the land is not yet developed, fees for idle land which is equivalent to twenty percent or less of the fees for granting the land-use right shall be collected; where two years have elapsed and the land is still not developed, the land-use right may be reclaimed without compensation, however, the circumstances where in the delay of starting the development is caused by force majeure or acts of governments or their departments concerned or by the early preparations necessary for starting the development shall be excepted.
Article 26 The design and construction of a project of real estate development must conform to the relevant standards and norm of the State.
A completed project of real estate development may be turned over for use only after it is checked and accepted.
Article 27 The land-use right obtained pursuant to the law may, in accordance with the provisions of this Law and relevant laws, administrative rules and regulations, be valued and contributed as shares in developing and operating real estate in the form of joint ventures or contractual joint ventures.
Article 28 The State shall adopt preferential measures in aspects such as taxation to encourage and support real estate development enterprises to develop and construct residential houses.
Article 29 A real estate development enterprise is an enterprise engaged in real estate development and operation for purpose of profit. To establish a real estate development enterprise, the following conditions shall be met:
- to have a name and institutional structure of its own;
- to have fixed premises for business operation;
- to have registered assets conforming to the provisions of the State Council;
- to have sufficient professional and technical personnel; and
- other conditions as provided by laws, administrative rules and regulations.
To establish a real estate development enterprise, an application for registration of establishment shall be made to the administrative department for industry and commerce. Where conditions specified in this Law are met, the administrative department for industry and commerce shall register the establishment and issue a business license. And registration shall not be made, where such conditions are not met.
To establish a limited liability company or a joint stock limited company engaged the real estate development and operation, relevant provisions of the Company Law shall also be complied with.
A real estate development enterprise shall, within one month after obtaining a business license, report its establishment for the record to the department designated by the local people's government at or above the county level in the place where the registration authority is located.
Article 30 The proportion of registered assets of a real estate development enterprise to its total investment shall comply with the relevant provisions of the State.
Where a real estate development enterprise develops real estate in phases, the amount of phased investment shall be commensurate with the scale of the project and the capital shall be put into construction of the project on schedule as agreed upon in the contract for granting the land-use right.
Chapter IV Transaction of Real Estate
Section 1 General Conditions
Article 31 In the transfer or mortgage of real estate, the ownership of the house and the land-use right to the house site shall be transferred or mortgaged therewith.
Article 32 The basic land price, standard land price and replacement prices for houses of various types shall be determined and made public regularly. Specific measures shall be formulated by the State Council.
Article 33 The State shall practise an appraisal system for real estate prices.
The appraisal of real estate prices shall adhere to the principles of justice, fairness and openness, and be carried out according to the technical standard and appraisal procedures prescribed by the State, based on the basic land price, standard land price and replacement prices for houses of various types and in the light of local market prices.
Article 34 The State shall practise a report system for real estate transaction prices.
An obligee of real estate shall, in transfer of his real estate, faithfully report the transaction price to the department designated by the local people's government at or above the county level and shall not make a concealed or false report.
Article 35 Where real estate is transferred or mortgaged, the party concerned shall register the ownership of the real estate pursuant to the provisions of Chapter V of this Law.
Section 2 Transfer of Real Estate
Article 36 Transfer of real estate refers to acts that an obligee of real estate transfers his real estate to another person through sale, donation or other legal means.
Article 37 No following real estate shall be transferred:
- The land-use right is obtained by mode of granting, but not meeting conditions set forth in Article 38 of this Law;
- The rights of real estate are sealed up by order of the judicial organ or decision of the administrative organ pursuant to law or limited by other ways;
- The land-use right is reclaimed in accordance with the law;
- For jointly-owned real estate, written consent of other co-owners has not been obtained;
- The ownership is under dispute;
- The real estate is not registered in accordance with the law and the certificate of the ownership is not obtained; or
- Other circumstances under which transfer is prohibited by the provisions of laws, administrative rules and regulations.
Article 38 Where the land-use right is obtained by mode of granting, transfer of the real estate shall meet the following conditions:
1. to have paid all the fees for the granting of the land-use right as agreed upon in the granting contract and obtained the certificate of the land-use right; and
2. to have invested for development as agreed upon in the granting contract and have fulfilled twenty-five percent or more of the total investment for development in the case of housing projects, or have constituted conditions of land-use for industrial purposes or other construction projects in the case of developing tracts of land.
Where real estate is transferred with the construction of houses completed, the certificate of the house ownership shall be acquired.
Article 39 Where the land-use right is obtained by mode of allocation, the transfer of the real estate shall, according to the provisions of the State Council, be reported for examination and approval to the people's government that has the authority for approval. Upon approval of the transfer by the people's government with the authority for approval, the transferee shall go through the formalities for the granting of the land-use right and pay the fees therefor according to the relevant provisions of the State.
Where the land-use right is obtained by mode of allocation and the transfer of the real estate is reported for approval, and where the people's government that has the authority for approval decides in accordance with the provisions of the State Council that the formalities for granting the land-use right need not be gone through, the transferor shall, pursuant to the provisions of the State Council, turn over to the State the proceeds obtained from land in the transfer of the real estate or dispose of such proceeds otherwise.
Article 40 For the transfer of real estate, a written transfer contract shall be concluded in which the mode of obtaining the land-use right shall be stated.
Article 41 When real estate is transferred, the rights and obligations stated in the contract for granting the land-use right shall be transferred therewith.
Article 42 Where the land-use right is obtained by mode of granting and after the real estate is transferred, the term for the use of the land-use right shall be the remaining years after subtracting the years of use by the former land user from the original term agreed upon in the contract for granting the land-use right.
Article 43 Where the land-use right is obtained by mode of granting and after the real estate is transferred, the transferee modifies the land-use purpose agreed upon in the contract for granting the land-use right, the transferee must obtain consent from the transferor and the administrative department in charge of urban planning under the people's government of the relevant city or county, and conclude an agreement on the modification of the contract for granting the land-use right or enter into a new contract for granting the land-use right and readjust the fees for granting the land-use right accordingly.
Article 44 For the presale of commercial houses, the following conditions shall be met:
- to have paid all the fees for the granting of the land-use right and obtained the certificate of the land-use right;
- to have a permit for construction project planning;
- the funds put into the development construction have reached twenty-five percent or more of the total investment for the construction project, computed on the basis of the commercial houses provided for presale, and the schedule of construction and the date of completion for delivery have been set; and
- to make registration for presale at the administrative department in charge of house property under the people's government at or above the county level and to obtain the certificate of permission for the presale of commercial houses.
Pre-sellers of commercial houses shall, in accordance with the relevant provisions of the State, submit the presale contracts to the departments of housing administration and departments of land administration under the people's governments at or above the county level for registration and record.
The proceeds obtained from the presale of commercial houses must be used for the relevant construction projects.
Article 45 In the case of presale of commercial houses, matters concerning the transfer of incomplete pre-sold commercial houses that the buyers have purchased shall be prescribed by the State Council.
Section 3 Mortgage of Real Estate
Article 46 Mortgage of real estate refers to acts that a mortgagor provides the mortgagee security for the payment of a debt with his legal real estate in the manner that the possession of his real estate is not transferred. Where a debtor fails to pay his debt, the mortgagee shall have the right in accordance with the law to enjoy the priority in compensation to be paid with funds obtained from auction of the real estate mortgaged.
Article 47 A mortgage may be created on the ownership of a house obtained according to law together with the land-use right to the house site.
A mortgage may be created on the land-use right obtained by mode of granting.
Article 48 The mortgage of real estate shall be dealt with on the strength of the certificate of the land-use right and the certificate of ownership of the house.
Article 49 For the mortgage of real estate, the mortgagor and the mortgagee shall enter into a written mortgage contract.
Article 50 Where the land-use right on which a mortgage is created is obtained by mode of allocation, the mortgagee may enjoy the priority in compensation only after the amount equal to the fees for the granting of the land-use right is paid from the funds obtained from auction of the real estate done in accordance with the law.
Article 51 After a contract for the mortgage of the real estate is concluded, newly-built houses on the land shall not be regarded as the mortgaged asset. If the mortgaged real estate needs to be sold by auction, the newly-built houses on the land may be auctioned off according to law together with the mortgaged assets. However, the mortgagee shall not have the priority in compensation with respect to the funds obtained from auction of the newly-built houses.
Section 4 Lease of Houses
Article 52 Lease of houses refers to acts that an owner of a house in the capacity of a leaser leases his house to a lea see for use and the lea see pays rent for the house to the leaser.
Article 53 In the lease of a house, the leaser and the lea see shall conclude a written lease contract defining such matters as the term, purpose, and price of the lease, liability for repair, as well as other rights and obligations of both parties, and shall register the lease with the department of housing administration for the record.
Article 54 Lease of residential houses shall be carried out in accordance with policies on lease formulated by the State and the people's government of the city where the houses are located. Where houses are leased for activities of production and business operation, the rent and other terms for the lease shall be determined by both parties through consultation.
Article 55 Where an owner of a house, for profit-making purposes, leases the house built on the State-owned land, the land-use right for which is obtained by mode of allocation, he shall turn over to the State the proceeds derived from the land and contained in the rent. The specific measures shall be prescribed by the State Council.
Section 5 Intermediary Service Agencies
Article 56 Intermediary service agencies for real estate include real estate consultant agencies, real estate price appraisal agencies and real estate broking agencies.
Article 57 Intermediary service agencies for real estate shall meet the following conditions:
- to have names and institutional structures of their own;
- to have fixed premises to provide services;
- to have necessary property and funds;
- to have sufficient professional personnel; and
- other conditions provided by laws, administrative rules and regulations.
For establishing an intermediary service agency for real estate, an application for registration of the establishment shall be submitted to the administrative department for industry and commerce and a business licence shall be obtained, before it starts its business.
Article 58 The State shall practise a qualification authentication system for real estate price appraisers.
Chapter V Administration of Real Estate Ownership Registration
Article 59 The State shall practise a system of registration and certification for land-use right and ownership of houses.
Article 60 Where the land-use right is obtained by mode of granting or allocation, an application for registration shall be submitted to the department of land administration under the local people's government at or above the county level. Upon verification by the department of land administration under the local people's government at or above the county level, the certificate of the land-use right shall be issued by the people's government at the corresponding level.
Where a house is built on the land for real estate development obtained pursuant to the law, an application for registration shall, on the strength of the certificate of land-use right, be submitted to the department of housing administration under the local people's government at or above the county level. The department of housing administration under the local people's government at or above the country level shall issue the certificate of ownership of the house after verification.
Where transfer or modification of real estate is made, an application for registration of the modification of house property shall be submitted to the department of housing administration under the local people's government at or above the county level and on the strength of the certificate of the ownership of the house after modification, an application for registration of the modification of the land-use right shall be submitted to the department of land administration under the people's government at the corresponding level. Upon verification by the department of land administration under the people's government at the corresponding level, a new or a modified certificate of the land-use right shall be issued by the people's government at the corresponding level. Where provided otherwise by laws, the provisions of relevant laws shall apply.
Article 61 Where real estate is mortgaged, registration of mortgage shall be made with the department designated by the local people's government at or above the county level.
Where the land-use right and the ownership of a house are obtained from disposal of mortgaged real estate, the change of ownership for the land-use right and the house shall be registered in accordance with the provisions of this Chapter.
Article 62 Where a department of the local people's government at or above the county level is in charge of both housing administration and land administration as determined by the people's government of the relevant province, autonomous region or municipality directly under the Central Government, such department may make and issue the uniform certificate of the ownership of real estate, in which the confirmation and modification of the ownership of houses and the land-use right of the house site shall be recorded respectively in accordance with the provisions of Article 60 of this Law.
Chapter VI Legal Liability
Article 63 Where anyone, in violation of the provisions of Article 10 or Article 11 of this Law, approves without authorization the granting of land-use right or grants land-use right without due approval for development of real estate, the person who is held responsible shall be given an administrative sanction by an organ at a higher level or by the unit to which he belongs.
Article 64 Whoever, in violation of the provisions of Article 29 of this Law, engages in business of real estate development without obtaining a business license shall be ordered to stop activities of real estate development and confiscated of his unlawful proceeds and may be concurrently imposed a fine by the administrative department for industry and commerce under the people's government at or above the county level.
Article 65 Whoever, in violation of the provisions of paragraph 1 of Article 38 of this Law, transfers the land-use right shall be confiscated of his unlawful proceeds and may be concurrently imposed a fine by the department of land administration under the people's government at or above the county level.
Article 66 Whoever, in violation of the provisions of paragraph 1 of Article 39 of this Law, transfers real estate shall be ordered to pay the fees for the granting of the land-use right, confiscated of his unlawful proceeds and may concurrently be imposed a fine by the department of land administration under the people's government at or above the county level.
Article 67 Whoever, in violation of the provisions of paragraph 1 of Article 44 of this Law, pre-sells commercial houses shall be ordered to stop activities of presale, confiscated of his unlawful proceeds and may concurrently be imposed a fine by the department of housing administration under the people's government at or above the county level.
Article 68 Whoever, in violation of the provisions of Article 57 of this Law, engages in intermediary services for reale state business without obtaining a business license shall be ordered to stop activities of intermediary services for realestate business, confiscated of his unlawful proceeds and may concurrently be imposed a fine by the administrative department for industry and commerce under the people's government at or above the county level.
Article 69 Whoever collects fees from a real estate development enterprise without the basis of laws, rules and regulations shall be ordered by the organ at a higher level to return the fees thus collected; if the circumstances are serious, the person who is held directly responsible shall be given an administrative sanction by the organ at a higher level or by the unit to which he belongs.
Article 70 Where functionaries of departments of housing administration or land administration commit negligence of duty or abuse of power and the case constitutes a crime, they shall be investigated for criminal responsibilities in accordance with the law; if the case does not constitute a crime, they shall be given administrative sanctions.
Where functionaries of departments of housing administration or land administration take advantage of their functions and powers to extort money or properties from others or to illegally receive money or properties from others, thus seeking gains for others, and the case constitutes a crime, they shall be investigated for criminal responsibilities in accordance with the supplementary provisions on punishing crimes of embezzlement and bribery; if the case does not constitute a crime, they shall be given administrative sanctions.
Chapter VII Supplementary Provisions
Article 71 Obtaining the land-use right for development of real estate, engaging in development of real estate and transaction of real estate, and exercising administration of real estate in the State-owned land outside of a planne durban district shall be carried out by making reference to this Law.
Article 72 This Law shall enter into force as of January 1,1995.
5.3 Appendix 3: Construction Law
(Adopted at the 28th Meeting of the Standing Committee of the Eighth National People's Congress on November 1, 1997 and promulgated by Order No. 91 of the President of the People's Republic of China on November 1, 1997)
Contents
Chapter I General Provisions
Chapter II Building Permit
Section 1 Building Permit for Construction Project
Section 2 Qualifications for Operations
Chapter III Construction Project Contract Issuance and Contracting
Section 1 General Rules
Section 2 Contract Issuance
Section 3 Contracting
Chapter IV Construction Project Supervision and Control
Chapter V Construction Production Safety Management
Chapter VI Construction Project Quality Control
Chapter VII Legal Liability
Chapter VIII Supplementary Provisions
Chapter I General Provisions
Article 1 This Law is enacted with a view to enhancing supervision and administration over building operations, maintaining order in the construction market, ensuring the quality and safety of construction projects and promoting the sound development of the building industry.
Article 2 This Law shall be adhered to in engaging in building operations and in the exercise of supervision and administration over building operations within the territory of the People's Republic of China.
The building operations referred to in this Law mean construction of all types of housing and the construction of their ancillary facilities as well as their matching installation operations of wiring, piping and equipment.
Article 3 The building operations shall ensure the quality and safety of construction projects and ensure that they are in conformity with the state safety standards for construction projects.
Article 4 The State supports the development of the building industry, supports scientific and technological research in construction to improve the levels in the design of housing construction, encourages energy economy and environmental protection, encourages adoption of advanced technologies, advanced equipment, advanced techniques and new building materials and modern mode of management.
Article 5 In engaging in building operations, laws and regulations shall be adhered to, and public interest of society and the legitimate rights and interests of others shall not be infringed upon.
No unit or individual shall hinder or obstruct the building operations conducted in accordance with law.
Article 6 The competent department of construction administration under the State Council exercises uniform supervision and administration over building operations nationwide.
Chapter II Building Permit
Section 1 Building Permit for Construction Project
Article 7 A construction unit shall, prior to the start of construction of a construction project, apply to the competent department of construction administration of the people's government at or above the county level of the place where in the project is to be located for a building permit pursuant to the relevant state provisions; however, the below-ceiling small projects determined by the competent department of construction administration under the State Council are exceptions.
A construction project the report for the start of construction of which has been approved pursuant to the terms of reference and procedures prescribed by the State Council shall no longer obtain a building permit.
Article 8 Application for a building permit shall meet the following terms:
- having completed the formalities for the approval of land use for the said construction project;
- having obtained the planning permit in the case of the construction project in an urban planning zone;
- in the case of necessity of demolition and shifting, the pace of demolition and shifting conforming to the requirements of construction;
- having determined the construction enterprise;
- having construction drawings and technical information which meet the requirements for construction;
- having specific measures for ensuring project quality and safety;
- the construction funds having been made available; and
- other terms prescribed by laws and administrative regulations.
The competent department of construction administration shall, within 15 days from the date of receipt of an application, issue a building permit for the application which conforms to the terms.
Article 9 A construction unit shall start the construction within three months from the date of acquisition of the building permit. For inability to start the construction in time due to unforeseen reasons, an application for extension shall be filed with the permit-issuing organ; the extension shall be limited to two times, and each time shall not exceed three months. The building permit shall be automatically annulled in the case of a construction project which neither gets started nor applies for extension, or which has exceeded the time limit for extension.
Article 10 For suspension of construction of a construction project under construction due to unforeseen reasons, the construction unit shall, within one month from the date of suspension of the construction, submit a report to the permit-issuing organ and carry out maintenance and administration of the construction project in accordance with rules.
A report shall be submitted to the permit-issuing organ when the construction project resumes construction; prior to resumption of construction of a construction project whose construction has been suspended for a year, the construction unit shall submit a report to the permit-issuing organ for the verification and examination of the building permit.
Article 11 For inability to start construction in time or suspension of construction due to unforeseen reasons, a construction project the report for the start of construction of which has been approved pursuant to the relevant provisions of the State Council shall submit a report to the approval authority in time on the situation. For inability to start construction in time exceeding six months due to unforeseen reasons, formalities for the approval of the report for the start of construction shall be completed again.
Section 2 Qualifications for Operations.
Article 12 Building construction enterprises, survey units, design units and project supervision units engaging in building operations shall have the following qualifications:
- having a registered capital conforming to state provisions;
- having specialized technical personnel with qualifications for legal operations commensurate with the building operations engaged in;
- having technical equipment for engaging in related building operations; and
- other qualifications prescribed by laws and administrative regulations.
Article 13 Building construction enterprises, survey units, design units and project supervision units engaging in building operations shall be classified into different grades of human quality in accordance with such human quality qualifications as the registered capital, specialized technical personnel, technical equipment in their possession and achievements in construction projects completed, and may engage in building operations within the scope permitted by their respective human quality grades on acquisition of the corresponding grade human quality certificates upon passing human quality examination.
Article 14 Specialized technical personnel engaging in building operations shall obtain corresponding qualification certificates for operations in accordance with law and engage in building operations within the scope permitted by the qualification certificates for operations.
Chapter III Construction Project Contract Issuance and Contracting
Section 1 General Rules
Article 15 The contract issuing unit and contracting unit of a construction project shall conclude a contract in writing according to law expressly defining the rights and obligations of the parties.
The contract issuing unit and contracting unit shall comprehensively fulfil the obligations agreed in the contract. The party that fails to fulfil the obligations pursuant to the agreement in the contract shall bear the liability for the breach of the agreement according to law.
Article 16 Invitation to tender and bidding of the tender of contract issuance and contracting of a construction project shall follow the principle of openness, fairness and equal competition and the contracting unit shall be selected on merit.
For invitation to tender and bidding of the tender of construction projects not prescribed by this Law, provisions of laws relating to invitation to tender and bidding of the tender shall apply.
Article 17 A contract issuing unit and its staff members shall not, in the contract issuance of a construction project, accept bribes and commissions or seek other benefits.
A contracting unit and its staff members shall not employ such unfair means as offering bribes, commissions or giving other benefits to the contract issuing unit and its staff members to contract the project.
Article 18 The cost of a construction project shall, pursuant to relevant state provisions, be agreed upon by the contract issuing unit and the contracting unit in the contract. For a construction project with invitation to open tender, the agreement on its cost shall abide by the provisions of laws on invitation to tender and bidding.
The contract issuing unit shall, pursuant to the agreement in the contract, make allocations for the project in time.
Section 2 Contract Issuance
Article 19 Construction projects shall practise contract issuance by invitation to tender in accordance with law; those construction projects not suitable for contract issuance by invitation to tender may adopt direct contract issuance.
Article 20 For a construction project for invitation to open tender, the contract issuing unit shall, pursuant to the legal procedures and mode, publish a tender notice providing tender documents carrying such contents as major technical requirements of the project open to tender, main articles of the contract, standards and methods of bid evaluation as well as procedures of bid opening, bid evaluation and bid finalization.
Bid opening shall be held in public at the time and place prescribed in the tender document. Evaluation and comparison of bid proposals shall be carried out pursuant to the standards and procedures for bid evaluation prescribed in the tender document after the bids are opened, and selection of the winning bidder made from among bidders with corresponding human quality qualifications on merit.
Article 21 Bid opening, bid evaluation and bid selection of the construction project open to tender shall be organized and carried out by the construction unit according to law and subject to the supervision of the competent administrative departments concerned.
Article 22 For a construction project following contract issuance through tender, the contract issuing unit shall award the contract of the construction project to the contracting unit winning the bid in accordance with law. For a construction project following direct contract issuance, the contract issuing unit shall award the contract of the construction project to the contracting unit with corresponding human quality qualifications.
Article 23 The Government and its subordinate departments shall not abuse their administrative powers in restricting contract issuing units in awarding contracts of construction projects following contract issuance through tenders to designated contracting units.
Article 24 General contracting of construction projects shall be encouraged and dismemberment of contract issuance of construction projects shall be prohibited.
The contract issuing unit of a construction project may award in total the contract of surveying, design, construction and equipment procurement of the construction project to a general contracting unit of the project. It may also award one item or several items of surveying, design, construction and equipment procurement of the construction project to a general contracting unit of the project; however, it shall not dismember a construction project which should be completed by one single contracting unit into several parts for awarding contracts to several contracting units.
Article 25 For building materials, building structural pieces and parts and equipment to be procured by the contracting unit of the project pursuant to the agreement in the contract, the contract issuing unit shall not designate the contracting unit in the procurement of building materials, building structural pieces and parts and equipment for the project, nor shall it designate the manufacturers and suppliers of the same.
Section 3 Contracting
Article 26 The contracting units of construction projects shall contract projects with human quality certificates obtained in accordance with law and within the business scope permitted by their human quality grades.
Building construction enterprises shall be prohibited to contract projects beyond the business scope permitted by their respective human quality grades or in the name of other building construction enterprises in any form. Building construction enterprises shall be prohibited to permit in any form other units or individuals in the use of their human quality certificates, business licences to contract projects in the name of their respective enterprises.
Article 27 Large construction projects or construction projects with complex structures may be jointly contracted by more than two contracting units. Parties to the joint contract shall bear joint responsibilities in the implementation of the contract.
In the case of a joint contract by more than two units with different human quality grades, the project shall be contracted in accordance with the business scope granted to the unit with lower human quality grade.
Article 28 Subcontracting to others of the entire construction project contracted by the contracting unit shall be prohibited. Subcontracting to others in the name of subcontracting after dismemberment of the entire construction project contracted by the contracting unit shall be prohibited.
Article 29 The general contracting unit of a construction project may award contracts of parts of the contracted project to subcontracting units with corresponding human quality qualifications; however, except for the subcontracting agreed upon in the general contracting contract, acknowledgement of the construction unit shall be obtained. In the case of general contracting of construction, construction of the main structure of the construction project must be completed by the general contracting unit itself.
The general contracting unit of a construction project shall, pursuant to the agreement in the general contracting contract, be responsible to the construction unit; subcontracting units shall, pursuant to the agreement in the subcontracts, be responsible to the general contractor. The general contracting unit and subcontracting units shall bear joint responsibility to the construction unit in respect of the subcontracted projects.
The general contracting unit is prohibited to subcontract the project to units with no corresponding human quality qualifications. The subcontracting unit shall be prohibited to re-subcontract the project it has contracted.
Chapter IV Construction Project Supervision and Control
Article 30 The State practises the construction project supervision and control system.
The State Council may determine the scope of mandatory supervision and control of construction projects.
Article 31 The construction unit of a construction project under supervision and control shall entrust the supervision and control with an engineering supervision and control unit with corresponding human quality qualifications. The construction unit and its entrusted engineering supervision and control unit shall conclude a contract for entrustment of supervision and control in writing.
Article 32 The construction project supervisor-controller shall, pursuant to the laws, administrative regulations as well as relevant technical standards, design documents and the construction project contractual contract, exercise supervision over the contracting unit in construction quality, construction schedule and use of construction funds on behalf of the construction unit.
Engineering supervisors have the power to ask the building construction enterprise to make corrections when they hold that construction of the project does not conform to engineering design requirements, construction technical standards and agreement in the contract.
Engineering supervisors shall, upon discovery of engineering design not in conformity with construction project quality standards or quality requirements agreed in the contract, report to the construction unit to ask the design unit to make corrections.
Article 33 The construction unit shall, prior to the exercise of supervision and control over the construction project, notify the building construction enterprise to be put under supervision and control in writing of the entrusted engineering supervision and control unit, the contents of supervision and control and terms of reference in supervision and control.
Article 34 An engineering supervision and control unit shall undertake engineering supervision and control business within the scope of supervision and control permitted for its human quality grade.
The engineering supervision and control unit shall, in accordance with the entrustment of the construction unit, conduct the missions of supervision and control objectively and fairly.
The engineering supervision and control unit and the contracting unit of the project under supervision and control as well as supply units of building materials, building structural pieces and parts and equipment shall not have subordinate relationship or other relations of interest.
The engineering supervision and control unit shall not transfer its engineering supervision and control business.
Article 35 An engineering supervision and control unit shall bear corresponding liability of compensation in the case of failure to fulfil the obligations of supervision and control agreed in the contract of entrustment of supervision and control, not carrying out inspection or carrying out inspection not in accordance with the provisions over items which should have been put under supervision and inspection, thus causing losses to the construction unit.
An engineering supervision and control unit shall bear joint liability of compensation with the contracting unit for collusion in gaining illegal interests for the contracting unit thus causing losses to the construction unit.
Chapter V Construction Production Safety Management
Article 36 Construction project production safety management must adhere to the policy of safety first and prevention first, establish and perfect the responsibility system of production safety and the system of prevention and treatment by the masses.
Article 37 Construction project design shall conform to the construction safety procedures and technical standards formulated in accordance with state provisions to ensure the safety performance of the project.
Article 38 A building construction enterprise shall work out corresponding safety technical measures according to the characteristics of the construction project in the compilation of design for construction organization; for speciality-intensive items of the project, design for special-purpose safety construction organization shall be compiled and safety technical measures taken.
Article 39 A building construction enterprise shall take such measures as the maintenance of safety, precautions against danger and fire prevention at the construction site; where there are the required conditions, construction site closed management shall be followed.
A building construction enterprise shall take safety protection measures in the case of the construction site causing possible damage to its adjoining buildings, structures or special operational environment.
Article 40 The construction unit shall provide the building construction enterprise with the relevant information on underground piping and wiring of the construction site, and the building construction enterprise shall take measures for their protection.
Article 41 The building construction enterprise shall abide by the provisions of the laws and regulations relating to environmental protection and safety in production and take control and disposal measures at the construction site of various kinds of dust, waste gas, waste water, solid waste as well as noise, vibration polluting and damaging the environment.
Article 42 A construction unit shall, pursuant to the relevant state provisions, go through the formalities of application for approval in case of any of the following circumstances:
- need of temporarily occupying sites beyond the approved planned scope;
- possibility of damaging such public facilities as roads, pipes and cables, electricity, postal service and telecommunications;
- need of temporary suspension of water supply, electricity supply and suspension of road traffic;
- need to conduct explosion operations; and
- other circumstances requiring going through the formalities of application for approval as prescribed by laws and regulations.
Article 43 The competent department of construction administration shall be responsible for the administration of construction safety in production and subject to the guidance and supervision of the competent department of labour in construction safety in production in accordance with law.
Article 44 A building construction enterprise must, in accordance with law, strengthen construction safety production management, implement the safety production responsibility system and take effective measures to prevent casualties and other accidents in safety production from taking place.
The legal representative of a building construction enterprise shall be responsible for the safety in production of the enterprise.
Article 45 The building construction enterprise shall be responsible for the construction site safety. The general contracting unit shall be responsible for the construction site safety of the project under general contract for construction. Subcontracting units shall be responsible to the general contracting unit and subordinate themselves to the management of the general contracting unit for construction site safety in production.
Article 46 Building construction enterprises shall establish and perfect the educational and training system of safety in labour and production, step up the education and training of workers and staff members in safety in production; no personnel without undergoing education and training in safety in production shall take up posts in operations.
Article 47 Building construction enterprises and their personnel shall, in the process of construction, abide by the laws and regulations relating to safety in production and safety regulations and procedures of the building industry, and shall not give command in contravention of regulations or operate in contravention of regulations. Operators have the right to put forth suggestions for improvement with regard to the operational procedures and operational conditions adversely affecting physical health and have the right to obtain protective gear necessary for safety in production. Operators have the right to make criticism, report the case of and file charges against acts endangering lives, safety and physical health.
Article 48 Building construction enterprises must insure workers and staff members engaging in dangerous operations against accidental injuries and pay the insurance premium.
Article 49 In restoration or rehabilitation project involving the main body of the building and changes in the weight-bearing structure, the construction unit shall, prior to the construction, entrust the original design unit or a design unit with corresponding human quality qualifications to put forth a design proposal; where there is no design proposal, no construction shall be undertaken.
Article 50 Dismantling of houses shall be undertaken by building construction units with conditions to ensure safety and the person-in-charge of the building construction units shall be responsible for the safety.
Article 51 In the event of an accident in the process of construction, the building construction enterprise shall take emergency measures to reduce casualties of personnel and losses caused by the accident, and submit a report in time to the departments concerned pursuant to relevant state provisions.
Chapter VI Construction Project Quality Control.
Article 52 The quality of survey, design and construction of a construction project must conform to the requirements of state safety standards relating to construction projects. Specific control measures shall be formulated by the State Council.
State standards relating to safety in construction projects shall be revised in time when they are unable to adapt to the requirements of ensuring safety in building.
Article 53 The State practises the quality system authentication system with respect to units engaging in building operations. Units engaging in building operations may, in accordance with the principle of voluntarism, apply for quality system authentication to authentication agencies acknowledged by the department of product quality supervision administration under the State Council or by the authorized departments of the department of product quality supervision administration under the State Council. Authentication agencies shall issue quality system authentication certificates to those having qualified for the authentication.
Article 54 No construction unit shall, with whatever reasons, ask the building design unit or building construction enterprise to lower the project quality in project design or construction operations in violation of the laws, administrative regulations and quality and safety standards of construction projects.
The building design unit and building construction enterprise shall reject the requests of the construction unit for lowering the project quality in violation of the provisions of the preceding paragraph.
Article 55 For a construction project under general contract, the general contracting unit shall be responsible for the project quality. In the case of the general contracting unit subcontracting out the construction project to other units, the former shall bear joint responsibility with the subcontracting units of the quality of the subcontracted projects. The subcontracting units shall subject themselves to the quality control of the general contracting unit.
Article 56 The survey and design units of a construction project shall be responsible for the quality of their survey and design. Survey and design documents shall conform to the provisions of relevant laws and administrative regulations and construction project quality and safety standards and technical standards for construction project survey and design as well as the agreement in the contract. Such technical indexes as the specifications, types and characteristics of building materials, building structural pieces and parts and equipment selected in the design documents shall be annotated and their quality requirements shall conform to the standards prescribed by the state.
Article 57 No building design unit shall designate manufacturers or suppliers of the building materials, building structural pieces and parts and equipment selected in the design documents.
Article 58 The building construction enterprise shall be responsible for the construction quality of a project.
The building construction enterprise must proceed with the construction in accordance with the project design drawings and construction technical standards and shall not do shoddy work and use inferior materials. The original design unit shall be responsible for revisions in the project design and the building construction enterprise shall not revise the project design on its own.
Article 59 The building construction enterprise must carry out inspections over the building materials, building structural pieces and parts and equipment in accordance with the requirements of the project design, construction technical standards and agreement in the contract and shall not use those that fail to pass the inspection.
Article 60 A building must ensure the quality of its ground foundation project and the main part of the structure within its life expectancy of rational use.
No such quality flaws as leakage, seepage and cracks in roofs and on wall surfaces shall remain upon completion of a construction project; the building construction enterprise shall repair the quality flaws discovered.
Article 61 A construction project handed over for completion acceptance checks must conform to the prescribed construction project quality standards, have complete project technical and economic information and signed project warranty, and have qualified other conditions for completion prescribed by the state.
A construction project may only be handed over for use upon passing the acceptance checks; no construction project shall be handed over for use without going through the acceptance checks or passing the acceptance checks.
Article 62 Construction projects practise the quality warranty system.
The scope of warranty of a construction project shall include the ground foundation project, main part structural project, roof waterproof project and other civil engineering projects as well as installation projects of electrical wiring and water piping and drainage and projects of the heating and cooling systems; the duration of warranty shall be determined in accordance with the principle of ensuring the normal use of the building within its rational life expectancy and safeguarding the legitimate rights and interests of the user. Specific warranty scope and minimum warranty duration shall be laid down by the State Council.
Article 63 Any unit or individual has the right to report to, file a charge or lodge a complaint with the competent department of construction administration or other departments concerned about quality accidents and quality flaws of construction projects.
Chapter VII Legal Liability.
Article 64 For construction on one's own without obtaining a building permit or without obtaining approval of the report for the start of construction in violation of the provisions of this Law, an order shall be issued for making corrections; that which does not conform to the conditions for the start of construction shall be ordered to stop construction and maybe imposed a fine.
Article 65 In the case of the contract issuing unit issuing contracts of a construction project to contracting units without corresponding human quality qualifications or issuing contracts of a construction project after dismemberment in violation of the provisions of this Law, the violator shall be ordered to make a rectification and imposed a fine.
For contracting a project beyond the human quality grade of the unit, the violator shall be ordered to stop the illegal act and imposed a fine, it may be ordered to suspend operations for consolidation and lower its human quality grade; where the circumstances are serious, its human quality certificate shall be revoked; where there are illegal gains, they shall be confiscated.
Contracting a project without obtaining the human quality certificate shall be banned and imposed a fine; where there are illegal gains, they shall be confiscated.
For obtainment of the human quality certificate by fraud, the human quality certificate shall be revoked and a fine imposed; where a crime has been constituted, criminal liability shall be investigated according to law.
Article 66 Any building construction enterprise that transfers or lends its human quality certificate or permits others to contract a project in the name of the enterprise in other forms shall be ordered to make a rectification, its illegal gains shall be confiscated and a fine imposed, and may be ordered to suspend operations for consolidation and lower its human quality grade; where the circumstances are serious, the human quality certificate shall be revoked. For losses caused by non-compliance with the prescribed quality standards to the said contracted project, the building construction enterprise and the unit or individual using the name of the enterprise shall share joint responsibility for compensation.
Article 67 Any contracting unit that subcontracts its contracted project or subcontracts it in violation of the provisions of this Law shall be ordered to make a rectification, its illegal gains shall be confiscated, and a fine imposed, may be ordered to suspend operations for consolidation and lower its human quality grade; where the circumstances are serious, the human quality certificate shall be revoked.
Any contracting unit having committed the illegal act of the preceding paragraph shall share joint responsibility for compensation with the unit accepting subcontract or the subcontracting unit for losses caused by non-compliance with the prescribed quality standards to the subcontracted project or the illegally subcontracted project.
Article 68 Whoever seeks bribes, accepts bribes or gives bribes in issuing contract of a project or contracting a project shall, if a crime has been constituted, be investigated of criminal liability; where a crime has not been constituted, fines shall be imposed separately, property of bribes confiscated, and sanctions imposed on the person-in-charge held directly responsible and other persons directly responsible.
In addition to the penalties prescribed in the preceding paragraph, any contracting unit that gives bribes in the contracting of a project may be ordered to suspend operations for consolidation, lower its human quality grade or its human quality certificate shall be revoked.
Article 69 Any project supervision and control unit that acts in collusion with the construction unit or building construction enterprise, practising fraud and lowering project quality shall be ordered to make a rectification, imposed a fine and its human quality grade shall be lowered or the human quality certificate revoked; where there are illegal gains, they shall be confiscated; where losses have been caused, joint responsibility for compensation shall be borne; where a crime has been constituted, criminal liability shall be investigated according to law.
Any project supervision and control unit that transfers its supervision and control business shall be ordered to make a rectification, confiscated of its illegal gains, may be ordered to suspend operations for consolidation and lower its human quality grade; where the circumstances are serious, the human quality certificate shall be revoked.
Article 70 Any construction of a restoration and rehabilitation project without authorization involving the main part of a building or changes in the weight-bearing structure in violation of the provisions of this Law shall be ordered to make a rectification and imposed a fine; where losses have been caused, liability for compensation shall be borne; where a crime has been constituted, criminal liability shall be investigated according to law.
Article 71 Any building construction enterprise that fails to take measures to eliminate the hidden causes of safety accidents in construction in violation of the provisions of this Law shall be ordered to make a rectification and may be imposed a fine; where the circumstances are serious, it shall be ordered to suspend operations for consolidation and lower its human quality grade or its human quality certificate shall be revoked; where a crime has been constituted, criminal liability shall be investigated according to law.
Managerial staff of a building construction enterprise giving command in contravention of regulations and forcibly ordering workers and staff members to engage in operations in the face of dangers thereby leading to an accident of heavy casualties or causing other serious consequences shall be investigated of the criminal liability according to law.
Article 72 Any construction unit that asks the building design unit or building construction enterprise to lower project quality in contravention of construction project quality and safety standards in violation of the provisions of this Law shall be ordered to make a rectification and may be imposed a fine; where a crime has been constituted, criminal liability shall be investigated according to law.
Article 73 Any building design unit that fails to design in accordance with construction project quality and safety standards shall be ordered to make a rectification and imposed a fine; the unit that has caused an accident in project quality shall be ordered to suspend operations for consolidation, lower its human quality grade or its human quality certificate shall be revoked, the illegal gains confiscated and a fine imposed; where losses have been caused, liability for compensation shall be borne; where a crime has been constituted, criminal liability shall be investigated according to law.
Article 74 Any building construction enterprise that does shoddy work and uses inferior materials in construction, uses substandard building materials, building structural pieces and parts and equipment, or has any other acts of construction not in accordance with the project design drawings or construction technical standards shall be ordered to make a rectification and imposed a fine; where the circumstances are serious, it shall be ordered to suspend operations for consolidation and lower its human quality grade or its human quality certificate shall be revoked; the unit that has caused non-compliance with the prescribed quality standards of the quality of a construction project shall be responsible for its reconstruction and repair and the compensation of the losses caused therefrom; where a crime has been constituted, criminal liability shall be investigated according to law.
Article 75 Any building construction enterprise that fails to fulfil its obligations of warranty or delays to fulfil its obligations of warranty in violation of the provisions of this Law shall be ordered to make a rectification, may be imposed a fine, and shall bear the liability of compensation for the losses caused by such quality flaws as leakage and seepage in roofs and on wall surfaces during the warranty period.
Article 76 The administrative penalties of ordering suspension of operations for consolidation, lowering the human quality grade and revoking the human quality certificate prescribed in this Law shall be decided upon by the human quality certificate issuing organ; other administrative penalties shall be decided upon by the competent department of construction administration or the departments concerned in accordance with laws and the terms of reference prescribed by the State Council.
For any unit whose human quality certificate is revoked pursuant to the provisions of this Law, its business licence shall be revoked by the department of industry and commerce administration.
Article 77 Any organ that issues a human quality certificate of a said grade to a unit which does not have the corresponding human quality qualifications in violation of the provisions of this Law shall be ordered by the organ at its next higher level to withdraw the human quality certificate issued and administrative sanctions shall be imposed on the person-in-charge held directly responsible and other persons directly responsible; where a crime has been constituted, criminal liability shall be investigated according to law.
Article 78 Any functionary of the government and its subordinate departments who, in violation of the provisions of this Law, restricts the contract issuing unit in issuing the contract of a project open to invitation to tender for contracting to the designated contracting unit shall be ordered by the organ at the next higher level to make a rectification; where a crime has been constituted, criminal liability shall be investigated according to law.
Article 79 Any department and its functionaries responsible for the issuance of construction project building permits which issue a building permit to a construction project that fails to meet the requirements for construction, any department and its functionaries responsible for project quality supervision and inspection or acceptance checks on completion of construction that issue a quality qualification document to or complete the acceptance checks as a qualified project of a substandard construction project shall be ordered by the organ at the next higher level to make a rectification, and administrative sanctions shall be imposed on persons held responsible; where a crime has been constituted, criminal liability shall be investigated according to law; where losses have been caused, the said department shall bear corresponding liability of compensation.
Article 80 Any party that suffers from damage due to substandard quality of a construction project within the life expectancy of rational use of the construction project has the right to claim compensation from the person held responsible.
Chapter VIII Supplementary Provisions
Article 81 The provisions of this Law relating to the building permit, building construction enterprise human quality examination and construction project contract issuance and contracting and prohibition of subcontracting as well as construction project supervision and control and construction project safety and quality control apply to building operations of other specialized construction projects. The specific measures shall be formulated by the State Council.
Article 82 The departments of construction administration and other departments concerned shall not collect fees other than those to be collected pursuant to the relevant provisions of the State Council in the exercise of supervision and control over building operations.
Article 83 Reference shall be made to this Law in governing building operations of small housing construction projects determined by people's governments of provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government.
Rehabilitation and restoration of memorial buildings and ancient architecture legally verified as protection sites of cultural relics shall be carried out pursuant to the relevant laws on cultural relics protection.
This Law shall not apply to building operations of rescue and disaster relief and other temporary housing construction and peasants' self-constructed low-storey residences.
Article 84 Specific control measures for building operations of military housing construction projects shall be formulated by the State Council and the Central Military Commission pursuant to this Law.
Article 85 This Law shall enter into force as of March 1, 1998.
5.4 Appendix 4: Environmental Protection Law of the People’s Republic of China
(Adopted at the 11th Meeting of the Standing Committee of the Seventh National People's Congress on December 26, 1989, promulgated by Order No. 22 of the President of the People's Republic of China on December 26, 1989, and effective on the date of promulgation)
Contents
Chapter I General Provisions
Chapter II Supervision and Management of the Environment
Chapter III Protection and Improvement of the Environment
Chapter IV Prevention and Control of Environmental Pollution and Other
Public Hazards
Chapter V Legal Liability
Chapter VI Supplementary Provisions
Chapter I General Provisions
Article 1
This Law is formulated for the purpose of protecting and improving
people's environment and the ecological environment, preventing and controlling pollution and other public hazards, safeguarding human health and facilitating the development of socialist modernization.
Article 2
"Environment" as used in this Law refers to the total body of all natural elements and artificially transformed natural elements affecting human existence and development, which includes the atmosphere, water, seas, land, minerals, forests, grasslands, wildlife, natural and human remains, nature reserves, historic sites and scenic spots, and urban and rural areas.
Article 3
This Law shall apply to the territory of the People's Republic of China and other sea areas under the jurisdiction of the People's Republic of China.
Article 4
The plans for environmental protection formulated by the state must be incorporated into the national economic and social development plans; the state shall adopt economic and technological policies and measures favourable for environmental protection so as to coordinate the work of environmental protection with economic construction and social development.
Article 5
The state shall encourage the development of education in the science of environmental protection, strengthen the study and development of the science and technology of environmental protection, raise the scientific and technological level of environmental protection and popularize scientific knowledge of environmental protection.
Article 6
All units and individuals shall have the obligation to protect the
environment and shall have the right to report on or file charges against units or individuals that cause pollution or damage to the environment.
Article 7
The competent department of environmental protection administration under the State Council shall conduct unified supervision and management of the environmental protection work throughout the country.
The competent departments of environmental protection administration of the local people's governments at or above the county level shall conduct unified supervision and management of the environmental protection work within areas under their jurisdiction. The state administrative department of marine affairs, the harbour superintendency administration, the fisheries administration and fishing harbour superintendency agencies, the environmental protection department of the armed forces and the administrative departments of public security, transportation, railways and civil aviation at various levels shall, in accordance with the provisions of relevant laws, conduct supervision and management of the prevention and control of environmental pollution. The competent administrative departments of land, minerals, forestry, agriculture and water conservancy of the people's governments at or above the county level shall, in accordance with the provisions of relevant laws, conduct supervision and management of the protection of natural resources.
Article 8
The people's government shall give awards to units and individuals that have made outstanding achievements in protecting and improving the environment.
Chapter II Supervision and Management of the Environment
Article 9
The competent department of environmental protection administration under the State Council shall establish the national standards for environment quality. The people's governments of provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government may establish their local standards for environment quality for items not specified in the national standards for environment quality and shall report them to the competent department of environmental protection administration under the State Council for the record.
Article 10
The competent department of environmental protection administration under the State Council shall, in accordance with the national standards for environment quality and the country's economic and technological conditions, establish the national standards for the discharge of pollutants.
The people's governments of provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government may establish their local standards for the discharge of pollutants for items not specified in the national standards; with regard to items already specified in the national standards, they may set local standards which are more stringent than the national standards and report the same to the competent department of environmental protection administration under the State Council for the record. Units that discharge pollutants in areas where the local standards for the discharge of pollutants have been established shall observe such local standards.
Article 11
The competent department of environmental protection administration under the State Council shall establish a monitoring system, formulate the monitoring norm and, in conjunction with relevant departments, organize a monitoring network and strengthen the management of environmental monitoring.
The competent departments of environmental protection administration under the State Council and governments of provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government shall regularly issue bulletins on environmental situations.
Article 12
The competent departments of environmental protection administration of the people's governments at or above the county level shall, in conjunction with relevant departments, make an investigation and an assessment of the environmental situation within areas under their
jurisdiction, draw up plans for environmental protection which shall, subject to overall balancing by the department of planning, be submitted to the people's government at the same level for approval before implementation.
Article 13
Units constructing projects that cause pollution to the environment must observe the state provisions concerning environmental protection for such construction projects. The environmental impact statement on a construction project must assess the pollution the projects is likely to produce and its impact on the environment and stipulate the preventive and curative measures; the statement shall, after initial examination by the authorities in charge of the construction project, be submitted by specified procedure to the competent department of environmental protection administration for approval. The department of planning shall not ratify the design plan descriptions of the construction project until after the environmental impact statement on the construction project is approved.
Article 14
The competent departments of environmental protection administration of the people's governments at or above the county level or other departments invested by law with power to conduct environmental supervision and management shall be empowered to make on-site inspections of units under their jurisdiction that discharge pollutants. The units being inspected shall truthfully report the situation to them and provide them with the necessary information. The inspecting authorities shall keep confidential the technological know-how and business secrets of the units inspected.
Article 15
Work for the prevention and control of the environmental pollution and damage that involve various administrative areas shall be conducted by the relevant local people's governments through negotiation, or by decision of the people's government at a higher level through mediation.
Chapter III Protection and Improvement of the Environment
Article 16
The local people's governments at various levels shall be responsible for the environment quality of areas under their jurisdiction and take measures to improve the environment quality.
Article 17
The people's governments at various levels shall take measures to protect regions representing various types of natural ecological systems, regions with a natural distribution of rare and endangered wild animals and plants, regions where major sources of water are conserved, geological structures of major scientific and cultural value, famous regions where karst caves and fossil deposits are distributed, traces of glaciers, volcanos and hot springs, traces of human history, and ancient and precious trees. Damage to the above shall be strictly forbidden.
Article 18
Within the scenic spots or historic sites, nature reserves and other zones that need special protection, as designated by the State Council, the relevant competent department under the State Council, and the people's governments of provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government, no industrial production installations that cause environmental pollution shall be built; other installations to be built in these areas must not exceed the prescribed standards for the discharge of pollutants. If the installations that have been built discharge more pollutants than are specified by the prescribed discharge standards, such pollution shall be eliminated or controlled within a prescribed period of time.
Article 19
Measures must be taken to protect the ecological environment while natural resources are being developed or utilized.
Article 20
The people's governments at various levels shall provide better protection for the agricultural environment by preventing and controlling soil pollution, the desertification and alkalization of land, the impoverishment of soil, the deterioration of land into marshes, earth subsidence, the damage of vegetation, soil erosion, the drying up of sources of water, the extinction of species and the occurrence and development of other ecological imbalances, by extending the scale of a comprehensive prevention and control of plant diseases and insect pests, and by promoting a rational application of chemical fertilizers, pesticides and plant growth hormone.
Article 21
The State Council and the people's governments at various levels in coastal areas shall provide better protection for the marine environment.
The discharge of pollutants and the dumping of wastes into the seas, the construction of coastal projects, and the exploration and exploitation of offshore oil must be conducted in compliance with legal provisions so as to guard against the pollution and damage of the marine environment.
Article 22
The targets and tasks for protecting and improving the environment shall be defined in urban planning.
Article 23
In urban and rural construction, vegetation, waters and the natural landscape shall be protected and attention paid to the construction of gardens, green land and historic sites and scenic spots in the cities in the light of the special features of the local natural environment.
Chapter IV Prevention and Control of Environmental Pollution and Other Public Hazards
Article 24
Units that cause environmental pollution and other public hazards shall incorporate the work of environmental protection into their plans and establish a responsibility system for environmental protection, and must adopt effective measures to prevent and control the pollution and harms caused to the environment by waste gas, waste water, waste residues, dust, malodorous gases, radioactive substances, noise, vibration and electromagnetic radiation generated in the course of production, construction or other activities.
Article 25
For the technological transformation of newly-built industrial enterprises and existing industrial enterprises, facilities and processes that effect a high rate of the utilization of resources and a low rate of the discharge of pollutants shall be used, along with economical and rational technology for the comprehensive utilization of waste materials and the treatment of pollutants.
Article 26
Installations for the prevention and control of pollution at a construction project must be designed, built and commissioned together with the principal part of the project. No permission shall be given for a construction project to be commissioned or used, until its installations for the prevention and control of pollution are examined and considered up to the standard by the competent department of environmental protection administration that examined and approved the environmental impact statement. Installations for the prevention and control of pollution shall not be dismantled or left idle without authorization. If it is really necessary to dismantle such installations or leave them idle, prior approval shall be obtained from the competent department of environmental protection administration in the locality.
Article 27
Enterprises and institutions discharging pollutants must report to and register with the relevant authorities in accordance with the provisions of the competent department of environmental protection administration under the State Council.
Article 28
Enterprises and institutions discharging pollutants in excess of the prescribed national or local discharge standards shall pay a fee for excessive discharge according to state provisions and shall assume responsibility for eliminating and controlling the pollution. The provisions of the Law on Prevention and Control of Water Pollution shall be complied with where they are applicable.
The income derived from the fee levied for the excessive discharge of pollutants must be used for the prevention and control of pollution and shall not be appropriated for other purposes. The specific measures thereof shall be prescribed by the State Council.
Article 29
If an enterprise or institution has caused severe environmental pollution, it shall be required to eliminate and control the pollution within a certain period of time. For enterprises and institutions directly under the jurisdiction of the Central Government or the people's government of a province, an autonomous region, or a municipality directly under the
Central Government, the decision on a deadline for the elimination or control of pollution shall be made by the people's government of the province, autonomous region and the municipality directly under the Central Government. For enterprises and institutions under the jurisdiction of a people's government at or below the city or county level, such decision shall be made by the people's government of the city or county. Such enterprises and institutions shall accomplish the elimination or control of pollution within the specified period of time.
Article 30
A ban shall be imposed on the importation of any technology or facility that fails to meet the requirements specified in the regulations of our country concerning environmental protection.
Article 31
Any unit that, as a result of an accident or any other exigency, has caused or threatens to cause an accident of pollution, must promptly take measures to prevent and control the pollution hazards, make the situation known to such units and inhabitants as are likely to be endangered by such hazards, report the case to the competent department of environmental protection administration of the locality and the departments concerned and accept their investigation and decision. Enterprises and institutions that are likely to cause severe pollution accidents shall adopt measures for effective prevention.
Article 32
If the safety of the lives and property of inhabitants is endangered by severe environmental pollution, the competent department of environmental protection administration of the local people's government at or above the county level must promptly report to the local people's government. The people's government concerned shall take effective measures to remove or alleviate the hazard.
Article 33
The production, storage, transportation, sale and use of toxic chemicals and materials containing radioactive substances must comply with the relevant state provisions so as to prevent environmental pollution.
Article 34
No unit shall be permitted to transfer a production facility that causes severe pollution for use by a unit that is unable to prevent and control pollution.
Chapter V Legal Liability
Article 35
Any violator of this Law shall, according to the circumstances of the case, be warned or fined by the competent department of environmental protection administration or another department invested by law with power to conduct environmental supervision and management for any of the following acts:
- refusing an on-site inspection by the competent department of environmental protection administration or another department invested by law with power to conduct environmental supervision and management, or resorting to trickery and fraud while undergoing inspection;
- refusing to report or submitting a false report on items for which declaration is required by the competent department of environmental protection administration under the State Council;
- failing to pay, as provided for by the state, the fee for the excessive discharge of pollutants;
- importing technology or a facility that fails to meet the requirements specified in the state provisions concerning environmental protection; or
- transferring a production facility that causes severe pollution for use by a unit that is unable to prevent and control pollution.
Article 36
When a construction project is commissioned or put to use in circumstances where facilities for the prevention and control of pollution either have not been completed or fail to meet the requirements specified in state provisions, the competent department of environmental protection administration responsible for the approval of the environmental impact statement on the construction project shall order the suspension of its operations or use and may concurrently impose a fine.
Article 37
A unit which dismantles or leaves idle the installations for the prevention and control of pollution without prior approval by the competent department of environmental protection administration, thereby discharging pollutants in excess of the prescribed discharge standards, shall be ordered by the competent department of environmental protection administration to set up the installations or put them to use again, and shall concurrently be fined.
Article 38
An enterprise or institution which violates this Law, thereby causing an environmental pollution accident, shall be fined by the competent department of environmental protection administration or another department invested by law with power to conduct environmental supervision and management in accordance with the consequent damage; in a serious case, the persons responsible shall be subject to administrative sanction by the unit to which they belong or by the competent department of the government.
Article 39
An enterprise or institution that has failed to eliminate or control pollution by the deadline as required shall, as provided for by the state, pay a fee for excessive discharge; in addition, a fine may be imposed on it on the basis of the damage incurred, or the enterprise or institution may be ordered to suspend its operations or close down. The fine as specified in the preceding paragraph shall be decided by the competent department of environmental protection administration. An order for the suspension of operations or shut-down of an enterprise or institution shall be issued by the people's government that set the deadline for the elimination or control of pollution. An order for the suspension of operations or shut-down of an enterprise or institution directly under the jurisdiction of the Central Government shall be submitted to and approved by the State Council.
Article 40
A party refusing to accept the decision on administrative sanction may, within 15 days of receiving the notification on such a decision, apply for reconsideration to the department next higher to the authorities that imposed the sanction; if the party refuses to accept the decision of reconsideration, it may, within 15 days of receiving the reconsideration decision, bring a suit before a people's court. A party may also bring a suit directly before a people's court within 15 days of receiving the notification on the sanction. If, upon the expiration of this period, the party has not applied for reconsideration or has neither brought a suit before a people's court nor complied with the sanction, the authorities that imposed the sanction may apply to the people's court for compulsory enforcement.
Article 41
A unit that has caused an environmental pollution hazard shall have the obligation to eliminate it and make compensation to the unit or individual that suffered direct losses. A dispute over the liability to make compensation or the amount of compensation may, at the request of the parties, be settled by the competent department of environmental protection administration or another department invested by law with power to conduct environmental supervision and management. If a party refuses to accept the decision on the settlement, it may bring a suit before a people's court. The party may also directly bring a suit before the people's court.
If environmental pollution losses result solely from irresistible natural disasters which cannot be averted even after the prompt adoption of reasonable measures, the party concerned shall be exempted from liability.
Article 42
The limitation period for prosecution with respect to compensation for environmental pollution losses shall be three years, counted from the time when the party becomes aware of or should become aware of the pollution losses.
Article 43
If a violation of this Law causes a serious environmental pollution accident, leading to the grave consequences of heavy losses of public or private property or human injuries or deaths of persons, the persons directly responsible for such an accident shall be investigated for criminal responsibility according to law.
Article 44
Whoever, in violation of this Law, causes damage to natural resources like land, forests, grasslands, water, minerals, fish, wild animals and wild plants shall bear legal liability in accordance with the provisions of relevant laws.
Article 45
Any person conducting supervision and management of environmental protection who abuses his power, neglects his duty or engages in malpractices for personal gains shall be given administrative sanction by the unit to which he belongs or the competent higher authorities; if his act constitutes a crime, he shall be investigated for criminal responsibility according to law.
Chapter VI Supplementary Provisions
Article 46
If an international treaty regarding environmental protection concluded or acceded to by the People's Republic of China contains provisions differing from those contained in the laws of the People's Republic of China, the provisions of the international treaty shall apply, unless the provisions are ones on which the People's Republic of China has announced reservations.
Article 47
This Law shall enter into force on the date of promulgation. The
Environmental Protection Law of the People's Republic of China (for Trial
Implementation) shall be abrogated there from.
5.5 Appendix 5: Land Administration Law of the People‘s Republic of China
Order [1998]No.8 of the President of the People's Republic of China
August 29, 1998
Adopted at the 16th Meeting of the Standing Committee of the Sixth National People's Congress on June 25, 1986, amended in pursuance of the(Decision on the Amendment of the Land Administration Law of the People's Republic of China) made at the 5th Meeting of the Standing Committee of the Seventh National People's Congress on December 29, 1988 and revised at the 4th Meeting of the Standing Committee of the Ninth National People's Congress on August 29, 1998.
Chapter I General Provisions
Article 1
This Law is enacted in accordance with the Constitution with a view to strengthening land administration, safeguarding the socialist public ownership of land, protecting and developing land resources, rationally utilizing the land, earnestly protecting the cultivated land and promoting sustainable socio-economic development.
Article 2
The People's Republic of China practises the socialist public ownership of land, namely ownership by the whole people and collective ownership by the laboring masses.
Ownership by the whole people namely the ownership of state-owned land shall be exercised by the State Council on behalf of the state.
No unit or individual shall infringe on and occupy, buy and sell or illegally transfer land in other forms. Land use right may be transferred in accordance with law.
The state may, one of necessity of public interest, requisition land collectively owned in accordance with law.
The state practises the system of paid-for use for state-owned land in accordance with law. However, appropriation of state-owned land use right by the state within the scope prescribed by law is excluded.
Article 3
Most sparing and rational land utilization and earnest protection of cultivated land constitute China's basic state policy. People's governments at all levels should take measures in overall planning, strict administration, protection and development of land resources and curbing illegal acts of occupation of land.
Article 4
The state practises the system of land use control.
The state compiles overall planning for land utilization, provides for land uses and classifies land as farm land, land for construction and un-utilized land. Strict restriction shall be imposed on turning farm land into land for construction, quantum of land for construction shall be controlled and special protection provided for cultivated land.
Farm land referred to in the preceding paragraph means land used directly for agricultural production including cultivated land, forest land, grassland, land for farmland water conservancy and water surface for cultivation and breeding; land for construction means land for building constructions and structures including land for urban and rural residences and public facilities, land for industries and mines, land for communications and water conservancy works, land for tourism and land for military installations; un-utilized land means land other than farm land and land for construction.
Any unit or individual that uses land must use the land in strict accordance with the uses determined by the overall planning for land utilization.
Article 5
The competent department of land administration under the State Council shall be uniformly responsible for the work of land administration and supervision nationwide.
The establishment of competent departments of land administration of local people's governments at or above the county level and their responsibilities shall be determined by the people's governments of the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government pursuant to the relevant provisions of the State Council.
Article 6
Any unit or individual has the obligation to abide by the laws and regulations on land administration and has the right to report on or file a charge against any act violating the laws and regulations on land administration.
Article 7
Units and individuals that have made remarkable achievements in the protection and development of land resources, rational utilization of land and conduct of related scientific research shall be rewarded by the people's government.
Chapter II Land Ownership and Use Right
Article 8
Land in urban areas of cities belongs to the state.
Land in rural areas and suburban areas of cities excluding those belonging to the state prescribed by law belongs to peasants' collective ownership; house sites, land allotted for personal needs and hilly land allotted for private use belongs to peasants' collective ownership.
Article 9
State-owned land and land collectively owned by peasants may be determined in accordance with law to be used by units or individuals. Units and individuals using the land have the obligation to protect, manage and rationally utilize the land.
Article 10
Peasants' collectively-owned land that belongs to peasants' collective ownership of a village according to law shall be managed and administered by the village collective economic organization or villagers' committee; the land that belongs separately to more than two rural collective economic organizations and owned collectively by peasants shall be managed and administered by the respective rural collective economic organizations or villagers' teams; the land that belongs to village(township) peasants' collective ownership shall be managed and administered by the village(township) rural collective economic organization.
Article 11
People's governments at the county level shall enter into registration in a register, issue certificates in confirmation of the ownership for the land collectively owned by peasants.
People's governments at the county level shall enter into registration in a register, issue certificates in confirmation of the land use right for construction for land collectively owned by peasants to be used for non-agricultural construction in accordance with law. People's governments at or above the county level shall enter into registration in a register and issue certificates in confirmation of the right to use for state-owned land used by units and individuals in accordance with law; among which the specific registration and certificate-issuing organ for state-owned land used by the Party and state organs shall be determined by the State Council. Confirmation of ownership or the right to use of forest land and grassland, confirmation of the right to use for cultivation and breeding of water surface and beaches and shoals shall be handled pursuant to the relevant provisions of the ((Forest Law of the People's Republic of China)),the ((Grassland Law of the People's Republic of China)) and the ((Fishery Law of the People's Republic of China)).
Article 12
Whoever changes land ownership and use in accordance with law should go through formalities of change in registration of land.
Article 13
The land the ownership and the right to use of which have been registered in accordance with law is protected by law, upon which no unit and individual shall infringe.
Article 14
Land collectively owned by peasants shall be contracted for management by members of the respective collective economic organization for cultivation, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery production. The duration of land contracting and management shall be 30 years. The contract issuing party and the contractor should conclude a contract agreeing on the rights and obligations of both parties. Peasants who contract management of the land have the obligation to protect and utilize the land pursuant to the agreement in the contract. Peasants' right to contract land for management is protected by law.
Within the duration of land contracting and management, in the event of appropriate adjustment of land contracted among individual contractors, it must have the consent of over two thirds of the members of the villagers' conference or over two thirds of the villagers' representatives, and be submitted to the competent department of agriculture administration of village(township) people's government and people's government at the county level for approval.
Article 15
State-owned land may be contracted for management by units or individuals for cultivation, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery production. Land collectively owned by peasants may be contracted and managed by units or individuals other than those in the collective economic organization for cultivation, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery production. The contract issuing party and the contractor should conclude a contract agreeing on the rights and obligations of both parties. The duration of land contracting and management shall be agreed on in the contract. The units and individuals that contract the land for management have the obligation to protect and rationally utilize the land pursuant to the use agreed on in the contract.
For land collectively owned by peasants contracted out for management by units or individuals other than those in the respective collective economic organization, it must have the consent of over two thirds of the members of the peasants' conference or over two thirds of the villagers' representatives and be submitted to the village(township) people's government for approval.
Article 16
Disputes over land ownership and the right to use shall be resolved by the parties interested through consultation; it shall be handled by the people's government in the event of failure of consultation.
Disputes between units shall be handled by people's governments at or above the county level; disputes between individuals and those between an individual and a unit shall be handled by the village-level people's governments or people's governments at or above the county level.
The party interested that refuses to obey the decision on the handling by the people's government concerned may, within 30 days starting from the date of receipt of the notice on the decision on handling, file a suit at a people's court.
Neither party shall alter the status of land utilization prior to the resolution of the dispute over the land ownership and the right to use.
Chapter III Overall Planning for Land Utilization
Article 17
People's governments at all levels should, pursuant to the planning for national socio-economic development, requirements of territorial treatment and resources and environment protection, land supply ability as well as the demand for land for various construction, organize the compilation of overall planning for land utilization.
The duration of planning for overall planning for land utilization shall be determined by the State Council.
Article 18
The overall planning for land utilization at the lower level shall be compiled pursuant to the overall planning for land utilization at the next higher level.
The quantum of land for construction in the overall planning for land utilization compiled by local people's governments at all levels shall not exceed the control targets determined in the overall planning for land utilization at the next higher level, and the quantum of preserved cultivated land shall not be lower than the control targets determined by the overall planning for land utilization at the next higher level.
The overall planning for land utilization compiled by people's governments of the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government should ensure that there is no reduction in the quantum of cultivated land within their respective administrative areas.
Article 19
The overall planning for land utilization shall be compiled in accordance with the following principles:
- strict protection of basic farmland, control of occupation of farmland for non-agricultural construction;
- improvement of land use rate;
- overall arrangement for land for various purposes and various areas;
- protection and improvement of the ecological environment, and guarantee of sustainable land use; and
- balance between occupation of cultivated land and development and reclamation of cultivated land.
Article 20
The overall planning for land utilization at the county level should delimit land use zones and define land uses.
Village(township) overall planning for land utilization should delimit land use zones, determine the use of every plot of land on the basis of the conditions for land use and an announcement to the effect shall be made
Article 21
Overall planning for land utilization shall be examined and approved by different levels.
The overall planning for land utilization of the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government shall be submitted to the State Council for approval.
The overall planning for land utilization of municipalities wherein the people's governments of the provinces and autonomous regions are located and municipalities of a population of over one million as the municipalities designated by the State Council shall, upon the examination and consent of the people's governments of the provinces and autonomous regions, be submitted to the State Council for approval.
The overall planning for land utilization other than those prescribed in the Second Paragraph and Third Paragraph of this Article shall be submitted level by level to the people's governments of the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government for approval; among which the village(township) overall planning for land utilization may be approved by the people's governments of municipalities and autonomous prefectures with subordinate districts with authorization by the people's governments at the provincial level.
The overall planning for land utilization once approved must be strictly implemented.
Article 22
The scale of land used for urban construction should meet the standards set by the state, full use of the existing land for construction should be made, and no farmland or as less as possible farmland should be occupied.
Urban overall planning, village and township planning should be coupled with overall planning for land utilization, the scale of land used for construction in urban overall planning, village and township planning must not exceed the scale of land used for urban, village and township construction determined in the overall planning for land utilization.
Within urban planning zones, village and township planning zones, land used for urban, village and township construction should accord with urban planning and village and township planning.
Article 23
Planning for integrated harnessing, development and exploitation of rivers and lakes should be coupled with overall planning for land utilization. Within the range of administration and protection of rivers, lakes and reservoirs as well as within flood storage areas and flood detention areas, land utilization should accord with the planning for integrated harnessing, development and exploitation of rivers and lakes, accord with the requirements for flood passage, flood storage and discharge of water in river courses and lakes.
Article 24
People's governments at all levels should strengthen administration of land utilization plan and practise quantum control of land used for construction.
Annual land use plan shall be compiled pursuant to the national socio-economic development plan, state industrial policies, overall planning for land utilization as well as the actual conditions of land used for construction and land utilization. The annual land use plan, the procedures for the compilation, examination and approval of which are identical to those for the compilation, examination and approval of the overall planning for land utilization, once examined, approved and transmitted to the lower levels, must be strictly adhered to.
Article 25
People's governments of the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government should list the state of implementation of the annual land use plan as content of the state of implementation of the national socio-economic development plan and report to the people's congresses at the corresponding level.
Article 26
Revision of the approved overall planning for land utilization must be submitted to the original approval organ for approval; no alteration shall be made in land uses determined in the overall planning for land utilization without approval.
In case of necessity of alteration in overall planning for land utilization for land for construction of big-size energy, transport and water conservancy infrastructure approved by the State Council, revision of the overall planning for land utilization shall be made pursuant to the approval document of the State Council.
In case of necessity of alteration in overall planning for land utilization for land for construction of energy, transport and water conservancy infrastructure approved by people's governments of the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government, where it falls within the authority of approval for the overall planning for land utilization of people's governments at the provincial level, revision of the overall planning for land utilization shall be made pursuant to the approval document of the people's governments at the provincial level.
Article 27
The state establishes the land survey system.
The competent departments of land administration of people's governments at and above the county level shall, in conjunction with the departments concerned at the corresponding level, conduct land survey. Land owners or users should cooperate in the survey and provide relevant materials.
Article 28
The competent departments of land administration of people's governments at and above the county level shall, in conjunction with the departments concerned at the corresponding level and in pursuance of land survey results, planned land uses and uniform standards set by the state, evaluate the grades of land.
Article 29
The state establishes land statistics system.
The competent departments of land administration of people's governments at and above the county level and the statistics departments at the corresponding level jointly formulate statistical survey schemes, carry our land statistics in accordance with law and publish land statistical information at regular intervals. Land owners or users should provide relevant information and must not make false reports, concealments, refuse to report and delay in report.
The competent departments' of land administration and statistics departments' jointly published land area statistical information constitute the basis of people's governments at all levels for the compilation of overall planning for land utilization.
Article 30
The state establishes the national land administration information system for dynamic monitoring of the state of land utilization.
Chapter IV Cultivated Land Protection
Article 31
The state protects cultivated land and strictly controls turning cultivated land into non-cultivated land.
The state practises the system of compensation for the occupation and use of land. For the occupation and use of cultivated land for non-agricultural construction with approval, the unit that occupies and uses cultivated land shall be responsible for the reclamation of cultivated land equivalent to the quantity and quality of cultivated land occupied and used in accordance with the principle of "quantity of reclaimed land being equivalent to that occupied"; where there are no conditions for reclamation or the reclaimed land does not conform to requirements, cultivated land reclamation fee should be paid as prescribed by the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government, the special-purpose fund shall be used for the reclamation of new cultivated land.
People's governments of the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government should work out cultivated land reclamation plan, supervise units that occupy and use cultivated land in the reclamation of cultivated land in accordance with the plan or in the organization of reclamation of cultivated land in accordance with the plan and carry out acceptance checks.
Article 32
Local people's governments at and above the county level may demand the units that occupy and use cultivated land to use the soil of the cultivated layer of cultivated land for soil improvement of newly reclaimed cultivated land, inferior quality land or other cultivated land.
Article 33
People's governments of the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government should strictly implement the overall planning for land utilization and annual land use plan and take measures to ensure that there is no decrease in the quantum of cultivated land within their respective administrative areas; where there is decrease in the quantum of cultivated land, the locality shall be ordered by the State Council to organize reclamation of cultivated land the quantity and quality of which is equivalent to those reduced within the specified time period, and the competent department of land administration under the State Council shall in conjunction with the competent department of agriculture administration conduct acceptance checks. Individual province or municipality directly under the Central Government whose quantum of newly reclaimed cultivated land is not adequate to compensate the quantum of cultivated land occupied and used after land used for newly added construction for paucity of reserve land resources, a report must be submitted to the State Council for approval for the reduction and exemption of the quantity of reclamation of cultivated land within the respective administrative area and reclamation be carried out in another place.
Article 34
The state practises the system of protection for basic farmland. The following cultivated land shall be included in the basic farmland protection zones in accordance with the overall planning for land utilization and strict administration exercised:
- cultivated land within production bases for food grains, cotton and oils determined upon approval by the competent departments concerned under the State Council or local people's governments at and above the county level;
- cultivated land with good water conservancy and water and soil conservation works, medium and low yield farmland the transformation plan of which is being carried out as well as those that may be transformed;
- production bases for vegetables;
- experimental plots for agricultural scientific research and teaching; and
- other cultivated land that should be included in basic farmland protection zones as prescribed by the State Council.
The basic farmland delimited by the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government should account for over eighty percent of the cultivated land within the respective administrative areas.
A basic farmland protection zone shall be delimited and demarcated with a village(township) as a unit, the delimitation of a zone and demarcation of the boundary shall be organized and carried out by the competent department of people's government at the county level in conjunction with the competent department of agriculture administration at the same level.
Article 35
People's governments at all levels should take measures to maintain irrigation and drainage works, improve soil and soil fertility, prevent land desertification, salinization, water and soil erosion and land pollution.
Article 36
Economy in land use must be practised for non-agricultural construction, no cultivated land shall be occupied and used where barren land can be used; no good land shall be occupied and used where inferior land can be used.
Occupation and use of cultivated land for setting up kilns, building tombs or building of houses, sand digging, quarrying, mining and earth gathering on cultivated land without authorization shall be prohibited.
Occupation and use of basic farmland for the development of forestry and fruit industry and digging of ponds for fish breeding shall be prohibited.
Article 37
All units and individuals shall be prohibited to let cultivated land lie idle or make it barren. The cultivated land occupied and used for non-agricultural construction the formalities of examination and approval of which have been completed which has been left unused within a year but may be cultivated and harvested should be recultivated by the collective or individuals that previously cultivated the said plot of cultivated land, and cultivation may be organized by the land use unit; where construction has not been started for over a year, idle fee should be paid in accordance with the provisions of the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government; where the land has not been used for two consecutive years, the people's government at the county level shall, subject to the approval of the original approval organ, withdraws the land use right of the land use unit without compensation; the said plot of land previously collectively owned by peasants should be handed back to the original rural collective economic organization for resumption of cultivation.
Idle land the land use right of which has been obtained in the form of transfer for real estate development within the range of an urban planning zone shall be handled in pursuance of the relevant provisions of the ((Urban Real Estate Administration Law of the People's Republic of China)).
For a unit or an individual contracting the management of cultivated land that let the land uncultivated and lie barren, the original contract issuing unit should terminate the contract and withdraw the cultivated land contracted.
Article 38
The state encourages units and individuals in the development of unexploited land in accordance with the overall planning for land utilization and under the prerequisite of protection and improvement of the ecological environment, prevention of water and soil erosion and land desertification; the land suitable to be developed into agricultural land should be developed into agricultural land on a priority basis.
The state protects the legitimate rights and interests of developers in accordance with law.
Article 39
Reclamation of unexploited land must undergo scientific authentication and evaluation and it must be carried out within the reclaimable areas delimited in the overall planning for land utilization upon approval in accordance with law. Reclamation of cultivated land through destruction of forests and prairie shall be prohibited, reclaiming farmland from lakes and infringement on shoals of rivers shall be prohibited.
The land reclaimed and land reclaimed from lakes with the destruction of the ecological environment shall, in accordance with the overall planning for land utilization, be returned to forests, grazing and lakes in a planned way and step by step.
Article 40
Development of state-owned barren hills, barren land and barren shoals the right to use of which is undetermined for cultivation, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery production may, subject to approval by people's government at or above the county level, be determined and given to development units or individuals for long-term use.
Article 41
The state encourages land arrangement. County, village(township) people's governments should organize rural collective economic organizations in integrated treatment of farmland, water, roads, woods and villages in accordance with the overall planning for land utilization to improve the quality of cultivated land, increase the area of effective cultivated land and improve conditions for agricultural production and the ecological environment.
Local people's governments at all levels should take measures to transform the medium and low yield plots, treat idle and scattered plots and abandoned plots.
Article 42
For destruction of land caused by damage due to digging, caving in and pressurized occupation, the land use unit and individual should, in accordance with relevant state provisions, be responsible for the reclamation; where there are no conditions for reclamation or reclamation does not conform to requirements, land reclamation fee should be paid to be used specifically for land reclamation. The reclaimed land should be used for agriculture on a priority basis.
Chapter V Land for Construction
Article 43
Any unit or individual that needs to use land for construction must apply for the use of state-owned land in accordance with law; however, use of land collectively owned by peasants by the respective collective economic organization approved in accordance with law for the establishment of rural and township enterprises and construction of residences by villagers, or use of land collectively owned by peasants approved in accordance with law for the construction of village(township)public facilities and non-profit undertakings is excluded.
Application for the use of state-owned land in accordance with law referred to in the preceding paragraph includes the state-owned land and the land that originally belonged to collective ownership by peasants and has been requisitioned by the state.
Article 44
For occupation and use of land for construction involving turning agricultural land into land for construction, formalities of examination and approval for turning agricultural land into other uses should be completed.
Occupation and use of land involving turning agricultural land into land for construction for construction projects of roads, pipelines, cables and big-size infrastructure approved by people's governments of the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government and construction projects approved by the State Council shall be subject to the approval of the State Council.
Turning agricultural land into land for construction for the implementation of the said planning within the scale of land for construction for municipalities and villages and townships determined by the overall planning for land utilization shall be subject to the approval of the organ that originally approved the overall planning for land utilization in batches in accordance with the annual land use plan. Within the scope of agricultural land turning into other uses already approved, land for specific construction projects can be approved by municipal and county people's governments.
Occupation and use of land involving turning agricultural land into land for construction for construction projects other than those prescribed in the Second Paragraph and Third Paragraph of this Article shall be subject to the approval of people's governments of the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government.
Article 45
Requisition of the following land shall be subject to the approval of the State Council:
- basic farmland;
cultivated land other than the basic farmland exceeding 35 hectares; and
other land exceeding 70 hectares.
Requisition of land other than those prescribed in the preceding paragraph shall be subject to the approval of people's governments of the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government, and submitted to the State Council for the record.
For the requisition of agricultural land, formalities of examination and approval for turning agricultural land into other uses should be completed beforehand in accordance with the provisions of Article 44 of this Law. Among which, for agricultural land turned into other use approved by the State Council, formalities for examination and approval for land requisition shall be processed simultaneously, and no separate formalities of examination and approval shall be gone through; for agricultural land turned into other uses approved by people's governments of the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government within the limits of authority for the approval of land requisition, formalities for examination and approval of land requisition shall be processed simultaneously, and no separate formalities of examination and approval for land requisition shall be gone through, where it is beyond the limits of authority for the approval of land requisition, separate formalities of examination and approval of land requisition should be completed pursuant to the provisions of the First Paragraph of this Article.
Article 46
For land requisitioned by the state, local people's governments at or above the county level shall, upon approval pursuant to legal procedures, make an announcement and and organize its implementation. Owners and persons of the right to use of the requisitioned land should, within the specified time period of the announcement, bring the ownership certificates to the competent departments of the local people's governments to enter into registration for compensation for land requisition.
Article 47
For requisition of land, compensation shall be given in accordance with the original use of the requisitioned land.
Compensation fee for the cultivated land requisitioned include land compensation fee, subsidy for resettlement as well as compensation fee for ground appendixes and young crops. Land compensation fee for the cultivated land requisitioned shall be six to ten times of the average annual output value in the three years prior to requisition. Subsidy for resettlement for the cultivated land requisitioned shall be calculated on the basis of the agricultural population that requires resettlement. The agricultural population that requires resettlement shall be calculated on the basis of the amount of cultivated land requisitioned divided by the average per capita occupancy of cultivated land of the unit requisitioned. The rate of subsidy for resettlement per head of the agricultural population that requires resettlement shall be four to six times of the average annual output value in the three years prior to requisition of the said cultivated land. However, the maximum subsidy for resettlement for cultivated land requisitioned per hectare shall not exceed fifteen times of the average annual output value in the three years prior to the requisition.
The rate of land compensation fee and subsidy for resettlement for the requisition of other lands shall be fixed by the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government, taking the rate of land compensation fee and subsidy for resettlement for the requisition of cultivated land as reference.
Rate of compensation for ground appendixes and young crops on the requisitioned land shall be fixed by the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government.
For requisition of suburban vegetable plots of municipalities, the land use unit should, pursuant to relevant state provisions, pay to the new vegetable plot development and construction fund.
Additional subsidy for resettlement may be provided for those peasants who require resettlement and cannot maintain their original living standards on the basis of land compensation fee and subsidy for resettlement the payment of which is effected pursuant to the provisions of the Second Paragraph of this Article subject to the approval of people's governments of the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government. However, the total of land compensation fee and subsidy for resettlement shall not exceed thirty times of the average annual output value in the three years prior to requisition of the land.
The State Council may, in accordance with the level of socio-economic level, increase the rate of land compensation fee and subsidy for resettlement under extraordinary circumstances.
Article 48
Upon determination of the scheme for compensation and resettlement for land requisition, the local people's government concerned should make an announcement and seek the views of the rural collective economic organization and peasants of the requisitioned land.
Article 49
The rural collective economic organization of the requisitioned land should publish the revenue and expenditure of the compensation fee of the requisitioned land for the members of the respective collective economic organization and accept supervision.
It is forbidden to embezzle or divert the land compensation fees and other related expenses.
Article 50
Local people's governments at all levels should provide support for rural collective economic organizations and peasants of the requisitioned land for development and management and establishment of enterprises.
Article 51
Rate of compensation for land requisitioned for construction of big- and medium-size water conservancy works and hydropower projects shall be fixed and measures for emigrant resettlement formulated separately by the State Council.
Article 52
The competent department of land administration may, during the feasibility study and authentication of a construction project, examine the matters related to the land for construction and put forth suggestions in accordance with the overall planning for land utilization, the annual land use plan and standards for land for construction.
Article 53
For an approved construction project that needs to use state-owned land for construction, the construction unit should bring the relevant documents prescribed by laws and regulations and file an application at the competent department of land administration of the people's government at or above the county level that has the authority of approval which shall be submitted to the people's government at the corresponding level for approval upon examination by the competent department of land administration.
Article 54
Use of state-owned land for a construction project should be obtained in the form of paid-for use such as transfer; however, the following use of land for construction may be obtained in the form of appropriation subject to the approval of the people's government at or above the county level in accordance with law:
- land use by state organs and land use for military purposes;
- land use for urban infrastructure and land use for non-profit undertakings;
- land use for such infrastructure as energy, communications and water conservancy to which the state renders key support; and
- other land uses prescribed by laws and administrative regulations.
Article 55
A construction unit with the obtainment of land use right of state-owned land in the form of paid-for use such as transfer may use the land only upon the payment of fee for paid-for land use and other fees such as land use right transfer fund in accordance with the standards and measures prescribed by the State Council.
As of the date of coming into effect of this Law, of the paid-for land use fee of newly-added land for construction, 30% shall be handed over to the central finance and 70% shall be retained by the local people's government concerned, and both shall be used specifically for the development of cultivated land.
Article 56 A
construction unit that uses state-owned land should use the land in accordance with the agreement in the contract for paid-for use for the transfer of land use right or the provisions of the approval document on the appropriation of land use right; where change in the use for construction of the said plot of land is necessitated, it should be subjected to the consent of the competent department of the people's government concerned and submitted to the people's government that originally approved the land use for approval. Among them, for change in the use of land within an urban planning zone, consent of the competent department of urban planning should be sought first prior to submission for approval.
Article 57
Construction of a construction project and geological survey that need to temporarily use state-owned land or land collectively owned by peasants, it shall be subject to the approval of the competent department of land administration of the people's government at or above the county level. Among which, for temporary use of land within an urban planning zone, consent of the competent department of urban planning should be sought first prior to submission for approval. The land user should conclude a contract for the temporary use of the land with the competent department of land administration concerned or the rural collective economic organization and villagers' committee in accordance with the ownership of the land, and effect the payment of compensation fee for the temporary use of the land.
User of temporary use of the land should use the land according to the use agreed on in the contract for the temporary use of the land and shall not construct permanent constructions thereon. The duration of temporary use of land shall generally not exceed two years.
Article 58
The right to use of state-owned land may, subject to the approval of the people's government that originally approved the use of land or the people's government with authority of approval upon submission by the competent department of land administration of the people's government concerned, be withdrawn for any of the following circumstances:
- land use required for public interest;
- adjustment in land use necessitated by reconstruction of old urban districts in implementing urban planning;
- failure of the land user to apply for extension or failure of obtaining approval for the application for extension on expiry of the duration of use agreed on in the contract for paid-for use in land transfer;
- stoppage of the use of state-owned land previously appropriated as a result of disbandment or moving of the unit; and
- highways, railways, airports and mines phased out upon verification and approval.
For withdrawal of the right to use of state-owned land pursuant to the First Section and Second Section of the preceding paragraph, appropriate compensation should be given to the land use right holder.
Article 59
Rural(township) construction such as rural and township enterprises, rural(township) public facilities, non-profit undertakings, and villagers' residences should, in accordance with village and township planning, have a rational layout, integrated development and matching construction; land for construction should conform to the rural(township)overall planning for land utilization and annual land use plan and formalities of examination and approval should be completed pursuant to the provisions of Articles 44, 60, 61, and 62 of this Law.
Article 60
For the establishment of an enterprise using the land for construction determined by the overall planning for rural(township) land utilization by a rural collective economic organization or joint establishment of an enterprise with other units and individuals in the form of equity participation of land use right and joint operations, an application should be filed at the competent department of land administration of the local people's government at or above the county level with the approval document which shall be subject to the approval of local people's government at or above the county level pursuant to the limits of authority of approval prescribed by the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government; among them, for cases involving occupation and use of agricultural land, formalities of examination and approval shall be completed pursuant to the provisions of Article 44 of this Law.
Land for construction for the establishment of enterprises pursuant to the provisions of the preceding paragraph must be strictly controlled. The provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government may, in accordance with the different trades and management scale of rural and township enterprises, provide respectively for the standards for land use.
Article 61
For land use required for the construction of rural(township)public facilities and non-profit undertakings, an application shall be filed at the competent department of land administration of the people's government at or above the county level upon examination and verification by the village(township) people's government and subject to the approval of the local people's government at or above the county level pursuant to the limits of authority of approval prescribed by the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government; among them, for cases involving use of agricultural land, formalities of examination and approval shall be completed pursuant to the provisions of Article 44 of this Law.
Article 62
One household of villagers in a rural area can only possess one house site the area of which shall not exceed the standards prescribed by the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government.
Construction of villagers' residences in the rural areas should conform to the overall planning for rural(township) land utilization, and the best possible use of original house sites and idle land in the villages should be made.
Land use for villagers' residences in the rural areas shall be subject to the approval of the people's government at the county level upon examination and verification by the village(township) people's government; among them, for cases involving occupation and use of agricultural land, formalities of examination and approval shall be completed pursuant to the provisions of Article 44 of this Law.
Reapplication for a house site by a villager in a rural area who has sold or rented out his/her house shall not be approved.
Article 63
The right to use of land collectively owned by peasants shall not be transferred, retransferred or rented out for non-agricultural construction; however, enterprises that obtained land for construction in accordance with law and conforming to the overall planning for land utilization where occurrences of transfer of land use right have been brought about by such circumstances as bankruptcy and merger are excluded.
Article 64
Constructions and structures completed prior to the formulation of the overall planning for land utilization that fail to conform to the uses determined by the overall planning for land utilization shall not be reconstructed and expanded.
Article 65
A rural collective economic organization may, subject to the approval of the people's government that previously approved the land use, withdraw the land use right for any of the following circumstances:
- land use required for the construction of rural(township) public facilities and non-profit undertakings;
- use of land not in accordance with the use approved; and
- stoppage of the use of the land due to reasons such as disbandment and moving.
For withdrawal of land collectively owned by peasants pursuant to the provisions of the First Section of the preceding paragraph, appropriate compensation shall be given to the land use right holder.
Chapter VI Supervision and Inspection
Article 66
Competent departments of land administration of people's governments at and above the county level shall conduct supervision and inspection over acts in violation of the laws and regulations on land administration.
Functionaries of supervision and inspection of land administration should be conversant with land administration laws and regulation, faithful in the discharge of duties and impartial in law enforcement.
Article 67
Competent departments of land administration of people's governments at and above the county level have, in fulfilling their duties and responsibilities of supervision and inspection, the power to take the following measures:
- to demand the unit or individual under inspection to provide documents and materials concerning land right for reading or copying;
- to demand the unit or individual under inspection to make explanations concerning questions relating to land right;
- to enter the site illegally occupied and used by the unit or individual under inspection for a survey; and
- to order the unit or individual illegally occupying and using the land to stop acts in violation of land administration laws and regulations.
Article 68
Functionaries of land administration supervision and inspection should, in fulfilling duties and responsibilities, deem it necessary to enter a site for survey, demand the unit or individual concerned to provide documents and materials and make explanations, produce identification papers for land administration supervision and inspection.
Article 69
Units and individuals concerned should support, cooperate with and facilitate the supervision and inspection conducted by competent departments of land administration of the people's governments at or above the county level on illegal acts related to land and must not refuse and obstruct functionaries of land administration supervision and inspection in the discharge of duties according to law.
Article 70
Competent departments of land administration of the people's governments at and above the county level should, upon uncovering of illegal acts by state functionaries in the work of supervision and inspection who should be imposed administrative sanctions, handle the case(s) according to law; when the department has no power to handle the case(s), a proposal for administrative sanctions shall be submitted to the administrative supervisory organ of the people's government at the corresponding level or at the next higher level, and the administrative supervisory organ concerned should handle the case(s) according to law.
Article 71
Competent departments of land administration of people's governments at and above the county level should, on uncovering of illegal acts related to land that constitute a crime in the work of supervision and inspection, transfer the case(s) to the organ concerned for investigation of criminal liability according to law; where a crime has not been constituted, administrative penalty should be imposed according to law.
Article 72
Where an administrative penalty should be imposed pursuant to the provisions of this Law and the competent department of land administration has failed to impose the administrative penalty, the competent department of land administration of the people's government at the next higher level has the power to order the competent department of land administration to take a decision on the administrative penalty or directly impose the administrative penalty, and impose administrative sanctions on the person in charge of the competent department of land administration concerned.
Chapter VII Legal Liability
Article 73
Whoever illegally transfers land by buying and selling or in other forms shall be confiscated of the illegal gains by the competent department of land administration of the people's government at or above the county level; whoever turns agricultural land into land for construction without authorization in violation of the overall planning for land utilization shall be given a specified time period to dismantle the newly-built constructions and other facilities on the illegally transferred land and restore the original state of the land, where it conforms to the overall planning for land utilization, the newly-built constructions and other facilities on the illegally transferred land shall be confiscated; and may concurrently be imposed a fine; the person-in-charge directly responsible and other personnel directly responsible shall be imposed administrative sanctions according to law; where a crime has been constituted, criminal liability shall be investigated according to law.
Article 74
Whoever occupies and uses cultivated land for building kiln(s) and tomb(s) or building house(s), digging sand, quarrying, mining and gathering earth on cultivated land without authorization, destroying conditions for cultivation or resulting in desertification and salinization of the land due to land development in violation of the provisions of this Law, shall be ordered by the competent department of the people's government at or above the county level to make a rectification or effect treatment within the specified time period, and may concurrently be imposed a fine; where a crime has been constituted, criminal liability shall be investigated according to law.
Article 75
Whoever refuses to fulfil the obligation of land reclamation in violation of the provisions of this Law shall be ordered by the competent department of land administration of the people's government at or above the county level to make a rectification within the specified time period; whoever fails to make a rectification on expiry of the specified time period shall be ordered to pay the reclamation fee to be used specifically for land reclamation, and may be imposed a fine.
Article 76
Whoever illegally occupies and uses land without approval or obtains approval by deceitful means shall be ordered by the competent department of land administration of the people's government at or above the county level to return the illegally occupied and used land, whoever turns agricultural land into land for construction without authorization in violation of the overall planning for land utilization shall be given a specified time period to dismantle the newly-built constructions and other facilities on the illegally occupied and used land and restore the original state of the land, where it conforms to the overall planning for land utilization, the newly-built constructions and other facilities on the illegally occupied and used land shall be confiscated and may concurrently be imposed a fine; administrative sanctions shall be imposed according to law on the person-in-charge directly responsible and other personnel directly responsible of the unit that illegally occupies and uses the land; where a crime has been constituted, criminal liability shall be investigated according to law.
For occupation and use of land exceeding the approved amount, the land thus occupied shall be construed and handled as illegally occupied and used land.
Article 77
Villagers in rural areas who illegally occupy and use land for building residences without approval or obtain approval by deceitful means shall be ordered by the competent departments of people's governments at or above the county level to return the illegally occupied and used land, and dismantle the newly-built houses on the illegally occupied and used land within the specified time period.
The land occupied exceeding the standards set by the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government shall be construed and handled as illegally occupied and used land.
Article 78
Units or individuals without power to approve requisition and use of land that illegally approve occupation and use of land, those that illegally approve occupation and use of land exceeding the limits of authority of approval, those that approve land use not in conformity with the uses determined by the overall planning for land utilization, or those that approve occupation and requisition of land in contravention of the legal procedures, their approval documents shall be null and void, the persons-in-charge directly responsible and other personnel directly responsible who illegally approve requisition and use of land shall be imposed administrative sanctions according to law; where a crime has been constituted, criminal liability shall be investigated according to law. The illegally approved and used land should be taken back, the party interested that refuses to return the land shall be construed and handled as illegal occupation and use of land.
Whoever illegally approves requisition and use of land causing losses to the party interested shall bear liability of compensation according to law.
Article 79
Whoever infringes on and uses the compensation fee and other related fees for land requisition of the requisitioned unit for other purposes constituting a crime shall be investigated of criminal liability according to law; where a crime has not been constituted, administrative sanctions shall be imposed according to law.
Article 80
The party interested that refuses to hand over the land for withdrawal of the right to use of state-owned land according to law, the party interested that refuses to return the land on expiry of temporary use of land, or the party interested that uses state-owned land not in accordance with the approved use shall be ordered by the competent departments of land administration of people's governments at or above the county level to return the land and a fine imposed.
Article 81
Whoever transfers, retransfers or rents out the right to use of the land collectively owned by peasants for non-agricultural construction without authorization shall be ordered by the competent department of land administration of the people's government at or above the county level to make a rectification within the specified time period, confiscated of the illegal gains and concurrently imposed a fine.
Article 82
Whoever fails to go through change in registration of land pursuant to the provisions of this Law shall be ordered by the competent department of land administration of the people's government at or above the county level to complete the formalities within the specified time period.
Article 83
Construction units or individuals that have been ordered to dismantle the newly-built constructions and other facilities on the illegally occupied and used land within the specified time period pursuant to the provisions of this Law must stop construction forthwith and dismantle them themselves; organs that make the penalty decision's have the power to stop those that continue construction. Construction units or individuals that refuse to obey the decisions of administrative penalty on dismantling within the specified time period may, within 15 days starting from the date of receipt of the decision of ordering the dismantling within the specified time period, file a suit at a people's court; the unit or individual that neither takes legal action nor dismantles itself/himself/herself on expiry, the organ that has taken the decision on penalty shall apply to a people's court for compulsory enforcement, and the expenses shall be borne by the violator of law.
Article 84
Functionaries of competent departments of land administration that neglect their duties, abuse their power and indulge in malpractices for selfish gains constituting a crime shall be investigated of criminal liability according to law; where a crime has not been constituted, administrative sanctions shall be imposed according to law.
Chapter VIII Supplementary Provisions
Article 85
This Law shall be applicable to the use of land by Sino-foreign joint ventures, Sino-foreign cooperative ventures and enterprises owned by foreign capital; where laws have separate provisions, those provisions shall prevail.
Article 86 This Law shall enter into effect as of January 1, 1999.
Attachment:
Relevant Articles of the Criminal Law
Article 228
Whoever illegally transfers and sells land use right with profit-making as the purpose in violation of land administration regulations when the circumstances are serious shall be sentenced to imprisonment under three years or hard labor in detention, and concurrently imposed a fine of more than 5% less than 20% of the amount of the illegally transferred and sold land use right price; where the circumstances are extremely serious, a sentence of more than three years less than seven years shall be passed, and a fine of more than5% less than e amount of the illegally transferred and sold land useright price concurrently imposed.
Article 342
Whoever illegally occupies and uses cultivated land and turns it into other uses in a big amount resulting in great destruction of cultivated land in violation of land administration regulations shall be sentenced to imprisonment under five years or hard labor in detention, and concurrently or separately imposed a fine.
Article 410
Functionaries of state organs who indulge in malpracticesfor selfish gains, abuse power in illegally approving requisition and occupation of land or illegally transfer the right to use of state-owned land at a low price in violation of land administration regulations where the circumstances are serious, shall be sentenced to imprisonment under three years or hard labor in detention; whoever causes extremely great losses to state or collective interests shall be sentenced to more than three years less than seven years of imprisonment.
Promulgated by The Standing Committee of the National People's Congress on 1998-8-29
APPENDIX 6: CITIES DIRECTLY GOVERNED BY THE STATE COUNCIL FOR MASTER PLAN
| Item | Names |
| Municipality | Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai,Chongqing |
| Provincial (Autonomous region) Capital cities | Wuhan, Shenyang, Guangzhou, Harbin, Nanjing, Xi’an, Chengdu, Changchun, Taiyuan, Jinan, Zhengzhou, Lanzhou, Hangzhou, Kunming, Changsha, Shijiazhuang, Guiyang, Nanchang, Urumqi, Huhhot, Fuzhou, Hefei, Nanning, Xining, Yinchuan, Haikou, Lhasa |
| Other cities | Dalian, Qingdao, Zibo, Anshan, Fushun, Tangshan, Jilin, Qiqihar, Xuzhou, Handan, Luoyang, Wuxi, Datong, Shenzhen, Suzhou, Benxi, Huainan, Shantou, Yichun, Yantai, Daqing, Liuzhou, Changzhou, Jixi, Baotou, Zaozhuang, Fuxin, Ningbo, Jinzhou, Zhangjiakou, Jinzhou, Zhuzhou, Mudanjiang, Weifang, Pingdingshan, Hegang, Xiangfan, Xinxiang, Dandong, Hengyang, Jiamusi, Xiamen, Zhanjiang, Liaoyang, Huangshi, Linqi, Baoding, Huaibei, Kaifeng, Jiaozuo, Tai’an, Anyang, Xiangtan, Xinjiang Production & Construction Corp. |
Version 1.0 April 2009, © Danish Environmental Protection Agency