Environmental Factors and Health
Appendix 1
Principles for derivation of health based guidance values and quality criteria for
chemical substances
In the following, the principles upon which the Danish Environmental Protection Agency derive health based guidance values and quality criteria for chemical substances are briefly outlined. The quality criteria are nationally derived criteria values, as the Minister of the Environment according to the environmental protection law is authorised to stipulate quality criteria for the protection of environment and health.
The quality criteria for air, soil and drinking-/ groundwater are supplementary values derived by the Danish EPA in areas where no quality standards/ limit values have been implemented by statutory orders. Thus the quality criteria are guidance values, for which deviation can be made in specific cases if this does not compromise the protection of human health.
Purpose
The purpose of setting health based guidance values and quality criteria for chemical substances is to prevent health hazards in the human population caused by chemicals as pollutants. The scientific method for setting of health based guidance values comprises a hazard identification and hazard assess-ment which together with an exposure assessment constitute the risk assessment part in the process.
Selection of data
Data concerning exposure and harmful effects of a chemical substance are collected from national and international criteria documents, monographs and original scientific literature. During the review of the data, the quality and reliability of the studies and research work are critically assessed. This is an important step since conflicting viewpoints regarding the hazards may be present. Unpublished data from industry or other sources are only seldom used, as such data have not been published in scientific journals and have not been subjected to critical review by other scientists.
If adequate human data are available these are preferred as the basis for the assessment. For most substances however, human data are not adequate or available. In these cases, health based objective values are based upon data from experimental animal studies.
When all the relevant data have been evaluated, the hazard considered most important - "the critical effect" - for setting the health based guidance value, is identified. In this step it is assessed whether an effect should be considered as adverse and of relevance to humans.
A substance may have different effects at different concentrations or doses. Generally, the effects are of more concern the lower the concentration or dose at which they occur, and the effect observed at the lowest concentration or dose often forms the basis for setting the guidance value.
Threshold chemicals, NOAEL or LOAEL
The next step for assessment of a health based guidance value is to identify the "no observed adverse effect level" (NOAEL) which is the highest dose at which the critical effect was not observed or, in cases where a NOAEL cannot be identified, the "lowest observed adverse effect level" (LOAEL) which is the lowest dose at which the critical effect was observed.
TDI / safety factors
Having identified a NOAEL or a LOAEL, three "safety factors" (SF) are used to extrapolate from NOAEL or LOAEL to the tolerable daily intake, TDI (expressed in mg/kg b.w. per day) or the tolerable concentration in air, TCair, (expressed in mg/m3). The purpose of the safety factors is to take into account the fact that:
SF1: The toxicological effect of a chemical substance on animals need not reflect the toxicological effect on "normal" humans, this factor is historically set at 10.
SF2: The toxicological effect of a chemical substance may vary considerably between different persons, and that i.e. children, elderly or sick people may be much more sensitive to exposure than "normal" people, this factor is often set at 10.
SF3: The data may be of varying quality and relevance to the actual problem, this factor is set at a value from 1 to 1000 depending on a concrete evaluation.
Thus in cases where a threshold value for the toxic effect is assumed and a NOAEL or a LOAEL can be identified, the TDI (or TC) are obtained by the following calculation:

Exposure routes
In general, guidance values for air are based upon data from inhalation studies and guidance values for soil (GVsoil) and drinking water (GVdw) are based upon data from oral studies. However, if data for the relevant exposure route are not available, data from alternative exposure routes may be used as well, although it is realized that the degree of uncertainty may increase. This will then influence the value of the SF3.
Analogy
In cases where no data on harmful effects are available, an evaluation may be made upon the basis of data for related substances and a consequent increase in the value of the SF3.
Non threshold chemicals
For chemical substances where a threshold value for the toxic effect cannot be assumed (i.e. genotoxic carcinogenic substances), the concept of lifetime risk is applied. Thus, for these potential carcinogenic substances, the TDI corresponding to a specific lifetime risk, is calculated upon the basis of animal studies by means of the "One Hit" model. A lifetime risk of 10-6 (life-time exposure to the dose that may lead to cancer for one in a million) is conside-red as tolerable.
Exposure
air, water, soil
Having obtained the tolerable daily intake (or concentration) for a chemical substance, the health based guidance values for drinking water and soil are calculated taking into account the daily exposure from the various media. The following exposure standard estimates for the various media are used in the calculation of guidance values:
|
Soil* |
Soil* |
Air |
Water |
Child, 10 kg |
|
|
|
|
average exposure |
0.2 g/d |
1 g/d |
10 m3/d |
1 liter/d |
maximum exposure |
10 g/d |
10 g/d |
12 m3/d |
2 liter/d |
Adult, 70 kg |
|
|
|
|
average exposure |
0.025 g/d |
0,1 g/d |
20 m3/d |
2 liter/d |
maximun expsoure |
0.1 g/d |
1 g/d |
30 m3/d |
4 liter/d |
*For the soil exposure estimates, it has to be emphasized that these are based upon exposure scenarios which cover the most sensitive applications, e.g. domestic gardens, play grounds or kindergartens.
To ensure that the total daily intake of a chemical substance from the various media does not exceed the tolerable daily intake, a certain percentage of the tolerable intake to the various media may be assigned (allocation).
Health based guidance values
The guidance values for soil and drinking water are obtained by the following calculations:
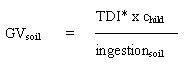

if the concentration is the critical parameter e.g. in relation to airborne irritants, or
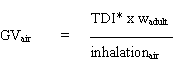
if the dose delivered through the air is the critical parameter e.g. in connection with substances systemic effects.
TDI*: often only a certain percentage (typically 10%) of the TDI is allocated to
the calculation of the quality criteria, as this procedure account for exposure
contributions from other media, e.g. exposure from food or exposure from every day
chemical products are considered.
w: body weight for a child (10 kg) or an adult person (70 kg)
C-value, quality criteria
Finally, the health based guidance values are used as the basis for the setting of quality criteria for soil, drinking water, ground water, and air (known as "C-values", which are contribution emission concentration values for air pollutants from industrial plants). In this step, other considerations than health based aspects may be taken into account. This may include aesthetical factors such as odour (all media), discoloration (soil, drinking water), or taste (drinking water). Furthermore, economic or political administrative factors may be taken into account as well.
It has to be stressed that no eco-toxicological considerations are taken into account in the process of setting health-based guidance and quality criteria values.
List of Danish soil quality criteria values and the corresponding groundwater quality criteria, air quality criteria and cut-off values.
The quality criteria values and cut off values are nationally derived guidance values. Soil quality criteriaare health-based values derived to secure most sensitive use of the soil i.e. domestic garden, kinder gartens and playgrounds. Especially direct soil-exposure of small children is considered. In addition to these health based criteria it is an overall quality demand that the soil by inspection must not look contaminated or possess odour from soil pollutants.
In the interval between the soil quality criteria and the cut-off value, the soil can only be used for most sensitive use if the local authorities inform and advise the public and the land owner with respect how to establish hygienic measures and soil-exposure reduction measures in a way that the risk for harmful effects is not increased. Cut-off values have only been made for some immobile and rather persistent chemicals (metals and polyaromatic hydrocarbons).
The groundwater quality criteria are used in connection with groundwater-protection, as groundwater is the major drinking-water resource in Denmark. The starting point for derivation of groundwater quality criteria are the nationally derived drinking water quality criteria(or the drinking water standards which are mandatory values following the implementation on the EU-directive on drinking-water quality). The ground-water quality criteria are for some substances set at a lower level than the drinking-water quality criteria, because account has to be taken to additional chemical sources in connection with water treatment procedures and releases of contaminants from the distributing system before the water reach the consumer as drinking-water.
The air quality criteria are used as a criteria for evaporation of the soil pollutant into indoor air. The air quality criteria are only meant to consider the contribution from the evaporation of the contaminated soil and thus are not meant as an overall quality criteria for indoor air.
The quality criteria for the different media are independent criteria, and therefore compliance with the soil quality criteria does not automatically ensure compliance to the quality criteria for evaporation to indoor air or leakage into the groundwater, i.e. each of the relevant criteria has to be considered separately.
The following list is based on values published earlier (see references below) together with the addition of new values not published earlier.
a: in soil, sum of benzo(a)pyrene, benzo(b+j+k)fluoranthene, dibenzo(a,h)anthracene, fluoranthene, and indeno(1,2,3-cd)pyrene
b: in water, sum of benzo(a)pyrene, benzo(b+k)fluoranthene, fluoranthene, indeno(1,2,3-cd)pyrene, and benzo(ghi)fluoranthene
Comments:
It should be noted that the soil quality criteria are health based values, and for some substances with low odour threshold (e.g. MTBE) the soil quality criteria may not comply with the overall quality objective that the soil should appear clean and be without odour from soil pollutants.
Some of the groundwater quality criteria may be subject to revision in order to cohere with proposals for new drinking water standards. Especially for MTBE, the groundwater quality criteria value is expected to be lowered.
References:
DEPA (1999): "Toxicological evaluation and limit values for methyltert-butyl ether (MTBE), formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde and furfural." Environmental project no. 511.
DEPA (1999): "Toxicological evaluation and limit values for nonylphenol, nonylphenol ethoxylates, tricresyl phosphates and benzoic acid." Environmental project no. 512.
DEPA (1995): "Toksikologiske kvalitetskriterier for jord- og drikkevand". (Toxicological quality criteria for soil and drinking water) Project no. 12.
DEPA (1996): "B-værdier" (C-values). Guideline no. 15.
DEPA (1998): "Oprydning på forurenede lokaliteter" (Remediation of contaminated sites). Guideline no. 7
DEPA (1990): "Begrænsning af luftforurening fra virksomheder" (Reduction of air pollution from industries), Guideline no. 6.
Drinking water quality criteria
The following list contain nationally derived drinking water quality criteria for selected substances which are not covered by drinking water standards in connection with the implementation of the EU directive on drinking water quality.
It should be noted that the drinking water quality criteria are health based values based on a toxicological evaluation of the specfic compund, i.e. no consideration has been made to the risk for microbial growth. The risk for microbial growth should be considered as well, as this may be relevant for organic substances having high drinking water quality criteria values.
Most of the values have been published in the publications given below, however, the table also includes some new values not published before.
Chemical name |
CAS-no |
Drinking water Quality criteria m g/ l |
Acetone |
67-64-1 |
2000 /L |
Benzotriazole (+ tolyltriazole) |
95-14-7 |
20 |
Butyl acetate (n-, iso-) |
123-86-4 110-19-0 |
10 /L |
Chlorophenols (sum of mono- , |
- |
0,1 |
Cyanide, driven off by acidization |
- |
10 |
Diethyl ether |
60-29-7 |
40 /L |
Dinitrophenoler |
25550-58-7 |
7 |
Furfural |
98-01-1 |
3 |
Isopropanol |
67-63-0 |
300 |
Lithium, inorganic |
- |
1000 |
Methanol |
67-56-1 |
3500 |
Methyl isoamyl ketone |
110-12-3 |
10 |
Methyl isobutyl ketone |
108-10-1 |
100 /L |
Molybdenum |
- |
20 |
Mononitrophenols |
- |
90 |
Nitrobenzene |
98-95-3 |
4 |
Tetraethyllead + Tetramethyllead |
78-00-2, 75-74-1 |
3 |
Thallium, inorganic |
- |
1 |
Tolyltriazole (+ benzyltriazole) |
29385-43-1 |
20 |
Tricresylphosphates, total o -TCP |
- |
250 10 |
Trinitrophenoles |
- |
20 |
/L : the value based on data on odour/taste that is considered most critical.
Comments
:It is an overall quality demand that the drinking water visually appears clean and is without any untoward taste or odour. Furthermore a content of organic constituents in the water may not constitute a media for microbial growth. Generally, microbial growth is not expected to occur with a content of organic chemicals below 10m µg/l.
References:
DEPA (1999): "Toxicological evaluation and limit values for methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE), formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde and furfural."
Environmental project no. 511.
DEPA (1999): "Toxicological evaluation and limit values for nonylphenol, nonylphenol ethoxylates, tricresyl phosphates and benzoic acid." Environmental project no. 512.
DEPA (1995): "Toksikologiske kvalitetskriterier for jord- og drikkevand" (Toxicological quality criteria for soil and drinking water). Project no. 12.
C-values, air
C-values (contribution values) are used as emission concentration values in outdoor air in connection with airborne emissions of pollutants from industrial plants. To comply with the C-values, the emission from a plant should be lower than the C-value in 99% of the time (i.e. the C-value can maximally be exceeded 7 hours during a month).
The C-values are contribution values and do not take background levels of the pollutants into account.
The C-values are also used as air quality criteria for the evaporation of volatile soil pollutants into indoor air.
Substance: |
CAS-no. |
C-value |
Acetaldehyde |
75-07-0 |
0.02 |
Acetic acid |
64-19-7 |
0.1 /L |
Acetic anhydride |
108-24-7 |
0.02 |
Acetone |
67-64-1 |
0.4 |
Acetonitrile |
75-05-8 |
0.1 |
Acetophenone |
98-86-2 |
0.01 |
Acrolein |
107-02-8 |
0.001 |
Acrylonitrile |
107-13-1 |
0.002 /C |
Acrylic acid |
79-10-7 |
0.02 /L |
Allyl alcohol |
107-18-6 |
0.01 |
Allyl ethyl ether |
557-31-3 |
0.001 |
Aluminium compounds in inorganic dust (measured as Al) |
- |
0.01 |
2-Aminoethanol |
141-43-5 |
0.01 |
Ammonia, anhydrous |
7664-41-7 |
0.3 |
Ammonium chloride |
12125-02-9 |
0.08 |
Aniline |
62-53-3 |
0.08 |
Anthracene |
120-12-7 |
|
Antimony compounds in inorganic dust (measured as Sb) |
- |
0.001 |
Antu = 1-(1-naphtyl)-2-thiourea |
86-88-4 |
0.0001 |
Aromatic hydrocarbons (C9) |
- |
0.03 /L |
Arsenic, inorganic compounds (measured as As) |
- |
0.00001 |
Arsine |
7784-42-1 |
0.00001 |
Asbestos |
1332-21-4 |
400 /F |
Aziridine |
151-56-4 |
0.0001 |
Benzene |
71-43-2 |
0.005 /C |
Benzoic acid |
65-85-0 |
0.02 |
Benzyl alcohol |
100-51-6 |
0.1 |
Beryllium compounds in inorganic dust (measured as Be) |
- |
0.00001 |
BHC or HCH = 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane |
608-73-1 |
0.001 |
Bis(2-chlorethyl) ether |
111-44-4 |
0.0001 |
m-Bis(2,3-epoxypropoxy)benzene |
101-90-6 |
0.001 |
Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate = DEHP |
117-81-7 |
0.005 |
Bis(tributyltin)oxide |
56-35-9 |
0.0005 |
Bromoethane |
74-96-4 |
0.1 |
Bromomethane |
74-83-9 |
0.1 |
1-Butanol |
71-36-3 |
0.2 |
2-Butanol |
78-92-2 |
0.7 |
Butanone |
78-93-3 |
1 |
2-Butoxyethanol = |
111-76-2 |
0.04 /L |
2-(2-Butoxyethoxy)ethanol = |
112-34-5 |
0.02 /L |
2-(2-Butoxyethoxy)ethyl acetate = |
124-17-4 |
0.03 /L |
2-Butoxyethyl acetate= |
112-07-2 |
0.1 /L |
(2-Butoxymethylethoxy)propanol = |
35884-42-5 |
0.4 |
2-Butoxy-1-methylethyl acetate = |
85409-76-3 |
0.1 |
1-Butoxypropan-2-ol = |
5131-66-8 |
0.4 |
n-Butyl acetate |
123-86-4 |
0.1 /L |
Butyl acrylate |
141-32-2 |
0.006 /L |
Butyl glycolate |
7397-62-8 |
1 |
Butyl lactate |
138-22-7 |
0.1 |
Butyraldehyde |
123-72-8 |
0.001 |
Butyric acid |
107-92-6 |
0.0001 /L |
g -Butyrolactone |
96-48-0 |
0.3 |
Cadmium compounds. (measured as Cd) |
- |
0.00001 |
e -Caprolactam |
105-60-2 |
0.005 |
Carbon disulphide |
75-15-0 |
0.02 |
Carbon monoxide |
630-08-0 |
1 |
Carbontetrachlorid = T Carbon tetrachloride = tetrachloromethane |
56-23-5 |
0.005 |
Chlorine |
7782-50-5 |
0.01 |
Chlorobenzene |
108-90-7 |
0.1 |
Chloroacetic acid |
79-11-8 |
|
1-Chloro-2,3-epoxypropane = epichlorhydrin |
106-89-8 |
0.002 |
Chloroethane |
75-00-3 |
0.1 |
Chloroethylene = Vinylchloride |
75-01-4 |
0.002 /C |
Chloroform = trichloromethane |
67-66-3 |
0.02 |
Chloromethane |
74-87-3 |
0.04 |
1-Chloro-3-nitrobenzene |
121-73-3 |
0.0005 |
1-Chloro-4-nitrobenzene |
100-00-5 |
0.0005 |
3-Chloropentane-2,4-dione |
1694-29-7 |
0.01 /L |
Chlorophenols (mono-,di-,tri-,tetra-) |
- |
0.0008 /C |
3-Chloropropene |
107-05-1 |
0.002 |
a -Chlorotoluene |
100-44-7 |
0.0008 |
Chromium compounds, other than Cr (VI) in inorganic dust (measured as Cr) |
- |
0.001 |
Chromates (measured as Cr VI) |
- |
0.0001 |
Coal tar destillates Bp > 200 ° C |
|
0.00003 |
Coal tar pitch 10% |
|
0.000004 |
Coal tar pitch 3% |
|
0.00001 |
Cobalt compounds in inorganic dust (measured as Co) |
- |
0.0005 |
Colecalciferol = Vitamin D3 |
67-97-0 |
0.002 |
Copper compounds in inorganic dust (measured as Cu) |
- |
0.01 |
Cresol |
1319-77-3 |
0.003 /L |
Cumene = isopropylbenzene |
98-82-8 |
0.03 /L |
Cyanides in inorganic dust (measured as CN) |
- |
0.06 |
Cyclohexane |
110-82-7 |
1 |
Cyclohexanol |
108-93-0 |
0.05 /L |
Cyclohexanone |
108-94-1 |
0.1 |
Cyclohexyldimethylamine |
98-94-2 |
0.01 |
Cyclopentanone |
120-92-3 |
0.1 |
Distillates (petroleum) hydrodesulfurized middle |
64742-89-9 |
0.01 |
Dialkyl sulphides |
- |
0.001 /L |
1,4-Diazabicyclooctane |
280-57-9 |
0.1 |
1,2-Dibromoethane |
106-93-4 |
0.0001 /C |
Dibutylamine |
111-92-2 |
0.01 |
2,6-Di-tert-butyl-p-cresol = butylhydroxytoluene |
128-37-0 |
0.01 |
1,2-Dichlorobenzene |
95-50-1 |
0.1 |
Dichlorodifluoromethane |
75-71-8 |
1 |
1,2-Dichloroethane |
107-06-2 |
0.004 /C |
1,1-Dichloroethylene |
75-35-4 |
0.01 |
1,2-Dichloroethylene |
540-59-0 |
0.4 |
1,1-Dichloro-1-flouroethane = HCFC-141b |
1717-00-6 |
1 |
Dichloromethane |
75-09-2 |
0.02 /C |
1,2-Dichloropropane |
78-87-5 |
0.02 /C |
Dieldrin |
60-57-1 |
0.0001 |
Diesel oil |
- |
0.1 /L |
Diethylamine |
109-89-7 |
0.02 |
Diethyl ether |
60-29-7 |
1 |
Diethyl sulphate |
64-67-5 |
0.000004 /C |
Dimethoxymethane |
109-87-5 |
1 |
N,N-Dimethylacetamide |
127-19-5 |
0.1 |
Dimethylamine |
124-40-3 |
0.04 |
2-Dimethylaminoethanol |
108-01-0 |
0.005 /L |
[4-[[4-(Dimethylamino)phenyl]
[4-[ethyl(3-sulfonatobenzyl)amino] |
1694-09-3 |
0.001 |
Dimethyl ether |
115-10-6 |
1 |
N,N-Dimethylformamide |
68-12-2 |
0.1 |
2,6-Dimethylheptan-4-one |
108-83-8 |
0.06 /L |
Dimethylnitrosoamine |
62-75-9 |
0.0001 |
Dimethyl sulphate |
77-78-1 |
0.1x10-6 |
Dimethyl sulphide |
75-18-3 |
0.001 /L |
Dinitrogenoxide |
10024-97-2 |
1 |
1,4-Dioxane |
123-91-1 |
0.01-0.1 |
Diphenyl ether |
101-84-8 |
0.0004 /L |
Dust from grinding stainless steel |
|
0.001 |
Dust from grinding (apart from the above mentioned) |
|
0.01 |
Dust, inert below 10 micrometer |
- |
0.08 |
D-vitamin |
|
|
Ergocalciferol = vitamin D2 |
50-14-6 |
0.002 |
Cholecalciferol = vitamin D3 |
67-97-0 |
|
Endotoxines |
- |
1x10-6 |
Enzymes, proteolytic |
- |
3x10-6 |
1,2-Epoxy-2-(epoxyethyl)cyclohexane |
4223-10-3 |
0.001 |
(Epoxyethyl)benzene |
96-09-3 |
0.001 |
Epoxy, dust from powder painting procedures |
- |
0.01 |
Ergocalciferol |
50-14-6 |
0.002 |
Ethan-1,2-diol = Ethylene glycol |
107-21-1 |
0.3 |
Ethanol |
64-17-5 |
5 |
2-Ethoxyethanol = |
110-80-5 |
0.2 |
2-(2-Ethoxyethoxy)ethanol = |
111-90-0 |
1 |
2-Ethoxyethyl acetate = |
111-15-9 |
0.1 |
2-Ethoxy-1-methylethyl acetate = |
54839-24-6 |
0.01 /L |
1-Ethoxypropan-2-ol = |
1569-02-4 |
1 |
Ethyl-2-cyanoacrylate |
7085-85-0 |
0.01 |
Ethyl acetate |
141-78-6 |
1 /L |
Ethylbenzene |
100-41-4 |
0.5 |
Ethyldimethylamine |
598-56-1 |
0.002 |
Ethylene oxide |
75-21-8 |
0.005 |
Ethyl formate |
109-94-4 |
1 /L |
Ethyl nitrite |
109-95-5 |
0.1 |
Flour, dust |
- |
0.02 |
Fluorides, inorganic compounds (measured as F) |
|
0.001 |
Fluorine |
7782-41-4 |
0.002 |
Formaldehyde |
50-00-0 |
0.01 |
Formic acid |
64-18-6 |
0.003 |
2-Furaldehyde |
98-01-1 |
0.002 |
Gasoline |
- |
0.1 |
Glutaral |
111-30-8 |
0.001 |
1-Heptanol |
111-70-6 |
1 |
2-Heptanone |
110-43-0 |
0.1 /L |
Hexamethylene diisocyanate |
822-06-0 |
0.0002 |
Hexamethylphosphoric triamide |
680-31-9 |
0.001 |
Hexane = n-hexane |
110-54-3 |
0.4 |
Hexanones |
- |
0.3 |
Hydrazine (and its salts ) |
302-01-2 |
0.0002 |
Hydrogen chloride |
7647-01-0 |
0.05 |
Hydrogen cyanide |
74-90-8 |
0.06 |
Hydrogen fluoride |
7664-39-3 |
0.002 |
Hydrogen sulphide |
7783-06-4 |
0.001 |
2-Hydroxyethyl-acetate = |
542-59-6 |
0.1 /L |
4-Hydroxy-4-methylpentan-2-one = |
123-42-2 |
0.1 |
Imidazolidine-2-thione |
96-45-7 |
0.001 |
2,2’-Iminodiethanol = |
111-42-2 |
0.01 |
3-iodo-2-propynyl butylcarbamate |
55406-53-6 |
0.1 |
Isobutyl acetate |
110-19-0 |
0.3 /L |
Isocyanates, organic compounds |
- |
0.0002 |
Isopentyl acetate |
123-92-2 |
0.02 /L |
Isopropyl acetate |
108-21-4 |
0.7 /L |
Isopropylamine |
75-31-0 |
0.3 |
4-Isopropylbenzyl-alcohol |
536-60-7 |
0.01 /L |
Isothiocyanates |
- |
0.001 |
Lactic acid bacteria |
- |
0.02 |
Lead compounds in inorganic dust (measured as Pb) |
- |
0.0004 |
Lithium compounds in inorganic dust (measured as Li) |
|
0.01 |
Magnesium compounds in inorganic dust, See "Dust, inert below 10 micrometer" |
|
|
Maleic anhydride |
108-31-6 |
0.001 |
Manganese compounds in inorganic dust (measured as Mn) |
- |
0.001 |
Mercury-compound in inorganic dust (measured as Hg) |
- |
0.0001 |
Mesitylene = 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene |
108-67-8 |
0.03 |
Methanol |
67-56-1 |
0.3 |
3-Methylbutanone |
563-80-4 |
0.5 /L |
3-Methoxybutyl acetate |
4435-53-4 |
0.2 |
2-Methoxyethanol = ethyleneglycol-monomethylether |
109-86-4 |
0.02 |
(2-(2-Methoxymethylethoxy) |
25498-49-1 |
1 |
(2-Methoxymethylethoxy)propanol = |
34590-94-8 |
1 |
2-Methoxy-1-methylethyl acetate = |
108-65-6 |
0.01 /L |
1-Methoxypropan-2-ol = |
107-98-2 |
0.03 /L |
Methyl acetate |
79-20-9 |
0.7 /L |
Methyl acrylate |
96-33-3 |
0.002 /L |
Methylamine |
74-89-5 |
0.07 |
1-Methylbutyl acetate |
626-38-0 |
0.001 /L |
Methyl tert-butyl ether = MTBE |
1634-04-4 |
0.03 /L |
Methyl carbamate |
598-55-0 |
0.2 |
Methylcyclohexane |
108-87-2 |
1 |
4,4’-Methylenebis[2-chloroaniline] (and its salts) |
101-14-4 |
0.001 |
Methyl formate |
107-31-3 |
0.2 |
5-Methylhexan-2-one = methylisoamylketone |
110-12-3 |
0.005 /L |
Methyl methacrylate |
80-62-6 |
0.03 |
4 -Methylmorpholine |
109-02-4 |
0.1 |
Methyloxirane = propylenoxid |
75-56-9 |
0.003 |
2-Methylpentan-1-ol |
105-30-6 |
0.05 /L |
4-Methylpentan-2-one = |
108-10-1 |
0.2 |
2-Methylpropan-1-ol |
78-83-1 |
0.4 |
2-Methylpropan-2-ol = |
75-65-0 |
1 |
2-Methylpropen |
115-11-7 |
0.06 /L |
1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone |
872-50-4 |
1 |
Mineral oil, aerosols |
- |
0.003 |
Mineral wool |
|
1300 /F |
Molybdenum compounds in inorganic dust (measured as Mo) |
- |
0.005 |
Naphta, hydrotreated heavy |
64742-48-9 |
1,0 /L |
Naphthalene |
91-20-3 |
0.04 /L |
Nicotine |
54-11-5 |
0.01 |
Nickel (measured as Ni) |
7440-02-0 |
0.0001 |
Nickel monoxide (measured as Ni) |
1313-99-1 |
0.0001 |
Nitric acid |
7697-37-2 |
0.01 |
2,2’,2’’-Nitrilotriethanol |
102-71-6 |
0.01 |
Nitrobenzene |
98-95-3 |
0.0002 /C |
2-Nitronaphthalene |
581-89-5 |
0.001 |
Nitrophenols |
- |
0.005 |
Nonylphenol |
84852-15-3 |
0,02 |
Nonylphenol ethoxylates |
|
0.05 |
Organic solvents, mixtures (1) |
|
0,15 /L |
Orthophosphoric acid = phosphoric acid |
7664-38-2 |
0.005 |
7-Oxa-3-oxiranylbicyclo(4.1.0)heptane = |
106-87-6 |
0.001 /C |
Ozone |
10028-15-6 |
0.01 |
Parafiner C2 og Parafins, C2 – C8 (except n-hexane) |
- |
1 |
Pentachlorophenol |
87-86-5 |
0.00004 /C |
Pentane-2,4-dione |
123-54-6 |
0.01 /L |
Pentane-2-one |
107-87-9 |
1 |
Pentane-3-one |
96-22-0 |
0.6 /L |
Pentyl acetate |
628-63-7 |
0.02 /L |
Phenol |
108-95-2 |
0.02 |
2-Phenoxyethanol |
122-99-6 |
0.1 |
m-Phenylenediamine |
108-45-2 |
0.001 |
1-Phenyl ethanol |
98-85-1 |
0.3 |
2-Phenylpropene |
98-83-9 |
0.06 |
Phosgene |
75-44-5 |
0.001 |
Phosphine |
7803-51-2 |
0.001 |
Phthalates except DEHP |
- |
0.01 |
Phthalic anhydride |
85-44-9 |
0.001 |
Pin-2(3)-ene = alpha-Pinene |
80-56-8 |
0.05 |
Piperidine |
110-89-4 |
0.01 |
Polyamides, dust |
- |
0.01 |
Polyaromatic hydrocarbons, PAHs |
- |
(2) /C |
Polyurethane foam, dust |
9009-54-5 |
0.04 |
Potassium hydroxide |
1310-58-3 |
0.005 |
Propane-1,2-diol = Propyleneglycol |
57-55-6 |
1 |
Propane-1,2-diol diacetate = |
623-84-7 |
1 |
Propanols |
62309-51-7 |
1 |
1-propanol |
71-23-8 |
|
2-propanol |
67-63-0 |
|
Propionic acid |
79-09-4 |
0.05 |
Propyl acetate |
109-60-4 |
0.1 |
2-(Propyloxy)ethanol = |
2807-30-9 |
0.3 |
Pyridine |
110-86-1 |
0.07 |
2-Pyrrolidone |
616-45-5 |
0.003 |
Quartz |
14808-60-7 |
0.005 |
Siliciumdioxide (amorphous) |
61790-53-2 |
0.005 |
Silver compounds in inorganic dust (measured as Ag) |
- |
0.0002 |
Sodium hydroxide in inorganic dust |
1310-73-2 |
0.005 |
Solventnaphtha, light aromatic |
64742-95-6 |
0.03 /L |
Solventnaphta (petroleum), heavy aromatic |
64742-94-5 |
0.05 /L |
Stannane, tributyl-, mono(naphthenoyloxy) derivatives |
85409-17-2 |
0.0005 |
Strontium chromate |
7789-06-2 |
0.0001 |
Styrene |
100-42-5 |
0.2 |
Subtilisin |
9014-01-1 |
3 x 10-6 |
Sulphuric acid |
7664-93-9 |
0.01 |
Sulphur trioxide |
7446-11-9 |
0.01 |
Soaps (Na-, K- and Ca- salts of fatty acids) |
- |
0.01 |
Tetrachloroethylene |
127-18-4 |
0.01 /C |
Tetraethyllead (measured as Pb) |
78-00-2 |
0.0003 |
Tetraethyl-orthosilicate = |
78-10-4 |
1 |
Tetrahydrofuran |
109-99-9 |
0.2 |
3a,4,7,7a-Tetrahydro-4,7-methanoindene =dicyclopentadiene |
77-73-6 |
0.05 |
Tetramethyllead (measured as Pb) |
75-74-1 |
0.0003 |
Thallium compounds in inorganic dust (measured as Tl) |
- |
0.0003 |
Thiols |
- |
0.0002 |
Thioalcohols |
- |
0.0002 |
Tin compounds in inorganic dust (measured as Sn) |
- |
0.02 |
Titanium dioxide |
13463-67-7 |
0.02 |
Toluene |
108-88-3 |
0.4 |
1,1,1-Trichlorethane |
71-55-6 |
0.5 |
Trichloroethylene |
79-01-6 |
0.04 /C |
Triethylamine |
121-44-8 |
0.04 |
Trimethoxyvinylsilane |
2768-02-7 |
0.001 |
Trimethylamine |
75-50-3 |
0.0002 |
3,5,5-Trimethylcyclohex-2-enone |
78-59-1 |
0.03 |
Tripropylenglycolmonoethylether |
20178-34-1 |
1 |
Trypsin |
9002-07-7 |
3x10-6 |
Vanadium compounds in inorganic dust (measured as V) |
- |
0.0003 |
Vegetable oils, aerosols |
- |
0.01 |
Vinyl acetate |
108-05-4 |
0.2 |
Waxes, primarely straight chained hydrocarbons > C20 |
- |
0.01 |
Welding fumes |
|
|
Fumes from welding in unalloyed steel: |
|
0.004 |
Fumes from welding in alloyedt steel, |
|
|
Sum of content of nickel and chromium (VI): |
|
0.0001 |
White spirit: |
|
|
Naphta, hydrosulfurized heavy |
64742-82-1 |
0.2 /L |
Stoddard-solvent |
8052-41-3 |
0.2 /L |
Solvent naphta, medium aliphatic |
64742-88-7 |
0.2 /L |
Wollastonite |
13983-17-0 |
1300 /F |
Wood, dust |
- |
0.025 |
Xylene, mixed isomers, pure |
1330-20-7 |
0.1 |
Xylenols |
- |
0.002 /L |
Zinc compounds in inorganic dust, except zinc chloride (measured as Zn) |
- |
0.06 |
Zinc chloride |
7646-85-7 |
0.005 |
/C: this notation is attached to specific compounds for which the cumulated exposure is considered to reflect the risk for adverse effect e.g. carcinogenic/ mutagenic compounds. The basis for the C-value is the health based air quality criteria which for such substances reflects an average exposure level (continuous exposure). The C-value, however, is set 40 times higher than the air quality criteria, because compliance with a C-value (i.e. the actual emis-sion concentration values should be below the C-value in 99% of the time) according to emission distribution models, represents an average exposure level in the surroundings of the emission source of about 1/40 of the C-value.
/F: fibers per m3..
/L: the C-value is based on protection against odour. For substances with this notation, odour is considered to occur at considerable lower levels (< 1/10) compared to a toxicological based value.
(1) Mixture of organic solvents used as thinners and solvents in paints and lacquers. The mixture must at least contain 3 or more organic solvents where none of the solvents may represent a content of more than 80 w/w % or less than 2 w/w %. None of the single solvents may be considered especially critical (e.g. be considered as a carcinogen), or appointed with a specific C-value of 0.01 mg/m3 or lower (the latter rule pertain to health based C-values and does not include substances having an L-notation attached to the C-value).
(2) C-value for PAHs: 2,5 ng benzo(a)pyrene equivalents/ m3
where Benzo(a)pyrene equivalents = S koncPAH x relative potency factor PAH .
For the calculation of the benzo(a)pyrene equivalent, the following PAHs and their relative potency factors are used:
PAH |
Relative potency factor |
Acenaphthene |
0,001 |
Acenapthylene |
0,001 |
Anthracene |
0,0005 |
Benzo[ a] anthracene |
0,005 |
Benzo[ b] fluoranthene |
0,1 |
Benzo[ k] fluoranthene |
0,05 |
Benzo[ ghi] perylene |
0,02 |
Benzo[ a] pyrene |
1 |
Chrysene |
0,03 |
Dibenzo[ a,h] anthracene |
1,1 |
Fluoranthene |
0,05 |
Fluorene |
0,0005 |
Indeno[ 1,2,3-c] )pyrene |
0,1 |
Phenanthrene |
0,0005 |
Pyrene |
0,001 |
Table of provisional C-values. Notified for future incorporation in the main table.
Substance: |
CAS-No.: |
C-value mg/m3 |
Acrylamide |
79-06-1 |
0.0002 /C |
3-aminomethyl-3,5,5-trimethylcyclohexylamine = isophoronediamine |
2855-13-2 |
0.01 |
Barium, inorganic compounds |
|
0.005 |
Bis(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)ether |
3033-62-3 |
0.01 |
Boron |
|
0.003 |
1-bromopropane |
106-94-5 |
0.1 |
Butane-1,4-diol |
110-63-4 |
0.1 |
Decahydronaphthalene = decalin |
91-17-8 |
0.01 |
Dichlorodiflouromethane |
75-71-8 |
1 |
Diethyl carbonate |
105-58-8 |
0.1 |
N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N,N’,N’- trimethylpropane-1,3-diamine |
3855-32-1 |
0.01 |
Dipropylenglycol = oxydipropanol |
|
1 |
Dipropylenglycoldimethylether = oxydipropanol dimethylether |
111109-77-4 |
1 |
Epoxy compounds, monomers |
|
0.001 |
2,3-epoxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride = GMAC |
3033-77-0 |
<0.001 |
Ethyl bromide |
74-94-4 |
0.1 |
Formamide |
75-12-7 |
0.01 |
Methyl iodide |
74-88-4 |
0.001 |
2-methylstyrene = 2-vinyltoluene |
611-15-4 |
0.1 |
Naphta (petroleum), hydrodesulfurized light, dearomatized (mainly heptanes) |
92045-53-9 |
1 |
Solvent Naphta (petroleum), light, aliphatic. |
64742-89-8 |
1 |
Nitroethane |
79-24-3 |
0.01 |
2-phenylpropan-2-ol = 1-hydroxycumen |
617-94-7 |
0.01 |
Polyester, dust from spray-painting |
|
0.01 |
Propylbenzene |
103-65-1 |
0.03 |
Silicon dioxide |
63231-67-4 |
0.005 |
Talc, inorganic dust |
14807-96-6 |
0.001 |
1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane = HFC 134a |
811-97-2 |
1 |
Trichlorofluoromethane = CFC 11 |
75-69-4 |
1 |
2,4,6-tinitrotoluene |
118-96-7 |
0.001 |
Reference: