|
| Front page | | Contents | | Previous | | Next |
Evaluation of Alternatives for Compounds under Risk Assessment in the EU, Bisphenol A
3 Search in the Danish Product Register
The Danish Product Register (DPR) is registering hazardous products for professional use according to the Danish legislation. This means that any person starting professional
manufacture or importation of products, which may constitute a danger to or in any other way adversely affect safety or health, prior to commencement of these activities must submit
notification to the DPR. The notification of a product includes among other things:
- Information on the composition of the product.
- Information on the use (product type and trade category)
- Information on volume manufactured/imported.
A manufacture or importer who has submitted a notification must inform the DPR about any changes in the information submitted. However, experience shows that some manufacturers
and importers fail to inform the DPR about such changes.
In the following sections, bisphenol A substances (BPA-substances) are defined by derivatives of bisphenol A (BPA) or polymers containing BPA as monomer.
The purpose of the search in the DPR was:
- To provide an overview of product types containing BPA-substances.
- To provide an overview of the trades in which the products containing BPA-substances are used.
- To provide information on the function of BPA-substances in products.
- To provide information on alternatives to BPA-substances related to the focus areas of this project.
The overview of product types containing BPA-substances and trades using the products was mainly used to verify the chosen focus areas or to state new areas of attention in respect to
this project. The information describing the function of BPA-substances in the products was used to identify alternatives to certain applications related to the selected focus areas.
The strategy of the DPR search is illustrated in Figure 3.1. The registered BPA-based substances were identified and subsequently grouped in three groups. The function of the
substances in the products was mapped out for each group. Furthermore, product types containing and industrial sector using BPA-substances were mapped out for each of the three
groups. Potential alternatives to BPA-substances were identified in selected product types and trade categories relevant to the focus areas of this project.
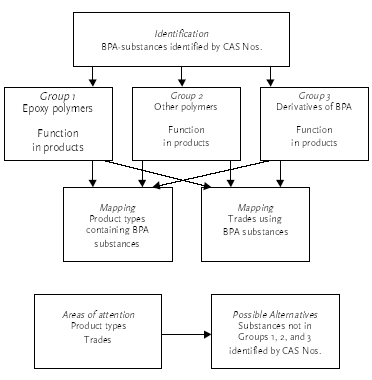
Figure 3.1 The strategy of the D P R search
The results of the DPR search related to the strategy are described in the following sections.
3.1 Identification of bisphenol A substances
The identification of BPA-substances registered in the DPR was based on several searches with different inputs. The CAS No. 80-05-7 for BPA and synonyms/names of BPA were
used as search inputs. A list with BPA-substances was generated. The list is divided into three groups:
Group 1: Epoxy polymers
Group 2: Other polymers with bisphenol A as monomer
Group 3: Derivatives of bisphenol A (not polymers)
Group 1 is a list of 347 substances. In this search, epoxy polymers are characterized as polymers containing monomers such as bisphenol A and epichlorhydrin or bisphenol A
diglycidylether (BADGE) as a minimum. In addition, the polymers may contain other monomers. It has not been possible to determine the molecular weight or the degree of free
epoxy-groups of the polymers from the search. Examples of polymers in group 1 are stated below:
- Bisphenol A/epichlorhydrin/methacrylic acid polymer
- Bisphenol A/epichlorhydrin/formaldehyde polymer
- Bisglycidyl ether bisphenol A resin
- Bisphenol A/epichlorhydrin/polyethylene glycol polymer
- Bisphenol A/epichlorhydrin/1,6-hexandiamine polymer
Group 2 is a list of 69 substances. The polymers of this group contain BPA as monomer without having epoxy group functionalities. Examples are:
- Bisphenol A, polymer with formaldehyde
- Bisphenol A/ethylene oxide polymer
- Bisphenol A/formaldehyde/pentaerythritol/rosin, maleated polymer
Group 3 is a list of 57 substances. Examples of derivatives of bisphenol A (not polymers) are stated below:
- Phenol, 4,4'-(1-methylethylidene)bis(2,6-dichloro)-
- Bisphenol A bis (2-hydroxypropyl)ether
- Phenol, 4,4'-(2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(trifluoromethyl)ethylidene)bis-
- Bisphenol A bis(2-hydroxyethylether)-dimethacrylat
The function registered in the DPR of BPA-substances in products is stated below according to the three groups:
- Group 1: mainly as binder
- Group 2: mainly as binder
- Group 3: mainly as binder and monomer
The function of the substances/polymers is mainly registered as binders in the DPR. The registered function "monomer" in group 3 is probably related to the acrylates represented by this
group. Acrylates are monomers used for the manufacture of thermosetting acrylic surface-coating resins.
The registered function of substances in products is based on a predetermined list of functions and on the knowledge of the persons working in the DPR. The manufacturer or the
supplier of a product is not required to provide this kind of information.
The substances mentioned in the three lists were mapped according to product types and trades in which the substances are used.
3.2 Mapping of bisphenol A substances
The results of mapping the BPA-substances in groups 1, 2 and 3 are stated below in Tables 3.1 and 3.2.
Table 3.1 lists the various product types containing BPA-substances from the three groups. Volume (T) is the total quantity (tonnes/year) of all BPA-substances used in products in a
certain product type. The number columns give the total of products containing BPA-substances within each product type.
Table 3.1 gives a selection of product types. The selection criterion was:
- Product types relevant to the focus areas of this project
- Product types with most products containing BPA-substances
In Table 3.1 the product types relevant to the focus area of this project are typed in italics.
Table 3.1 shows, for instance, that there are 72 "printing inks products" containing BPA-substances from Group 1 and that the total quantity of substances from all groups is 28
tonnes/year.
Table 3.1 shows a selection of product types containing BPA-based substances. For each of the three groups, the table states the number of products containing BPA-substances within
each product type (Number). Furthermore, the table gives the total amount (in tons) of BPA-substances from all three groups forming part of products within each product type
(Volume). Product types relevant to the focus areas of this project are typed in italics.
The product types
- Paint and lacquers/varnishes
- Surface treatment of metal (not paints etc.)
are related to the epoxy-coating of food and beverage containers, which is one of the focus areas of this project.
The product types
- Printing inks
- Writing materials
are related to toners, which are another focus area of this project.
The product types
- Surface treatment of paper and other non-metallic materials
- Impregnation agents
are related to thermographic printing, which is also a focus area of this project.
Table 3.1 Mapping of product types containing bisphenol A substances.
| PRODUCT TYPE |
All three groups |
Group 1 |
Group 2 |
Group 3 |
| |
Volume (T) |
Number |
Number |
Number |
| Paint and lacquers/ varnishes |
7064 |
1146 |
52 |
6 |
| Hardeners |
2121 |
457 |
19 |
|
| Binding agents (see also Adhesives) |
7635 |
353 |
6 |
9 |
| Adhesives (see also Binding agents) |
191 |
232 |
29 |
49 |
| Filling materials (see also Fillers; Insulation materials) |
162 |
212 |
13 |
25 |
| Flooring materials/Casting materials |
458 |
180 |
4 |
4 |
| Printing inks |
28 |
72 |
3 |
|
| Construction materials |
326 |
49 |
|
4 |
| Surface treatment of metal (not paints etc.) |
77 |
43 |
|
|
| Surface treatment of paper and other non-metallic materials |
56 |
38 |
|
|
| Anti-corrosion materials |
59 |
29 |
|
|
| Inhibitors |
38 |
22 |
3 |
|
| Impregnation agents |
9 |
11 |
3 |
|
| Writing materials |
1 |
|
5 |
|
Table 3.1 shows that Group 1, epoxy polymers, is the largest group both with regard to members and to quantity in the investigated product types. This is not surprising considering the
number of substances in Group 1. The table shows that epoxy polymers are widely used in many products.
Table 3.2 lists the various trades using the BPA-substances in the three groups. The volume (T) is the total quantity (tonnes/year) of all BPA-substances used in products within a certain
trade category. For each trade category the number columns specify the total products containing BPA-substances.
Table 3.2 gives a selection of trades. The selection criterion was:
- Trades relevant to the focus areas of this project
- Trades using most products containing BPA-substances
Table 3.2. shows, for instance, that there are 801 products containing Group 1 BPA-substances, which are used in the trade category "Manufacture of fabricated metal products,
except machinery and equipment", and that the total quantity of BPA-substances from all three groups is 6648 tonnes/year.
Table 3.2 gives a selection of trades using products containing BPA-based substances. For each of the three groups, the table states the number of products containing BPA-substances
within a certain trade (Number). Furthermore, the table gives the total amount (in tons) of BPA-substances from all three groups used by a certain trade (Volume). Trade categories
relevant to the focus areas of this project are typed in italics.
In Table 3.2 the product types relevant to the focus area of this project are typed in italics.
The trade categories
- Manufacture of fabricated metal products, except machinery and equipment
- Manufacture of chemicals and chemical products (manufactures of paints, lacquers/varnishes, printing inks, etc.)
are related to epoxy-coating of food and beverage containers as well as to toners, which are the focus areas of this project.
The trade category
- Manufacture of pulp, paper and paper products
is related to thermographic printing, which is another focus area of this project.
Table 3.2 Mapping of trade categories using products containing bisphenol A substances.
| TRADE CATEGORY |
All three groups |
Group 1 |
Group 2 |
Group 3 |
| |
Volume (T) |
Number |
Number |
Number |
| Construction |
3197 |
961 |
46 |
21 |
| Manufacture of fabricated metal products, except machinery
and equipment |
6648 |
801 |
36 |
29 |
| Manufacture of other transport equipment (not motor vehicles/cars) |
7073 |
547 |
18 |
5 |
| Manufacture of furniture; manufacturing (not otherwise specified) |
552 |
284 |
13 |
3 |
| Sale, maintenance and repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles;
retail sale of automotive fuel |
164 |
239 |
37 |
24 |
| Manufacture of wood and products of wood and cork, except furniture;
manufacture of articles of straw and plaiting materials |
437 |
269 |
10 |
|
| Manufacture of rubber and plastic products |
221 |
181 |
14 |
11 |
| Manufacture of chemicals and chemical products |
1840 |
159 |
7 |
3 |
| Manufacture of machinery and equipment |
991 |
116 |
14 |
30 |
| Manufacture of electrical machinery and apparatus |
5396 |
139 |
6 |
3 |
| Manufacture of motor vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers |
2442 |
89 |
9 |
4 |
| Publishing, printing and reproduction of recorded media |
267 |
90 |
4 |
|
| Extraction of crude petroleum and natural gas |
287 |
70 |
|
|
| Manufacture of electronic equipment |
23 |
54 |
6 |
9 |
| Manufacture of basic metals |
121 |
64 |
|
|
| Manufacture of radio, television and communication equipment |
90 |
56 |
|
|
| Manufacture of medical, precision and optical instruments, watches
and clocks |
74 |
29 |
6 |
13 |
| Manufacture of pulp, paper and paper products |
12 |
18 |
|
|
Table 3.2 also shows that Group 1 is the largest group both with regard to numbers and to quantity in the investigated trade categories.
There is not direct connection between Tables 3.1 and 3.2 as regards the figures and amounts stated. The individual product may be registered under more product types and especially
under more trade categories and subcategories. Tables 3.1 and 3.2 must thus be considered as independent tables and amounts and numbers in the two tables must be considered as
relative figures.
The two tables show that the BPA-substances are widely used in most product types and trade categories investigated and that the DPR thus covers the focus areas of this project.
However, some of the product types and trade categories cover more than just the focus areas. For instance, products, such as "paint and lacquers/varnishes" are not only related to the
application "epoxy coated food and beverage containers". Products as "paint and lacquers/varnishes" have other applications, such as floor varnishing. The product type "toner" is not
listed as containing BPA-substances. This may be due to the fact that toners do not have to be registered in the DPR or that they do not contain BPA-substances at all.
3.3 Information on alternatives
The search for information on substances/alternatives to BPA-substances from the DPR was divided into the following areas:
- Alternatives relating to coated food and beverage containers:
- Search on substances in products used by manufacturers of other fabricated metal products for instance manufacturing of light metal packaging (Table 3.3).
- Search on substances in products with product type "Surface treatment of metal (not paints etc.)" (Table 3.4).
- Search on substances in products of the product type "Paint, lacquers/varnishes" (Table 3.5).
- Alternatives relating to toners:
- Search on substances in products of the product type "Toners and Writing materials" (Table 3.6).
- Searching on substances in products of the product type. "Printing inks" (Table 3.7).
The generated lists of non-BPA-based substances in the above mentioned product types are only indications of possible alternatives to BPA-substances for the specified applications.
The proposals for alternative substances are based on polymers which do not contain the monomer bisphenol A. Tables 3.3 – 3.7 state the alternatives found with respect to the above
areas 1-5.
Table 3.3 Substances/polymers in products used by manufactures of other fabricated metal products, e.g. manufacturing of light metal packaging
| Substance group |
CAS No. |
Name |
| Polyalkenes |
9002-88-4 |
Polyethylene |
| Polyethers |
9016-45-9 |
Polyethylene glycol nonylphenyl ether (unspec.) |
| 9038-95-3 |
Polyethylene-polypropylene glycol, monobutyl ether |
| 25322-68-3 |
Polyethylene glycol |
| 109909-39-9 |
Poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl), alpha-sulfo-omega-(2,4,6-tris(1-methylpropyl)phenoxy)-,
sodium salt |
| Vinyl polymers |
63148-65-2 |
Polyvinyl butyral |
| Formaldehyde polymers |
28064-14-4 |
Phenol, polymer with formaldehyde, oxiranylmethyl ether |
| 9003-35-4 |
Phenol-formaldehyde resin |
| 68002-20-0 |
1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-triamine, polymer with formaldehyde, methylated |
| Silicones |
63148-62-9 |
Polydimethylsiloxane |
Alkydes
(polyester resins) |
64754-99-0 |
Fatty acids, C18-unsatd, dimers, compds. with polyethylenepolyamine-tall-oil
fatty acid reaction products |
| 999981-37-2 |
Diethylenetriamine/maleic acid anhydride/polyethylene glycol/tall oil fatty
acid polymer |
Table 3.4 Substances/polymers in products of the product type "Surface treatment of metal (not paints etc.)"
| Substance group |
CAS No. |
Name |
| Polyalkenes |
9002-88-4 |
Polyethylene |
| Polyethers |
9003-11-6 |
Polyoxyethylene - polyoxypropylene copolymer |
| 9004-78-8 |
Polyethylene glycol phenyl ether |
| 9016-45-9 |
Polyethylene glycol nonyl phenyl ether |
| 9036-19-5 |
Glycols, polyethylene, mono((1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)phenyl) ether |
| 9038-95-3 |
Polyethylene-polypropylene glycol, monobutyl ether |
| 25322-68-3 |
Polyethylene glycol |
| 69011-36-5 |
Poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl), alpha-tridecyl-omega-hydroxy-, branched |
| Vinyl polymers |
9002-89-5 |
Polyvinyl alcohol |
| 9003-44-5 |
Propane, 1-(ethenyloxy)-2-methyl-, homopolymer |
| 63148-65-2 |
Polyvinyl butyral |
| Formaldehyde polymers |
25085-50-1 |
p-tert-Butylphenol, formaldehyde resin |
| 28064-14-4 |
Phenol, polymer with formaldehyde, glycidyl ether |
| Silicones |
63148-62-9 |
Polydimethylsiloxane |
| 67762-85-0 |
Siloxanes and silicones, di-me, 3-hydroxypropyl me, ethers with polyethylene-polypropylene
glycol mono-me ether |
| 67762-90-7 |
Siloxanes and silicones, di-me, reaction products with silica |
| 162567-81-9 |
Siloxanes and silicones, me hydrogen, reaction products with 1-octene and
polypropylene glycol mono-bu ether |
| Styrene polymers |
9003-55-8 |
Butadiene-styrene resin |
| Polyacrylates |
9003-01-4 |
Acrylic acid homopolymer |
| 26376-86-3 |
Ethyl acrylate - 2-ethylhexyl acrylate copolymer |
Table 3.5 Substances/polymers in products with product type "Paint and lacquers/varnishes"
| Substance group |
CAS No. |
Name |
| Polyalkenes |
9002-88-4 |
Polyethylene |
| 9003-07-0 |
Polypropylene |
| 68131-87-3 |
Alkenes, ethylene-manuf-by-product dicyclopentadiene-conc, polymers with steam-cracked
petroleum distillates |
| Polyethers |
9003-13-8 |
Polypropylene glycol monobutyl ether |
| 9014-85-1 |
Poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl), alpha,alpha'-(1,4-dimethyl-1,4-bis(2-methylpropyl)-2-butyne-1,4-diyl)bis(omega-hydroxy- |
| 9016-45-9 |
Polyethylene glycol nonylphenyl ether |
| 9036-19-5 |
Polyoxyethylene (1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)phenyl ether |
| 25322-68-3 |
Polyethylene glycol |
| 51811-79-1 |
Poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl), alpha-(nonylphenyl)-omega-hydroxy-, phosphate |
| Vinyl polymers |
9002-86-2 |
Polyvinyl chloride |
| 9003-22-9 |
Vinyl chloride – vinyl acetate copolymer |
| 9005-09-8 |
2-Butenedioic acid (2Z)-, polymer with chloroethene and ethenyl acetate |
| 24937-78-8 |
Ethylenevinylacetate copolymer |
| 25086-48-0 |
Vinyl chloride, vinyl acetate and vinyl alcohol copolymer |
| 25213-24-5 |
Vinyl alcohol – vinyl acetate copolymer |
| 63148-65-2 |
Polyvinyl butyral |
| 68648-78-2 |
Polyvinylbutyral, vinyl alcohol, vinyl acetate copolymer |
| Formaldehyde polymers |
9003-08-1 |
Melamine/formaldehyde resin |
| 9003-35-4 |
Phenol-formaldehyde resin |
| 9011-05-6 |
Urea – formaldehyde resin |
| 25085-50-1 |
p-tert-Butylphenol, formaldehyde resin |
| 25155-81-1 |
Formaldehyde, polymer with methylbenzene |
| 28064-14-4 |
Phenol, polymer with formaldehyde, glycidyl ether |
| 68002-19-7 |
Butylated polyoxymethylene urea |
68002-20-0
68002-25-5 |
1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-triamine, polymer with formaldehyde, methylated
1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-triamine, polymer with formaldehyde, butylated |
| 68002-25-5 |
1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-triamine, polymer with formaldehyde, butylated |
| 68459-31-4 |
Fatty acids, C9-11-branched, glycidyl esters, polymers with castor oil, formaldehyde,
6-phenyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine and phthalic anhydride |
| Silicones |
63148-62-9 |
Polydimethylsiloxane |
| 67762-90-7 |
Dimethyl siloxane, reaction product with silica |
Alkydes
(polyester resins) |
67700-92-9 |
Fatty acids, tall-oil, polymers with pentaerytritol and phthalic anhydride |
| 68609-36-9 |
2,5-Furandione, reaction products with polypropylene, chlorinated |
| Styrene polymers |
9003-53-6 |
Polystyrene |
| 9003-55-8 |
Butadiene – styrene copolymer |
| 9011-11-4 |
Ethenylbenzene, copolymer with (1-methylethenyl)benzene |
| Polyacrylates |
9003-01-4 |
Polyacrylic acid |
| 9011-14-7 |
Methyl methacrylate homopolymer |
| 25035-69-2 |
2-Propenoic acid, 2-methyl-, polymer with butyl 2-propenoate and methyl 2-methyl-2-propenoate |
| 25608-33-7 |
Butyl methacrylate, methyl methacrylate polymer |
| 25767-47-9 |
Butyl acrylate, vinylbenzene polymer |
| 25852-37-3 |
Butyl acrylate, methyl methacrylate copolymer |
| 26376-86-3 |
Ethyl acrylate - 2-ethylhexyl acrylate copolymer |
| 26898-31-7 |
Acrylic acid, methyl methacrylate, butyl methacrylate polymer |
| 28262-63-7 |
Butyl methacrylate, methyl methacrylate, methacrylic acid polymer |
| 28961-43-5 |
Poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl), alpha-hydro-omega-((1-oxo-2-propenyl)oxy)-, ether
with 2-ethyl-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol (3:1) |
| 29299-77-2 |
Ethyl acrylate, methyl methacrylate, methacrylic acid, propylenimine polymer |
| 52408-84-1 |
Poly(oxy(methyl-1,2-ethanediyl)), alpha,alpha',alpha''-1,2,3-propanetriyltris(omega-((1-oxo-2-propenyl)oxy)- |
| 96591-17-2 |
Fatty acids, linseed-oil, reaction products with 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol
and formaldehyde, polymers with Bu methacrylate, 2-(diethylamino)ethyl methacrylate,
2-hydroxyethyl acrylate and Me methacrylate |
| 103991-32-8 |
,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, mono(1-methyl-2-((2-methyl-1-oxo-2-propenyl)oxy)ethyl)
ester, polymer with butyl 2-methyl-2-propenoate, butyl 2-propenoate and methyl
2-methyl-2-propenoate |
| Isocyanate polymers |
39527-44-1 |
1,3-Propanediol, 2-ethyl-2-(hydroxymethyl)-, polymer with 1,3-bis(isocyanatomethyl)cyclohexane |
| 128683-23-8 |
Fatty acids, tall-oil, polymers with pentaerythritol, phthalic anhydride and
2,4-TDI |
| Polyamides |
68082-29-1 |
Fatty acids, C18 unsaturated, dimers, polymers with tall oil fatty acids and
triethylenetetramine |
| 68604-06-8 |
Castor oil, hydrogenated, polymer with ethylenediamine, 12-hydroxyoctadecanoic
acid and sebacic acid |
| Others |
25038-74-8 |
Azacyclotridecane-2-one, homopolymer |
| 25667-42-9 |
4,4'-Sulfonyldiphenol polymer, sru |
| 63393-89-5 |
Coumarone – indene resins |
| 64742-16-1 |
Petroleum resins |
| 67746-08-1 |
Linseed oil, polymerized |
| 68002-18-6 |
Urea, polymer with formaldehyde, isobutylated |
Table 3.6 Substances/polymers in products with product type "Toners and Writing materials"
| Substance group |
CAS No. |
Name |
| Polyalkenes |
9002-88-4 |
Polyethylene |
| Polyethers |
9038-95-3 |
Polyethylene-polypropylene glycol, monobutyl ether |
| 25322-68-3 |
Polyethylene glycol |
| Vinyl polymers |
9003-22-9 |
Vinyl chloride - vinyl acetate copolymer |
| 63148-65-2 |
Polyvinyl butyral |
| Formaldehyde polymers |
25054-06-2 |
Formaldehyde, polymer with cyclohexanone |
| Silicones |
63148-62-9 |
Polydimethylsiloxane |
Alkydes
(polyester resins) |
999978-49-3 |
2,2-bis(Hydroxymethyl)butanol/ethylene glycol/3-hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpropionic
acid/phthalic acid anhydride/ sunflower oil fatty acids, conjugated polymer |
| Styrene polymers |
25085-34-1 |
Styrene acrylic acid copolymer |
| 52831-04-6 |
Acrylic acid-alpha-methylstyrene - styrene copolymer |
Table 3.7 Substances/polymers in products with product type. "Printing inks"
| Substance group |
CAS No. |
Name |
| Polyalkenes |
9002-88-4 |
Polyethylene |
| 9003-29-6 |
Polybutene |
| Polyethers |
9014-85-1 |
Poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl), alpha,alpha'-(1,4-dimethyl-1,4-bis(2-methylpropyl)-2-butyne-1,4-diyl)bis(omega-hydroxy- |
| Vinyl polymers |
9002-86-2 |
Polyvinyl chloride |
| 9002-89-5 |
Polyvinyl alcohol |
| 9003-22-9 |
Vinyl chloride - vinyl acetate copolymer |
| 25086-48-0 |
Vinyl chloride, vinyl acetate and vinyl alcohol copolymer |
| Formaldehyde polymers |
9003-08-1 |
Melamine/formaldehyde resin |
| Silicones |
63148-62-9 |
Polydimethylsiloxane |
Alkydes
(polyester resins) |
68333-69-7 |
Rosin, maleated, polymer with pentaerythritol |
| Styrene polymers |
9003-55-8 |
Butadiene - styrene copolymer |
| Polyacrylates |
9010-88-2 |
Ethyl acrylate, copolymer with methyl methacrylate |
| 9011-14-7 |
Methyl methacrylate homopolymer |
| 25608-33-7 |
Butyl methacrylate, methyl methacrylate polymer |
| 26376-86-3 |
Ethyl acrylate - 2-ethylhexyl acrylate copolymer |
| 28262-63-7 |
Butyl methacrylate, methyl methacrylate, methacrylic acid polymer |
3.4 The DPR and search for bisphenol A alternatives
The Danish Product Register (DPR) registers hazardous products for professional use according to Danish legislation. This means that non-hazardous product like paper, bottles and
other articles as well as products for private use are not covered by the DPR.
The mapping showed that BPA-substances are widely used in several product types.
The DPR registered function of BPA-substances in products is not designed for identifying alternative substances. The registration of function is not based on information from the
manufacturer or supplier but is an assessment made by the case officer at the DPR. In addition, the DPR has not registered the function of substances for the last two years. Instead, the
listed tables with possible alternatives are based on polymers relating to the focus areas of this project. Polymers are normally considered to have binding properties in the majority of
products. However, the binding properties depend on molecular weight and functionality groups. The listed tables with alternative substances are only a supplement to the information
from the industry.
It has not been possible to obtain information from the DPR on alternatives to BPA-substances in thermal paper. The function of pure BPA as developing agent in thermal paper has not
been considered in the DPR search.
| Front page | | Contents | | Previous | | Next | | Top |
Version 1.0 March 2004, © Danish Environmental Protection Agency
|