|
| Front page | | Contents | | Previous |
Substitution of Cobalt Driers and Methyl Ethyl Ketoxime
Appendix A
1 Technical evaluation example
The example shown is the outcome of running one product, DIY-3, through the technical evaluation procedure
described in section 7.1 and shown in figure 7.1. All the obtained data during the technical evaluation are shown in
the next sections.
The substitution of the cobalt drier system in DIY-P3 was less difficult than for most of the other air-drying
do-it-yourself products, for which reason the technical evaluation in the many other cases has been even more data
intensive than shown in this example. 6 different alternative driers have been tested in DIY-3 and the obtained
results are shown in the following sections.
1.1 Product description
DIY-3 is a waterborne stain based on tall oil alkyd with an original drier system consisting of Cobalt, barium and
zirconium (a Co/Ba/Zr system). As DIY-P3 is waterborne it contains no methyl ethyl ketoxime. DIY-P3 belongs to
the group of do-it-yourself products.
1.2 Alternative drier systems
19 samples of DIY-P3 with alternative drier systems were investigated. The drier systems are presented in table
A.1.1. Some of the drier systems are more or less identical, due to the system has been tested once or twice in the
initial stage and maybe once in the further testing.
Table A.1.1
Drier systems investigated in do-it-yourself product, DIY-P3. The concentrations are given as metal on solid
Air-drying binder, except For Mn1 and Mn5(w) where the concentrations are given as drier product on solid
air-drying binder.
| |
Drier (% w/w) |
| Sample |
Alternative
Code
|
Alternative |
Ca |
Ba |
Zr |
K |
Drying
accelerator |
| DIY-P3-1 |
Mn1 |
1,14 |
|
0,57 |
0,24 |
|
|
| DIY-P3-8 |
Mn1 |
1,05 |
|
0,55 |
0,25 |
|
|
| DIY-P3-13 |
Mn1 |
1,08 |
|
0,58 |
0,24 |
|
|
| DIY-P3-9 |
Mn4 |
0,05 |
|
|
|
|
|
| DIY-P3-10 |
Mn4 |
0,09 |
|
|
|
|
|
| DIY-P3-2 |
Mn5(w) |
5,07 |
|
|
|
|
|
| DIY-P3-6 |
Mn5(w) |
3,07 |
|
|
|
|
|
| DIY-P3-7 |
Mn5(w) |
4,17 |
|
|
|
|
|
| DIY-P3-3 |
Mn6(w) |
0,21 |
0,22 |
|
0,21 |
|
0,51 |
| DIY-P3-4 |
Mn6(w) |
0,44 |
0,22 |
|
0,25 |
|
0,44 |
| DIY-P3-5 |
Mn6(w) |
0,09 |
0,22 |
|
0,41 |
|
0,47 |
| DIY-P3-14 |
V3(w) |
0,07 |
|
|
|
0,36 |
|
| DIY-P3-15 |
V3(w) |
0,05 |
|
|
|
0,36 |
|
| DIY-P3-16 |
V3(w) |
0,07 |
|
0,32 |
|
|
|
| DIY-P3-17 |
V3(w) |
0,05 |
|
0,32 |
|
|
|
| DIY-P3-18 |
V3(w) |
0,06 |
|
0,55 |
|
|
|
| DIY-P3-19 |
V3(w) |
0,09 |
|
0,56 |
|
|
|
| DIY-P3-20 |
V3(w) |
0,08 |
|
|
|
0,36 |
|
| DIY-P3-21 |
V2 |
0,06 |
|
0,56 |
|
|
|
1.3 Initial drying time test
Drying times of the samples present in table A.1.1 were investigated by means of a straight-line drying time
recorder. Due to the large number of drying time tests performed within the experimental work only a few
determinations have been made. The drying profiles of the samples are described through four different drying
stages, which are described in 7.1.3.1. The drying profile of the reference product DIY-P3 has also been
investigated for comparison.
The drying time profiles of an aged alternative sample, DIY-P3-13 aged and the aged reference are included in the
table as well.
Table A.1.2. Drying times at different stages obtained on a straight-line drying time recorder. For the alternative
systems and for the aged reference the results are single determination. For the reference product the results are an
average of 8 determinations.
| |
Drying time at different stages (h) |
| Sample |
Alternative |
Set-to-
touch |
Tack-
free |
Dry-
hard |
Dry-
through |
| Reference |
|
0,3 |
2,1 |
10,2 |
> 20 |
| Reference aged |
|
0,2 |
1,3 |
17,7 |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-1 |
Mn1 |
0,3 |
- |
5,3 |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-8 |
Mn1 |
0,2 |
2,8 |
5,8 |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-13 |
Mn1 |
0,3 |
0,7 |
5,5 |
8,8 |
| DIY-P3-13 aged |
Mn1 |
0,2 |
1,3 |
14,3 |
15,2 |
| DIY-P3-9 |
Mn4 |
0,3 |
? |
? |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-10 |
Mn4 |
0,3 |
- |
18,5 |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-2 |
Mn5(w) |
0,3 |
- |
17,3 |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-6 |
Mn5(w) |
0,2 |
2,6 |
13,5 |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-7 |
Mn5(w) |
0,2 |
2,6 |
(10,1) |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-3 |
Mn6(w) |
0,3 |
- |
10,7 |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-4 |
Mn6(w) |
0,3 |
- |
17,7 |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-5 |
Mn6(w) |
0,2 |
2,3 |
(12,9) |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-14 |
V3(w) |
0,2 |
2,8 |
18,7 |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-15 |
V3(w) |
0,2 |
2,8 |
(18,8) |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-16 |
V3(w) |
0,3 |
2,8 |
19,2 |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-17 |
V3(w) |
0,3 |
2,8 |
19,2 |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-18 |
V3(w) |
0,2 |
2,2 |
? |
? |
| DIY-P3-19 |
V3(w) |
0,3 |
(6,6) |
> 20 |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-20 |
V3(w) |
0,3 |
3,5 |
(16,2) |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3-21 |
V2 |
0,2 |
1,7 |
? |
? |
1.4 Further testing
As DIY-P3 is waterborne no anti-skinning agent is present in the product. Investigation of the most promising drier
systems with an anti-skinning agent is therefore omitted in this case. The complementary tests and stability tests
were made on a system chosen directly from the initial drying time test.
1.4.1 Stability test/ageing
Sample DIY-P3-13 was selected for the stability test, as it had the most promising drying time profile in the initial
testing (the composition of DIY-P3-13 is identical with DIY-P3-1 and DIY-P3-8).
Both sample DIY-P3-13 and the reference product were stored at 40 ºC for 2 weeks. Both samples had changed
slightly to a more "creamy" consistency. DIY-P3-13 had a slight reddish discolouration after storage.
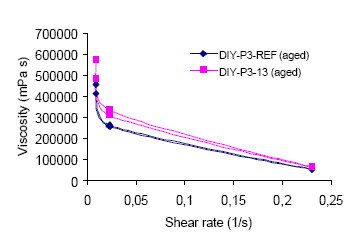
1.4.2 Viscosity
The viscosity has been measured as described in section 7.1.3.4. The viscosity measured at different shear rates at
23ºC can be seen in figure A.1 and A.2. Figure A.1 compares the viscosity of the DIY-P3 reference and
DIY-P3-13 before the samples are stored at elevated temperature for 2 weeks. Figure A.2 compares the viscosity
of the samples after they have been aged at elevated temperature. The results on which the viscosity curves are
based are given in table A.1.3.
Table A.1.3
Measured viscosities of DIY-P3 samples at different sheer rates at 23ºC.
| |
Viscosity (mPa s) |
| |
0,09 s -1 |
0,023 s-1 |
0,23 s-1</td>
| 0,023 s-1 |
0,09 s-1 |
| DIY-P3-REF |
373500 |
248500 |
54550 |
225500 |
364000 |
| DIY-P3-13 |
376000 |
290500 |
77950 |
314500 |
460500 |
| DIY-P3-REF (aged) |
376000 |
264000 |
54900 |
260000 |
459000 |
| PIY-P13-13 (aged) |
482500 |
310500 |
65100 |
355500 |
573500 |
DIY-P3-13 has a slightly higher viscosity than the reference product. The viscosity increases during storage for both
DIY-P3-13 and the reference product. The increase is slightly more noticeable for DIY-P3-13.
Figure a.1.1
Viscosity of DIY-P3-13 and The reference product, DIY-P3-REF measured at different shear rates at 23ºC. The
viscosity is measured before the samples have been aged.
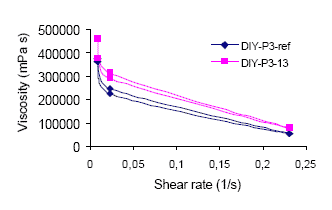
Figure a.1.2
Viscosity of DIY-P3-13 and The reference product, DIY-P3-REF measured at different shear rates at 23ºC. The
viscosity is measured after the samples have been aged.
1.4.3 Pendulum hardness
The hardness of the dry coating films was investigated by measuring the pendulum hardness of the films as
described in section 7.1.3.2.
The film hardness was determined for aged samples of DIY-P3 and the reference product of DIY-P3. A non-aged
sample of the reference was also included for comparison. The obtained film hardness is presented in table A.1.4.
The results are also shown in figure A.1.3.
table a.1.4
pendulum hardness after different drying periods For DIY-P3 samples that have been aged. A non-aged reference
sample was also included. The results are averages of three measurements.
| Drying time (h) |
Number of swings |
| DIY-P3-REF |
DIY-P3-REF (aged) |
DIY-P3-13 (aged) |
| 20 |
7 |
5 |
5 |
| 44 |
9 |
8 |
8 |
| 117 |
9 |
10 |
9 |
| 312 |
11 |
11 |
11 |
| 455 |
13 |
13 |
14 |
| 624 |
13 |
13 |
13 |
The film hardness of DIY-P3-13 is comparable to the reference. Both the aged reference and the aged sample of
DIY-P3-13 have a slightly softer film than the non-aged reference at the very start, but otherwise the hardness is
more or less identical for the three samples.
Figure a.1.3
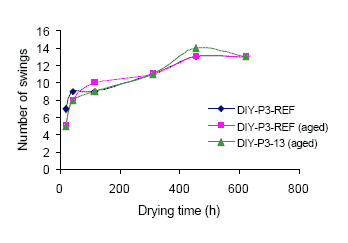
The film of DIY-P3 is relatively soft, as low numbers of pendulum swing have been observed. This accounts both
for the reference as well as the sample with the alternative drier system.
1.4.4 Gloss
The aged sample DIY-P3-13 has about the same gloss as the aged reference at 60ºC. The value being 47
compared to 53. The values are measured at 60º and are averages of three measurements.
1.4.5 Yellowing
DIY-P3-13 is comparable to the reference with regard to yellowing in dark places, as both samples got the ranking
2 – a small difference in colour is visible from more than one angle.
1.4.6 Drying time
DIY-P3-13 (aged) has a better drying profile than the aged reference product. See table A.1.2 where the results
have been included. The alternative and the reference have comparable set-to-touch and tack–free times, whereas
the alternative, DIY-P3-13 has a faster dry-hard and dry-through.
It should though be born in mind that the reference already had been stored for more than a year before it was aged
at elevated temperature together with the alternative. It could therefore be argued that the aged alternative rather
should be compared to the non-aged reference, but even so the DIY-P3-13 has comparable drying profile with the
reference. It takes longer before the aged alternative reaches the dry-hard condition. However, in return it reaches
the tack-free and dry-through conditions faster.
2 Performed test for all products
An overview of all the tests performed within this project during testing and evaluation of alternative driers and
anti-skinning agent is given below. The tests have been performed in accordance with the technical evaluation
procedures described in chapter 7.
2.1 Do-it-yourself products
Table A.2.1 describes the number of tests performed in connection with the investigation of alternatives to cobalt
driers and methyl ethyl ketoxime in the do-it-yourself products.
Table A.2.1
Test performed in connection with substitution of Co driers and methyl ethyl ketoxime in do-it-yourself (DIY)
products.
| Driers |
Number of tests performed |
| Product |
DIY-P1 |
DIY-P2 |
DIY-P3 |
DIY-P4 |
DIY-P5 |
DIY-P6 |
DIY-P7 |
DIY-P8 |
Total |
| Sample preparation |
22 |
27 |
19 |
36 |
23 |
40 |
16 |
39 |
222 |
| Drying time |
44 |
51 |
29 |
63 |
39 |
45 |
27 |
54 |
352 |
| Pendulum Hardness |
29 |
106 |
42 |
25 |
72 |
20 |
30 |
24 |
348 |
| Gloss |
5 |
7 |
5 |
7 |
9 |
4 |
6 |
6 |
49 |
| Viscosity |
4 |
6 |
4 |
6 |
8 |
0 |
4 |
6 |
38 |
| Stability |
2 |
3 |
2 |
3 |
3 |
0 |
2 |
3 |
18 |
| Yellowing |
2 |
3 |
2 |
3 |
7 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
21 |
| Anti-skinning agents |
Number of tests performed |
| Sample preparation |
7 |
7 |
0 |
8 |
7 |
0 |
7 |
0 |
36 |
| Skinning test |
14 |
14 |
0 |
8 |
14 |
0 |
14 |
0 |
64 |
A high number of sample preparations and drying time tests is in general an indication of that the product has been
particularly difficult to Co substitute. This especially accounts DIY-P1, DIY-P2, DIY-P4, DIY-P6 and DIY-P8. No
potential alternative drier system was identified in the case of DIY-P6. Alternative drier systems with some potential
to substitute cobalt driers were identified in case of DIY-P1, DIY-P2, DIY-P4 and DIY-P8, but in most cases,
except DIY-P1, a relatively high loss-of-dry was experienced after storage of the sample at elevated temperature,
as the drying times were increased considerably.
In the case of DIY-P1 and DIY-P7 substitution was possible with some success and for DIY-P3 and DIY-P5 the
substitutions came out quite successfully.
The most promising drier system for each solvent-borne product was chosen for use in the samples when
performing the skinning tests. The tests have been performed for one concentration only of each alternative
anti-skinning agent in each product. As DIY-P8 had an extent loss-of-dry after the ageing test, this product was not
included in the test of anti-skinning agent. Due to a limited amount of sample DIY-P4 was only tested with regard to
skinning in closed containers.
2.2 Industrial products
As the group of do-it-yourself products was tested and investigated before the group of industrial products, some
of the experiences could be used within this product group, and therefore fewer drier combinations and fewer tests
in general were needed for the industrial products. Table A.2.2 describes the number of tests performed in
connection with the investigation of alternatives to cobalt driers and methyl ethyl ketoxime in industrial air-drying
products. IND-P9 is already a cobalt-free product and has only been included for testing the alternative
anti-skinning agents.
Table A.2.2
Tests performed in connection with substitution of Co driers and methyl ethyl ketoxime in industrial products.
| Driers |
Number of tests performed |
| Product |
IND-P9 |
IND-P10 |
IND-P11 |
IND-P12 |
IND-P13 |
Total |
| Sample preparation |
- |
28 |
22 |
15 |
16 |
81 |
| Drying time |
- |
40 |
34 |
28 |
26 |
128 |
| Pendulum Hardness |
- |
129 |
54 |
104 |
79 |
366 |
| Gloss |
- |
5 |
9 |
9 |
5 |
28 |
| Viscosity |
- |
6 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
30 |
| Stability |
- |
3 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
15 |
| Yellowing |
- |
3 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
15 |
| Water resistance |
- |
0 |
4 |
5 |
5 |
14 |
| Anti-skinning agents |
Number of tests performed |
| Sample preparation |
10 |
7 |
7 |
7 |
0 |
31 |
| Skinning test |
20 |
14 |
7 |
14 |
0 |
55 |
As it can be seen from the number of sample preparations of drier systems and drying time tests, IND-P10 and
IND-P11 were more difficult to Co substitute than IND-P12 and IND-P13. Potential alternative drier systems
were identified for all four products, but in the case of IND-P10 a too high extent of loss-of-dry was observed
even though the drying times were quite low, as IND-P10 needs to be a very fast drying industrial coating. Even
though the film hardness of the alternative systems with time becomes comparable with those of the reference
product, the initial film hardness was too low.
In the case of IND-P11 the film hardness of the samples with alternative drier systems were far too low. This
problem might be overcome by adding Zn as an additional drier. Loss-of-dry after storage at elevated temperature
was also seen.
In IND-P12 and IND-P13 the cobalt driers were substituted with much higher success having comparable drying
time with the reference products even after the samples had been stored at elevated temperature. In the case of
IND-P12 three different manganese driers can be used as Co substitute all of them giving higher film hardness and
gloss, comparable or improved yellowing properties and comparable water resistance with reference product. Only
in one case, inferior water resistance was observed.
Also three driers could with success be used for substitution of Co in IND-P13, but in this case, the other film
properties as film hardness, gloss and water resistance were slightly inferior to the reference in most cases. All three
alternative systems were comparable to the reference with regard to yellowing.
The most promising drier system for each solvent-borne product was chosen to be used in the samples when
performing the skinning tests. The tests have been performed for one concentration only of each alternative
anti-skinning agent in each product. IND-P9 was supplied by the manufacturer with its original drier system.
2.3 Printing inks
The product group of printing inks differs quite a lot from the other investigated air-drying products. They are
typically used in a very thin film. Therefore they, also without hydroquinone, have relatively long drying times when
tested on a drying time recorder, even though they are applied in a much thinner film than the paint products.
Table A.2.3 describes the number of tests performed in connection with the investigation of alternatives to cobalt
driers and hydroquinone in sheet-fed printing inks.
Table a.2.3
Tests performed in connection with substitution of Co driers and hydroquinone in Sheet-fed printing inks.
| Driers |
Number of tests performed |
| Product |
INK-P14 |
INK-P15 |
INK-P16 |
INK-P17 |
Total |
| Sample preparation |
24 |
39 |
8 |
8 |
79 |
| Drying time |
31 |
49 |
10 |
10 |
100 |
| Set off |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
8 |
| Anti-skinning agents |
Number of tests performed |
| Auto-oxidation |
0 |
0 |
13 |
10 |
23 |
| Duct stability |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
40 |
The number of tested systems in INK-P16 and INK-P17 is much lower than in INK-P14 and INK-P15 as only the
two most promising alternatives, Mn1 and Mn2 from the testing of INK-P14 and INK-P15 were investigated. Mn4
has only been tested in INK-P15 due to late receipt of this drier, but it seems useful.
Only one drier system for each printing ink was chosen for the test of the set off effects. The set off effect of the
inks containing the alternative driers was compared to those of the reference inks.
The auto-oxidation measurements and test of duct were performed on samples containing original cobalt based
drier systems.
3 Comparison of drying times and film properties
The efficiency of the alternative driers has all been evaluated by measuring drying times of the samples containing
the alternative drier systems and comparing them to the drying times of the respective reference products.
More than 350 drying time measurements have been performed during the project to identify the most promising
cobalt substitute for each product included in the technical evaluation. The measurements are performed in
accordance with the description in section 7.1.3.1.
On basis of the initial drying time tests between 0 and 5 alternative drier systems were chosen for further testing for
each product. If no alternative drier systems were identified in the initial stage, as it e.g. is the case for DIY-P6, no
further testing was performed on the product.
In table A.3.1 and A.3.2 the presented results have been obtained from testing the alternative driers in
do-it-yourself products. The drying times of the respective reference product are presented as well for comparison.
Only drying times for the most promising alternative driers are shown. The used drier combinations and drier
concentrations are given as well. The systems having a cobalt drier are the reference products.
Table a.3.1
Drying time results before the product samples have been aged. The drying time profile is given as the drying times
at different stages. See description of stages in section 7.1.3.1.
| |
Drying time at different stages of the drying (h) |
| Product |
Primary
drier# |
Secondary
driers |
Set-to-
touch |
Tack-
free |
Dry-
hard |
Dry-
through |
| DIY-P1 |
Co |
Ca
Zr |
1,8 |
3,4 |
4,3 |
7,4 |
| Mn1 (1,84) |
Ca (0,17)
Zr (0,1) |
2,3 |
3,7 |
4,7 |
6,3 |
| Mn4 (0,06) |
None |
1,8 |
5,5 |
6,0 |
9,2 |
| DIY-P2 |
Co |
Ca
Zr |
0,7 |
2,9 |
14,1 |
> 20 |
| Mn1 (1,10) |
Ca (0,21)
Zr (0,3) |
0,8 |
3,3 |
19,1 |
19,1 |
| Mn2 (7,53) |
Ca (0,3) |
0,8 |
11,7 |
14,2 |
14,2 |
| Mn4 (0,06) |
Ca (0,1)
Zr (0,31) |
0,8 |
3,6 |
13,4 |
> 20 |
| DIY-P3 |
Co |
Ba
Zr |
0,3 |
2,1 |
10,2 |
> 20 |
| Mn1 (1,08) |
Ba (0,58)
Zr (0,24) |
0,3 |
0,7 |
5,5 |
8,8 |
| Mn5(w) (3,07) |
None |
0,3 |
2,6 |
13,3 |
> 20 |
| DIY-P4 |
Co |
Ca
Zr |
0,5 |
7,8 |
10,7 |
> 20 |
| Mn1 (2,07) |
Ca (0,2)
Zr (0,15) |
0,4 |
2,6 |
18,8 |
18,8 |
| Mn4 (0,08) |
Ca (0,05) |
0,4 |
5,3 |
14,2 |
> 20 |
| DIY-P5 |
C0 |
Ca
Zr |
2,7 |
11,0 |
14,3 |
- |
| Mn1 (2,99) |
Ca (0,2)
Zr (0,1) |
2,3 |
3,5 |
3,8 |
4,4 |
| Mn2 (7,82) |
Ca (0,3) |
2,4 |
7,7 |
10,3 |
> 20 |
| Mn3 (6,12) |
Ca (0,33) |
2,2 |
11,2 |
12,3 |
13,2 |
| Mn4 (0,11) |
None |
2,8 |
4,3 |
7,7 |
7,7 |
| DIY-p7 |
C0 |
Ca
Zn |
1,2 |
3,3 |
4,3 |
5,5 |
| Mn1 (3,01) |
Ca (0,16)
Zr (0,05) |
1,5 |
6,7 |
7,8 |
9 |
| DIY-P8 |
Co |
Ca
Zn |
1,8 |
4,2 |
5,5 |
6,9 |
| Mn1 (1,65) |
Ca (0,16)
Zr (0,04) |
0,9 |
9,8 |
11,5 |
12,4 |
| Mn4 (0,08) |
None |
0,8 |
7,3 |
8,5 |
9,2 |
# Concentration of Mn1, Mn2, Mn3, and Mn5(w) is given as concentration of the total drier product on solid
air-drying binder in the product. In the case of Mn4 and the secondary driers the concentration is given as metal on
the solid air-drying binder.
The results in table A.3.1 are for samples before they have been aged at elevated temperature, whereas table A.3.2
shows the results obtained after the ageing. In all solvent-borne products an anti-skinning agent has been added in
the same concentration as in the corresponding reference products.
Table a.3.2
Drying time results after the product samples have been aged. The drying time profile is given as the drying times at
different stages. See description of stages in section 7.1.3.1.
| |
Drying time at different stages of drying (h) |
| Product |
Primary
drier# |
Secondary
driers |
Set-to-
touch |
Tack-
free |
Dry-
hard |
Dry-
through |
| DIY-P1 |
Co |
Ca
Zr |
1,5 |
3,9 |
4,7 |
6,5 |
| Mn1 (1,84) |
Ca (0,17)
Zr (0,1) |
1,2 |
11,3 |
14,3 |
15,7 |
| Mn4 (0,06) |
None |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| DIY-P2 |
Co |
Ca
Zr |
0,5 |
4,8 |
17,8 |
17,8 |
| Mn1 (1,10) |
Ca (0,21)
Zr (0,3) |
0,4 |
9,7 |
17,8 |
17,8 |
| Mn2 (7,53) |
Ca (0,3) |
0,4 |
16,3 |
> 20 |
> 20 |
| Mn4 (0,06) |
Ca (0,1)
Zr (0,31) |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| DIY-P3 |
Co |
Ba
Zr |
0,3 |
1,3 |
17,7 |
> 20 |
| Mn1 (1,08) |
Ba (0,58)
Zr (0,24) |
0,3 |
1,3 |
14,3 |
15,2 |
| Mn5(w) (3,07) |
None |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| DIY-P4 |
Co |
Ca
Zr |
0,6 |
12,0 |
15,0 |
19,0 |
| Mn1 (2,07) |
Ca (0,2)
Zr (0,15) |
0,5 |
9,0 |
14,3 |
> 20 |
| Mn4 (0,08) |
Ca (0,05) |
0,6 |
7,5 |
16,8 |
> 20 |
| DIY-P5 |
C0 |
Ca
Zr |
2,8 |
> 20 |
> 20 |
> 20 |
| Mn1 (2,99) |
Ca (0,2)
Zr (0,1) |
2,3 |
18,3 |
> 20 |
> 20 |
| Mn2 (7,82) |
Ca (0,3) |
2,o |
> 20 |
> 20 |
> 20 |
| Mn3 (6,12) |
Ca (0,33) |
2,0 |
> 20 |
> 20 |
> 20 |
| Mn4 (0,11) |
None |
2,8 |
18,8 |
> 20 |
> 20 |
| DIY-p7 |
C0 |
Ca
Zn |
1,2 |
3,3 |
4,6 |
4,9 |
| Mn1 (3,01) |
Ca (0,16)
Zr (0,05) |
1,3 |
6,0 |
7,8 |
8,5 |
| DIY-P8 |
Co |
Ca
Zn |
4,0 |
6,5 |
7,9 |
9,2 |
| Mn1 (1,65) |
Ca (0,16)
Zr (0,04) |
1,5 |
> 20 |
> 20 |
> 20 |
| Mn4 (0,08) |
None |
- |
- |
- |
- |
# Concentration of Mn1, Mn2, Mn3, and Mn5(w) is given as concentration of the total drier product on solid
air-drying binder in the product. In the case of Mn4 and the secondary driers the concentration is given as metal on
the solid air-drying binder.
In the same way selected drying times are obtained from testing of the alternative driers in the industrial product
presented in table A.3.3 and A.3.4.
Table a.3.3
Drying time results before the product samples have been aged. The drying time profile is given as the drying times
at different stages. See description of stages in section 7.1.3.1.
| |
Drying time at different stages of drying (h) |
| Product |
Primary
drier# |
Secondary
driers |
Set-to-
touch |
Tack-
free |
Dry-
hard |
Dry-
through |
| IND-P10 |
Co |
Mn
Ca
Zr |
0,4 |
1,4 |
2,0 |
2,6 |
| Mn1 (2,67 ) |
Ca (0,08)
Zr (0,1) |
0,4 |
2,1 |
2,5 |
> 5 |
| Mn2 (4,44) |
Ca (0,06) |
0,4 |
2,3 |
3,5 |
(3.8) |
| Mn4 (0,06 ) |
None |
0,3 |
1,5 |
2,0 |
2,2 |
| IND-P11 |
Co |
Zn
Zr |
0,3 |
3,7 |
5,2 |
11,2 |
| Mn1 ( 2,57) |
Ca (0,1)
Zr (0,19 |
0,3 |
3,7 |
5,5 |
> 20 |
| Mn4 ( 0,08) |
Ca (0,1)
Zr (0,2) |
0,3 |
3,1 |
5,4 |
> 20 |
| IND-P12 |
Co |
Ca
Zr |
0,1 |
0,1 |
1,1 |
> 5 |
| Mn1 (2,72) |
Ca (0,12)
Zr (0,14) |
- |
0,06 |
0,5 |
> 1 |
| Mn2 (3,56) |
Ca (0,11) |
- |
0,06 |
0,2 |
> 5 |
| Mn3 (3,08) |
Ca (0,10) |
- |
0,07 |
0,15 |
> 5 |
| Mn4 ( 0,05) |
None |
- |
0,07 |
0,2 |
>5 |
| IND-P13 |
Co |
phenanthroline |
0,09 |
0,12 |
0,36 |
> 5 |
| Mn1 ( 1,71) |
Ca (0,1 ) |
- |
0,12 |
0,28 |
> 5 |
| Mn4 (0,08) |
None |
- |
0,1 |
0,23 |
> 5 |
| Mn5(w) (2,39) |
None |
- |
0,13 |
0,27 |
> 5 |
# Concentration of Mn1, Mn2, Mn3, and Mn5(w) is given as concentration of the total drier product on solid
air-drying binder in the product. In the case of Mn4 and the secondary driers the concentration is given as metal on
the solid air-drying binder.
Table a.3.4
Drying time results after the product samples have been aged. The drying time profile is given as the drying times at
different stages. See description of stages in section 7.1.3.1.
| |
Drying time at different stages (h) |
| Product |
Primary
drier# |
Secondary
driers |
Set-to-
touch |
Tack-
free |
Dry-
hard |
Dry-
through |
| IND-P10 |
Co |
Mn
Ca
Zr |
0,2 |
1,6 |
1,8 |
> 5 |
| Mn1 (2,67 ) |
Ca (0,08)
Zr (0,1) |
0,2 |
4,1 |
4,7 |
> 5 |
| Mn2 (4,44) |
Ca (0,06) |
0,2 |
> 5 |
> 5 |
> 5 |
| Mn4 (0,06 ) |
None |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| IND-P11 |
Co |
Zn
Zr |
1,7 |
3,4 |
4,4 |
5,5 |
| Mn1 ( 2,57) |
Ca (0,1)
Zr (0,19 |
1,7 |
10,3 |
13,2 |
14,0 |
| Mn4 ( 0,08) |
Ca (0,1)
Zr (0,2) |
1,7 |
7,0 |
8,3 |
13,0 |
| IND-P12 |
Co |
Ca
Zr |
0,08 |
- |
1,6 |
> 5 |
| Mn1 (2,72) |
Ca (0,12)
Zr (0,14) |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| Mn2 (3,56) |
Ca (0,11) |
- |
- |
1,6 |
> 5 |
| Mn3 (3,08) |
Ca (0,10) |
0,08 |
- |
0,6 |
> 5 |
| Mn4 ( 0,05) |
None |
0,08 |
- |
1,7 |
>5 |
| IND-P13 |
Co |
phenanthroline |
0,13 |
- |
0,35 |
> 5 |
| Mn1 ( 1,71) |
Ca (0,1 ) |
0,13 |
- |
0,35 |
> 5 |
| Mn4 (0,08) |
None |
0,10 |
- |
0,30 |
> 5 |
| Mn5(w) (2,39) |
None |
01,2 |
- |
0,33 |
> 5 |
# Concentration of Mn1, Mn2, Mn3, and Mn5(w) is given as concentration of the total drier product on solid
air-drying binder in the product. In the case of Mn4 and the secondary driers the concentration is given as metal on
the solid air-drying binder.
In table A.3.5 drying time results for printing inks are shown. Again only the most promising drier systems have
been included in the table. The inks with the cobalt drier system are the references.
Table a.3.5
Drying time results obtained for products in the group of printing inks. The drying times of the reference product are
given as well. The drying time profile is given as the drying times at different stages. See description is section
7.1.3.1.
| |
Drying time at different stages of drying (h) |
| Product |
Primary drier# |
Secondary
driers |
Set-to-touch |
Tack-free |
Dry-hard |
Dry-
through |
| INK-P14 |
Co |
Mn traditional |
28,3 |
31,3 |
> 50 |
> 50 |
| Mn1 (5,7) |
Mn traditional
(0,8) |
29,2 |
35,0 |
> 50 |
> 50 |
| INK-P15 |
Co |
Mn traditional |
14,6 |
36,3 |
43,3 |
44,2 |
| Mn1 (7,1) |
Mn traditional
(0,5) |
22,1 |
36,7 |
41,7 |
41,7 |
| Mn4 (0,07) |
Mn traditional (0,53) |
23,3 |
25,4 |
31,3 |
31,3 |
| INK-P16 |
Co |
Mn traditional |
16,3 |
26,7 |
> 50 |
> 50 |
| Mn1 (7,8) |
Mn traditional
(0,8) |
11,3 |
19,2 |
> 50 |
> 50 |
| INK-P17 |
Co |
Mn traditional |
4,6 |
5,8 |
35,4 |
35,4 |
| Mn1 (6,8) |
Mn traditional
(0,8) |
3,1 |
4,2 |
8,6 |
> 50 |
# Concentration of Mn1, Mn2, Mn3, and Mn5(w) is given as concentration
of the total drier product on solid air-drying binder in the product. In the case
of Mn4 and the secondary driers the concentration is given as metal on the solid
air-drying binder.
The drying time tests were performed without any anti-skinning in the case of INK-P16 and INK-P17 both for the
samples with alternative drier systems and for the corresponding reference. On basis of the obtained drying time
one drier system for each printing ink was chosen for test of set-off effect. The results of testing the inks with regard
to set-off effects can be seen in table A.3.6. The higher the measured density on the set-off paper the more set-off
the ink has. In general the set-off effects of the alternatives are comparable with the reference.
Table a.3.6
Set-off effects of printing inks containing alternative drier systems, and of reference inks. Obtained by measuring the
density of the set-off on paper.
| |
Density |
| Product |
Primary
drier# |
Secondary
driers |
30 s |
5 min |
10 min |
30 min |
| INK-P14 |
Co |
Mn traditional |
0,24 |
|
0,002 |
0,001 |
| Mn1 (5,7) |
Mn traditional
(0,8) |
0,17 |
|
0,005 |
0,004 |
| INK-P15 |
Co |
Mn traditional |
0,13 |
0,01 |
0,01 |
0,004 |
| Mn1 (7,1) |
Mn traditional
(0,5) |
0,14 |
0,02 |
0,01 |
0,007 |
| INK-P16 |
Co |
Mn traditional |
0,05 |
0,004 |
0,002 |
0,000 |
| Mn1 (7,8) |
Mn traditional
(0,8) |
0,13 |
- |
0,005 |
0,000 |
| INK-P17 |
Co |
Mn traditional |
0,19 |
0,012 |
0,006 |
0,006 |
| Mn1 (6,8) |
Mn traditional
(0,8) |
0,16 |
0,013 |
0,009 |
0,005 |
# Concentration of Mn1, Mn2, Mn3, and Mn5(w) is given as concentration of the total drier product on solid
air-drying binder in the product. In the case of Mn4 and the secondary driers the concentration is given as metal on
the solid air-drying binder.
After ageing the samples at 40ºC for 2 weeks the number of promising drier systems was reduced even further for
some products, mainly due to loss-of dry. The loss-of-dry can be observed by comparing the drying times of the
respective product before and after the ageing.
In the case of do-it-yourself products and industrial products film properties, film hardness, gloss, and yellowing in
dark places were also investigated to evaluate the efficiency of the alternative driers. Some of the industrial
products were further investigated with regard to early water resistance. The investigations have been performed as
described in various sections in chapter 7.
The results obtained are presented in table A.3.7 for both do-it-yourself and industrial products. Only the most
promising alternatives after the ageing are included in the table. The results for the aged reference products
are included as well.
Table a.3.7
Film properties of product samples that have been aged. The properties of the aged reference product are given as
well.
| Product |
Primary
drier# |
Secondary
driers |
Gloss (º) |
Hardness
(Number of
swings) |
Yellowing |
| DIY-P1 |
Co |
Ca
Zr |
40 |
24 |
1 |
| Mn1 (1,84) |
Ca (0,17)
Zr (0,1) |
44 |
20 |
3-4 |
| DIY-P2 |
Co |
Ca
Zr |
47 |
41 |
2 |
| Mn1 (1,10) |
Ca (0,21)
Zr (0,3) |
57 |
28 |
2 |
| Mn2 (7,53) |
Ca (0,3) |
63 |
34 |
3 |
| DIY-P3 |
Co |
Ba
Zr |
53 |
13 |
2 |
| Mn1 (1,08) |
Ba (0,58)
Zr (0,24) |
47 |
13 |
2 |
| DIY-P4 |
Co |
Ca
Zr |
69 |
24 |
2 |
| Mn1 (2,07) |
Ca (0,2)
Zr (0,15) |
88 |
19 |
3 |
| Mn4 (0,08) |
Ca (0,05) |
83 |
16 |
4 |
| DIY-P5 |
C0 |
Ca
Zr |
101 |
25 |
0 |
| Mn1 (2,99) |
Ca (0,2)
Zr (0,1) |
101 |
23 |
0 |
| Mn3 (6,12) |
Ca (0,33) |
96 |
30 |
0 |
| Mn4 (0,11) |
None |
101 |
20 |
0 |
| DIY-p7 |
C0 |
Ca
Zn |
65 |
11 |
0 |
| Mn1 (3,01) |
Ca (0,16)
Zr (0,05) |
77 |
14 |
0-2 |
| DIY-P8 |
Co |
Ca
Zn |
- |
- |
1 |
| Mn1 (1,65) |
Ca (0,16)
Zr (0,04) |
- |
- |
0 |
| IND-P10 |
Co |
Mn, Ca, Zr |
34 |
41 |
2 |
| Mn1 (2,67 ) |
Ca (0,08), Zr (0,1) |
49 |
36 |
2 |
| Mn2 (4,44) |
Ca (0,06) |
45 |
43 |
2 |
| IND-P11 |
Co |
Zn, Zr |
117 |
63 |
1 |
| Mn1 ( 2,57) |
Ca (0,1), Zr (0,19 |
126 |
27 |
0/1 |
| Mn4 ( 0,08) |
Ca (0,1), Zr (0,2) |
112 |
26 |
1 |
| IND-P12 |
Co |
Ca, Zr |
6 |
58 |
1 |
| Mn2 (3,56) |
Ca (0,11) |
5 |
58 |
0 |
| Mn3 (3,08) |
Ca (0,10) |
5 |
59 |
0 |
| Mn4 ( 0,05) |
None |
5 |
61 |
1 |
| IND-P13 |
Co |
phenanthroline |
9 |
34 |
0 |
| Mn1 ( 1,71) |
Ca (0,1 ) |
8 |
33 |
0 |
| Mn4 (0,08) |
None |
7 |
32 |
0 |
| Mn5(w) (2,39) |
None |
8 |
27 |
0 |
# Concentration of Mn1, Mn2, Mn3, and Mn5(w) is given as concentration of the total drier product on solid
air-drying binder in the product. In the case of Mn4 and the secondary driers the concentration is given as metal on
the solid air-drying binder.
Both the drying time and the investigated film properties have been taken into account when suggestions for the
most promising alternative drier systems have been made for each product. These selections can be seen in chapter
8.
| Front page | | Contents | | Previous | | Top |
Version 1.0 December 2003, © Danish Environmental Protection Agency
|