| 8. | Decabromobiphenyl | |
| 8.1 | Identification of the substance | |
| 8.1.1 | CAS No. | 13654-09-6 |
| 8.1.2 | EINECS No. | 237-137-2 |
| 8.1.3 | EINECS Name | 1,1'-Biphenyl, 2,2',3,3',4,4',5,5',6,6'-decabromo- |
| 8.1.4 | Synonyms | 2,2',3,3',4,4',5,5',6,6'-Decabromo-1,1'-biphenyl
DeBB Commercial DeBB (ex. Adine 0102) contains about 96-98% DeBB, 2-4% nonabromodiphenyl (NoBB, CAS No. 27753-52-2) and 0-0.3% octabromodiphenyl (OcBB, CAS No. 61288-13-9) (2) |
| 8.1.5 | Molecular Formula | C12Br10 |
| 8.1.6 | Structural Formula | 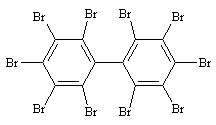 |
| 8.1.7 | Known uses | DeBB (Adine 0102) is used as a flame retardant for thermoplastics thermosets, for elastomers, and for cellulosics. It is sometimes applied with antimony trioxide (5) |
| 8.1.8 | EU Classification | Not included in Annex I to Directive 67/548/EEC |
| 8.2 | Physico-chemical Characteristics | |
| 8.2.1 | Physical Form | Solid |
| 8.2.2 | Molecular Weight | 943 |
| 8.2.3 | Melting Point/range (°C) | 380-386 (5) |
| 8.2.4 | Boiling Point/range (°C) | No data were available |
| 8.2.5 | Decomposition Temperature (°C) | 395 or > 400 (5) |
| 8.2.6 | Vapour Pressure (Pa (°C)) | < 6 x 10-6 (temperature
unknown) (5)
Volatility: <5% weight loss at 341°C (5) |
| 8.2.7 | Relative Density (D420) | 3.2 (5) |
| 8.2.8 | Vapour Density (air=1) | No data were available |
| 8.2.9 | Conversion Factor (1011 hPa at 25 °C) | No data were available |
| 8.2.10 | Solubility | Water: < 30 mg/l
(25°C)
Carbon tetrachloride: 10 g/kg (28°C)(5) |
| 8.2.11 | Partition Coefficient (log P ow) | 8.6 (calculated) (5) |
| 8.2.12 | Flammability | Not applicable |
| 8.2.13 | Explosivity | No data were available |
| 8.2.14 | Oxidising properties | No data were available |
| 8.3 | Toxicological Data | |
| 8.3.1 | Observations in humans | Human exposure to polybrominated biphenyls (PBB) has occurred through occupational contact and as a result of the accidental contamination of livestock feed in Michigan, U.S.A., in 1973. The unintentional addition of FireMaster FF-1 (mainly hexabromobiphenyl, but also some pentabromobiphenyl and heptabromobiphenyl), instead of magnesium oxide, to farm feed, resulted in exposure of large numbers of rural population Michigan (2). The general PBB half-life in humans has been estimated to approx. 11 years (4). |
| 8.3.2 | Acute Toxicity | |
| 8.3.2.1 | Oral | Oral LD50, rats: > 5
g/kg b.w.
No mortality was observed after oral administration of 5 g/kg b.w. DeBB (96.8% pure) to rats during an observation period of 14 days (2) Oral LD50, rats: > 20 g/kg b.w. (5) |
| 8.3.2.2 | Dermal | Dermal LD50, rats: > 5
g/kg b.w.
No mortality was observed after cutaneous administration of 5 g/kg b.w. DeBB (96.8% pure) to rats during an observation period of 14 days (2) |
| 8.3.2.3 | Inhalation | No data were available |
| 8.3.2.4 | Other Routes | No data were available |
| 8.3.2.5 | Skin Irritation | 50% DeBB in olive oil was mild skin irritating (5) |
| 8.3.2.6 | Eye Irritation | 50% DeBB in olive oil was not eye irritating. DeBB powder caused mild irritation (5) |
| 8.3.2 7 | Irritation of Respiratory Tract | No data were available |
| 8.3.2.8 | Skin Sensitisation | No data were available |
| 8.3.2.9 | Sensitisation by Inhalation | No data were available |
| 8.3.3 | Subchronic Toxicity | |
| 8.3.3.1 | Oral | No data were available |
| 8.3.3.2 | Inhalation | No mortality was observed after exposure to 5 mg DeBB dust/l for 6 hours/day, 5 days/week, for 4 weeks. An increase in liver weights was observed. No details were available.(2, 5) |
| 8.3.3.3 | Dermal | No data were available |
| 8.3.4 | Chronic Toxicity and Carcinogenicity | No data were available |
| 8.3.5 | Mutagenicity | |
| 8.3.5.1 | Gene Mutation | A commercial DeBB was not mutagenic to Salmonella typhimurium strains TA-1535, TA-1537 and TA-1538, in the presence or absence of metabolic activation. The product was also negative in a host-mediated assay with strain TA-1538, in mice receiving oral doses of 5, 10 and 20 g/kg b.w. (3) |
| 8.3.5.2 | Chromosome Abnormalities | A micronucleus test was performed on male and female mice administered a total dose of 5, 10 or 20 g/kg b.w. at 2 doses. DeBB was negative in this test (5). |
| 8.3.5.3 | Other Genotoxic Effects | No data were available |
| 8.3.6 | Reproductive Toxicity, Embryotoxicity, and Teratogenicity | |
| 8.3.6.1 | Reproductive Toxicity | No data were available |
| 8.3.6.2 | Teratogenicity | Groups of Sprague-Dawley rats were administered doses of 0, 10 or 1,000 mg/kg/day gestation day 6 through 15. No maternal effects were noted. No teratogenicity or embryotoxicity was observed (5) |
| 8.3.7 | Other Toxicity Studies | No data were available |
| 8.3.8 | Toxicokinetics | No data were available |
| 8.4 | Ecotoxicity | The LC50 for fish was 250 mg/l (48h). The bioconcentration factor was 0.6-5.4 (6w, 0.15 mg/l) (1) |
| 8.5 | Environmental Fate | DeBB is not readily biodegradable (0.8% of BOD, 2w, 100 mg/l substance, 30 mg/l sludge) (1) |
| 8.6 | Environmental Concentrations | No data were available |
| 8.7 | Conclusion | |
| 8.7.1 | Health Assessment | Only few data on mainly
acute toxicity and genotoxicity were available.
DeBB apparently has a low toxicity by the oral, dermal and pulmonal route of exposure. It was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium assays or in a micronucleus test. Based on carcinogenicity studies with Firemaster FF-1, composed mainly on hexabromobiphenyl with smaller amounts of penta- and heptabrominated isomers, IARC found sufficient evidence for the carcinogenicity of commercial mixtures of PBB to experimental animals. There was inadequate evidence for the carcinogenicity of PBB to humans. PBB is in general considered to be bioaccumulative. |
| 8.7.2 | Environmental Assessment | As very few ecotoxicity and
environmental fate data were available for DeBB, data for the
analogous substance decachlorobiphenyl (CAS No. 2051-24-3) were
searched, but no data were available on that substance.
Too few ecotoxicity and environmental fate data for DeBB were available for environmental assessment. |
| 8.8 | References | 1. Chemical Inspection and
Testing Institute. Biodegradation and bioaccumulation data of
existing chemicals based on the CSCL Japan, compiled under the
supervision of chemical products safety Division Basic industries.
Japan: Japanese Chemical Industry Ecology-Toxicology &
Information Center, 1992.
2. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Some Halogenated Hydrocarbons and Pesticide Exposures. Switzer-land: International Agency for Research on Cancer, World Health Organisation, 1986: 261-92. (IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans; 41). 3. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Overall Evaluations of Carcinogenicity: An Updating of IARC Monographs Volumes 1 to 42. Switzerland: International Agency for Research on Cancer, World Health Organisation, 1987: 73. (IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans; Supplement 7). 4. Rosen DH, Flanders WD, Friede A, Humphrey HE, Sinks TH. Half-life of polybrominated biphenyl in human sera. Environmental Health Perspectives 1995; 103(3):272-4. 5. WHO working group. Polybrominated Biphenyls. Environmental Health Criteria 1994; 152. |