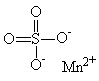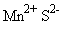Appendices 1-18 to: Report on the Health Effects of Selected Pesticide CoformulantsAppendix 1: Manganese (II) sulphate, Manganese (II) sulphide1 General description1.1 Identity1.2 Physical / chemical properties Because limited data are available specifically for manganese sulphate and manganesse sulphide, and most manganese compounds seem to cause the same adverse effects, this paper includes several studies with other inorganic manganese compounds.s Manganese displays oxidation states: +2, +3, +4, +6 and +7. Compounds in which manganese is in its +2 oxidation state are the most stable ones, but bivalent manganese can be readily oxidized to the +3 and +4 states. (Beliles 1994). In this paper, the following manganese compounds are addressed: Manganese (II) sulphate (MnSO4) 1.1 IdentityMolecular formula: a) MnSO4 Structural formula: a) b) Molecular weight: a) 151.00 CAS-no.: a) 7785-87-7 Synonyms: a) Manganese sulphate 1.2 Physical / chemical propertiesDescription: a) Manganese sulphate forms several hydrates. The b) Manganese sulphide is a pink, green or brown- In moist conditions manganese sulphide readily
Melting point: a) 700°C Boiling point: a) 850°C (decomposes) Density: a) 3.25 g/ml Vapour pressure: - Concentration of saturated vapours: - Solubility: a) Water: 520 g/l (at 5°C), 700 g/l (at 70°C) b) Insoluble in water. Soluble in diluted acids. References: ATSDR (2000), ChemFinder (2001), HSDB (2000),
|