Development and use of screening methods to determine chromium (VI) and brominated flame retardants in electrical and electronic equipment
2 Presence of PBDEs and PBBs in electrical and electronic equipment
- 2.1 What are PBDEs and PBBs?
- 2.2 Applications of the substances in electrical and electronic products
- 2.3 Decision tree
2.1 What are PBDEs and PBBs?
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs) are two groups of substances that are or have been used as flame retardants in plastic and textiles. In some countries, including the USA, PBDEs are also known as PBDOs.
Both groups of substances are characterised by consisting of two benzene rings with 1 - 10 bromine atoms attached.
The figure below shows a PBDE with 10 bromine atoms called deca-bromodiphenyl ether (deca-BDE). Greek numerals are used to designate the substances based on the number of bromine atoms. The most common types are tetra-BDEs (with 4 bromine atoms), penta-BDEs (with 5 bromine atoms), hexa-BDEs (6), hepta-BDEs (7), octa-BDEs (8), nona-BDEs (9) and deca-BDEs (10). Corresponding designations are used about PBBs with different numbers of bromine atoms.²
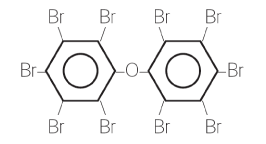
Commercial PBDE and PBB products normally consist of a mix of substances with different numbers of bromine atoms. The limit value of 0.1% applies to the sum of all PBDEs or the sum of all PBBs in the material.
Until recently, three commercial PBDE mixtures were marketed under the slightly confusing designations: penta-BDEs, octa-BDEs and deca-BDEs. The composition varies somewhat from one producer to the next, but the composition of products from Western producers has typically been in accordance with the below table.
| Commer-cial product | composition by percentage of a commercial product | |||||||
| tri- | tetra- | penta- | hexa- | hepta- | octa- | nona- | deca- | |
| Deca-BDE | 0.3-2 | 97-98 | ||||||
| Octa-BDE | 10-12 | 43-44 | 31-35 | 9-11 | 0-1 | |||
| Penta-BDE | 0-1 | 24-38 | 50-62 | 4-8 | ||||
PBDEs and PBBs are always used together with antimony trioxide (Sb2O3), which acts as a synergist, i.e. the presence of antimony trioxide increases the flame-retardant effect of PBDEs and PBBs. The bromine (Br)-antimony (Sb) ratio is typically about 3:1, but it may vary considerably.
2.2 Applications of the substances in electrical and electronic products
Presence of deca-BDEs
Deca-BDEs are the most commonly used PBDEs, and the world's total consumption amounted to more than 50,000 tons in about 2007. For a period of time, deca-BDEs were subject to an exemption from the RoHS Directive, but the exemption expired on 30 June 2008.
Deca-BDEs are produced by a number of companies. The most commonly used commercial products in Western countries are SAYTEX® 102E (Albemarle Corp.), Great Lakes DE-83 RTM (Great Lakes Corp.) and FR 1210 (ICL Industrial Products).
The table below states the most typical applications of deca-BDEs and the amount of deca-BDE and antimony trioxide (Sb2O3) the plastic should contain in order to comply with the highest fire safety standards, i.e. V-0 quality. Lower-level fire safety applications use smaller amounts of deca-BDE and antimony trioxide, which means that the cabinets of appliances will often contain smaller concentrations than stated in the table.
| Type of plastic | Typical applications in electrical and electronic products | Deca-BDE in V-0 quality plastic (percentage of plastic) | Antimony trioxide (percentage of plastic) |
| HIPS (high-impact polystyrene) | Cabinets for TV sets, mobile phones, AV equipment, remote controls | 12-13% | 4-5% |
| ABS | Cabinets and small moulded structural parts of many appliances | 13-15% | 5% |
| PBT/PET (thermoplastic polyester) | Switches, relays, plugs, connectors - components requiring a high level of durability | 10,4 % | 4% |
| Polyamide (PA, nylon) | Switches, relays, plugs, connectors - components requiring a high level of durability | 16-18 % | 6-7 % |
| Polyethylene and polypropylene (collectively often called polyolefins) | Cables and wires, film in capacitors, lamp sockets | 20-30% | 6-10% |
Until recently, the most common global application by far of deca-BDEs was in HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) for back panels of TV sets for the American market. Deca-BDEs have generally not been used in TV back panels on the European market for many years. It is not possible to point out any obvious places to look for deca-BDEs, but in general deca-BDEs have not been used as flame retardants in printed circuit boards and casings for electronic components. For example, Deca-BDEs were used in about 10% of all flame-retardant plastic components of PBT/PET and polyamids, but in principle, they may be present in any plastic component; the application is mainly determined by the producers' attitude to using the substance.
In addition to the deliberate application, deca-BDEs may be present in plastic parts made of recycled plastic. In such parts, deca-BDEs may be present in lower concentrations with the addition of another brominated flame-retardant to obtain a sufficient flame-retardant level.
For several years, a number of major producers have announced that their products do not contain PBDEs and PBBs. PBDEs and PBBs are therefore not likely to be found products from those producers, which include: Dell, Hewlett-Packard Company (including HP and Compaq), Sony, IBM, Ericsson, Apple, Matsushita (including Panasonic), Intel and B&O.
Presence of octa-BDEs
Octa-BDEs have mainly been used for ABS-type plastic, which is used for cabinets and moulded structural parts in electrical and electronic products. Octa-BDEs used to be the preferred ABS flame retardant. ABS is used for many small parts where high-strength plastic is not required.
In about 2001, global consumption amounted to approx. 4000 tons. For several years, Octa-BDEs and penta-BDEs have been prohibited in all types of products sold in the EU, and production seems to have been more or less discontinued worldwide.
Octa-BDEs were typically used in concentrations of 12-18% with 4-7% antimony trioxide.
Consequently, it is not likely that octa-BDEs have been deliberately added to electrical and electronic products, but as ABS plastic is suitable for recycling, octa-BDEs may well be present in all parts manufactured of recycled ABS.
In cases where octa-BDEs have been present in part of the recycled plastic, small amounts of octa-BDEs may be present in the plastic with the addition of another brominated flame retardant to obtain a sufficient flame-retardant level. Small, moulded, dark grey or black parts will often be manufactured of recycled glass where the black pigment ensures a homogeneous appearance regardless of the recycled plastic parts used in the lot.
Presence of penta-BDEs
Penta-BDEs have mainly been used in foam products, and penta-BDEs are not very likely to be found in electrical and electronic products.
Presence of PBBs
PBBs have not been manufactured for a number of years, and deliberately added PBBs are not very likely to be found in new electrical and electronic products. The only type of PBB that has been in commercial use is deca-BB, small amounts of which were used in HIPS, PBT and PET in concentrations of about 10%. PBBs may be present in recycled plastic in lower concentrations with the addition of another brominated flame retardant to obtain a sufficient flame-retardant level.
Rule-of-thumb applying to all PBDEs and PBBs
PBDEs and PBBs are always used together with antimony trioxide, which acts as a synergist.
A number of brominated flame retardants are not used together with antimony, and the presence of antimony can therefore be used to rule out plastic with such flame retardants from further examination. Unfortunately, typical alternatives to PBDEs and PBBs are also used together with antimony trioxide, so it cannot be concluded that the presence of Br and Sb together indicates the presence of PBDEs or PBBs.
The following rule-of-thumb can be used to interpret the results of an XRF analysis:
- Br is not present > the plastic does not contain PBDEs or PBBs;
- Br is present, but Sb is not present > the plastic does not contain PBDEs or PBBs;
- Br and Sb are both present > the plastic may contain PBDEs or PBBs.
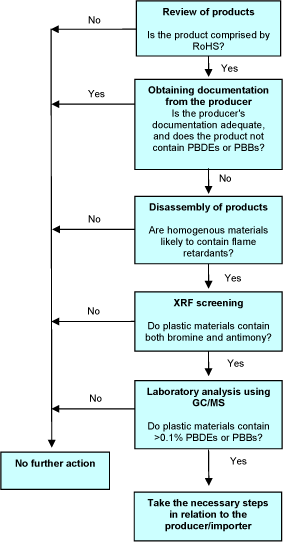
2.3 Decision tree
The decision tree below illustrates the procedure of the proposed method.
As regards documentation from producers of products or components, control may obviously be necessary even though the documentation seems to be adequate, but when planning the control measures, it may be relevant to give higher priority to products with less adequate documentation. Minimum documentation is a producer's certificate stating that the product does not contain RoHS substances above the limit value, but it is better if such a certificate is supported by an analysis report from an independent analysis laboratory. In this connection it should be noted that an analysis report may often be available which states the results of the analyses of a number of the product's components without all components having necessarily been analysed. It is therefore necessary to critically review the analysis report in terms of components that may contain RoHS substances.
Figure 1 Decision tree in relation to PBDEs and PBBs
[2] Apart from deca-BDE, which only exists in one form, there may be different isomers of each type - substances with the same number of bromine atoms, but with the bromine atoms in different positions. For example, there are 3 nona-BDE isomers and 12 octa-BDE isomers. In total, there may be 209 different PBDE combinations, in this connection referred to as 209 congeners. The term congeners is used about substances built around the same basic structure, but with a varying number of bromine atoms in different positions.
Version 1.0 May 2009, © Danish Environmental Protection Agency