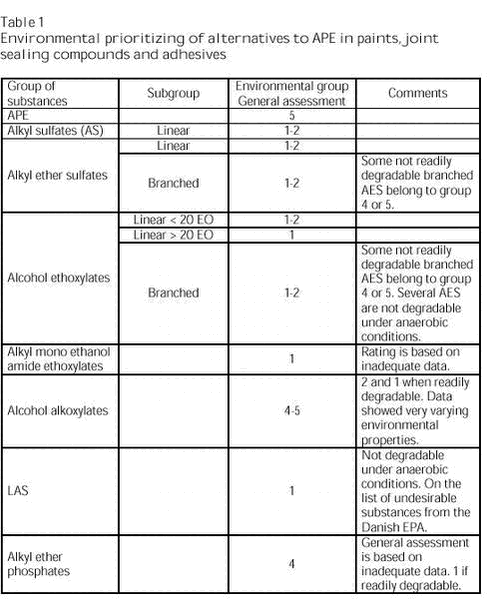
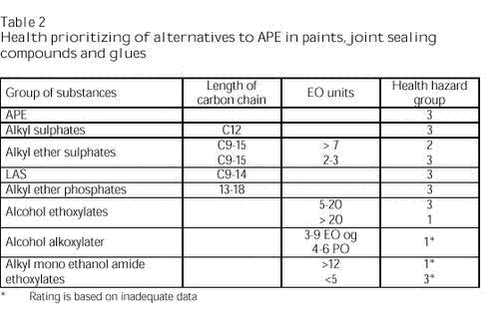
Substitution of APE in Paint, Wood Preservatives, Adhesives and Joint Fillers Summary and conclusionsAlkyl phenol ethoxylates (APE) were previously used in the production of water-borne paints, wood protection systems, joint fillers, sealants and adhesives. The major part of the APE content in the products originated from the production of binders, which had typically been developed with APE as the tenside. The tensides used during production greatly influence the properties of the binder. Substitution of APE in paints is thus very resource-consuming as the substitution considerably affects the binder, which is the foundation of paints and adhesives. Alkyl phenol ethoxylate (APE) has some properties that are problematic with respect to health and the environment. APE is not readily degradable according to standardized tests for ready biodegradability and is found in high concentrations in sewage sludge. Furthermore, the degradation products of APE (alkyl phenol (AP) and APE with one or two ethoxy groups) are very toxic to aquatic organisms. Some APs are under suspicion of having endocrine disrupting effects. In the initial phase of the project, information on alternatives to APE was collected by contacting producers of binders and tensides. All tensides proposed as an alternative to APE were screened on the basis of the environmental and health data in the material safety data sheets. In order to make the environmental and health screening, we used a rating system dividing the tensides into five groups from 1 to 5 and 0, of which 1 is best, 5 is worst and 0 expresses lack of data. Tables 1 and 2 present the results of the screening.
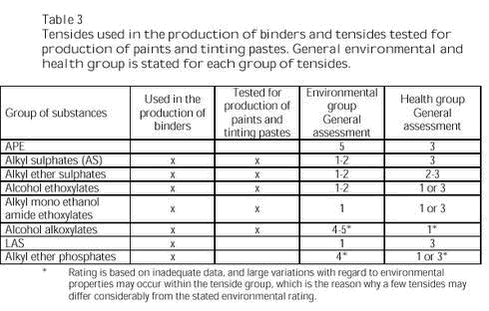
The screenings were supplemented with more general environmental and health assessments of the types of tensides proposed as alternatives. Furthermore, criteria for acceptable and good alternatives to APE were elaborated. Acceptable alternatives are tensides that, when discharged via wastewater treatment plants (WWTP), will have minimal environmental impacts, and their health properties make their handling during the production of paints acceptable, and allow normal use of the finished product without influence on health. Good alternatives are tensides that, when discharged via WWTP as well as directly to recipient, will have minimal environmental impacts and that may be used without considerable precautions in the production and application of paints. Furthermore, potential focus areas not yet implemented in the chemicals regulations have been taken into account. The alternatives include tensides that in normal use will have minimal impacts on health and the environment during the production and application of paints and that are expected to be usable in paints without any special restrictions or precautions now as well as in future. The criteria for good and acceptable alternatives to APE are developed in order to provide companies and others working within the chemicals area with easily accessible guidelines for chemicals that have minimal impacts on humans and the environment. The criteria for good alternatives are based on assumptions of which criteria must be met in order to ensure that – with currently available knowledge - the chemicals can be considered lasting alternatives. The best alternatives stated by tenside producers and users are: Alternatives with acceptable environmental properties: Alternatives with acceptable health properties: APE was given an environmental rating of 5 and a health rating of 3. Furthermore, in the closing phase of the project, the producers of binders were contacted for an estimate of which tensides are used today. Some producers stated which tensides (types of tensides) had replaced APE. Parallel with this project, Akzo Nobel Deco A/S developed paints and wood protection systems without use of APE during the production of paints as well as tinting pastes. The substitution of APE was successful for both producers of binders and Akzo Nobel Deco A/S, and today only very few niche products from Akzo Nobel Deco A/S contain APE. It has not been possible to obtain information on the specific tensides that have replaced APE, but the producers of binders have stated the types of tensides used. Table 3 shows the tensides used in the production of binders today and the tensides that have been tested in the production of paints and tinting pastes. The applied types of tensides are all among the types proposed by the producers of binders and tensides in the initial phase of the project. It should be noted, however, that the list below does not cover all producers of binders and is, thus, not exhaustive for tensides used in the production of binders and paints. Most of the tensides used today can be characterized as acceptable and some of them even as good alternatives to APE. Most of the tensides used today can be characterized as acceptable and some of them even as good alternatives to APE.
|