[Front page] [Contents] [Previous] [Next] |
Reduction of Environmental Pressure from Car Transport - Extended Summary
Chapter 3: State and Development of Danish Road Transport
Inventory of transport and environmental impact today
Chapter 3 describes Danish road transport in a number of quantitative entities that
provide the background and yardstick for the future reduction targets. This includes an
inventory of the passenger transport work, the breakdown of the transport by branches and
purposes of travel, and the transport's consumption of materials and energy and emission
of carbon dioxide (
The inventories of the consumption of materials and energy and emission of
- Construction and maintenance of roads;
- consumption of motor fuel and the energy for its production; and
- consumption of materials, spare parts, and energy for the production of motorcars.
The results of the inventories for passenger car transport are shown in Table 1. In the
table the inventory of total consumption is complemented with figures for the intensity of
materials consumption (MIPS)[1], the consumption of
energy, and the emission of
Table 1. Materials, energy use and
In Fig. 1 the distribution of materials and energy consumption, as well as the emission
of
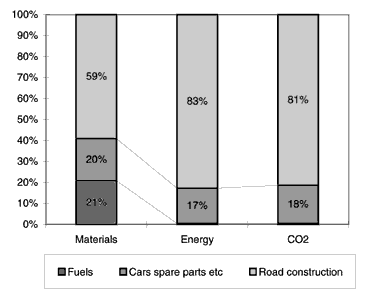
Fig. 1. The breakdown of materials, energy and the emission of
Fuels are the biggest item
Motor fuel – including the production of the fuel – generally represent the biggest share, although the share has been somewhat reduced in respect of the consumption of materials, where road construction and maintenance account for the biggest share.
Road construction and maintenance account for a substantial part of the consumption of
materials from car transport, but their role in connection with energy consumption and
In contrast, the production of motorcars and spare parts represent approximately the
same share of the consumption/emission for materials, energy and
[1] MIPS = Materials Intensity per
Service Unit
[Front page] [Contents] [Previous] [Next] [Top] |