Danish-Polish Environmental Co-operation 1991-2000
Enclosure 1Country characteristics
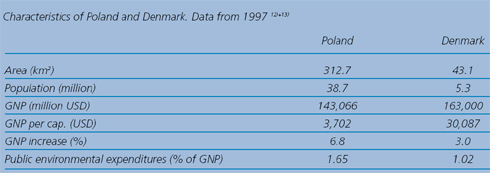
Measured in terms of area and population Poland has a size, which is approximately seven times the size of Denmark. The GNP per capita is significantly higher in Denmark. However, a high GNP growth in Poland continues to reduce the existing difference in the economic capacity of the two countries.
The table below summarises the most important differences between Poland and Denmark in terms of size and economy.
Poland has applied for EU membership. The accession to the EU requires that Poland in the future allocates considerable financial resources to fulfil the EU legislation. Several estimates of the costs for this are given from various sources. The latest is in the range of 35 billion EUR and distributed as follows:
In the period from 1989 up to present Poland has been through a transformation to a modern democratic state. The reforms of the public administration in Poland, which were adopted by the Polish Parliament in 1998 and were into force by 1.1.1999 have been an essential step in this process.
The Republic of Poland is headed by the President and the Government, while the lawmaking bodies are the Polish Parliament, the "Sejm" (the lower house), which has 460 members, and the "Senat" (the upper house), which has 100 members.
The administrative structure of the country consist of voivodships, districts and communes.
Voivodships
Poland is divided into 16 voivodships. As a kind of province, a voivodship is governed by a Voivode, who performs tasks similar to those of the French Prefect. The Voivode is appointed by and accountable to the Prime Minister, as the Central Government representative in the voivodship. On the basis of powers established in laws, a Voivode has the right to impose local legal regulations, which are in force in the voivodship.
There also are elective local government bodies, at voivodship level called Sejmiks or Regional Assemblies. The executive body of the Assemblies is the Regional Voivodship Council, led by a Marshal. The Voivodship authorities (the Voivode and the Council) have numerous, legally established powers concerning the protection of the environment (they design environmental protection programmes, issue administrative decisions, etc.).
12 Danish Statistical Office - Website
13Polish Statistical Office - Website
Districts (Counties)
Districts (Powiaty in Polish) were created on January 1st, 1999 and are selfgoverned Countylike structures. There are 373 in Poland (including 65 cities and towns with equivalent rights). District authorities comprise an elective Council and a District Board led by the Starosta. District authorities have considerable power concerning environmental protection. Amongst other things, they issue administrative decisions concerning the emission of air pollutants, water law licences, waste production licences, etc.
Communes
Communes (Gminy in Polish) are the basic administrative units in the country. There are 2489 of them in Poland. They are selfgoverned entities with elective governments. Executive functions are performed by a Commune Board, led by a Chief Officer, Mayor or President. Commune authorities have detailed powers concerning environmental protection. Amongst other things, they draw up and establish local physical development plans and basic documents concerning prevention of environmental threat. They also issue administrative decisions (e.g. concerning waste treatment, green space) and comment on practically all decisions of district and voivodeship authorities.
Within their basic powers districts and communes can impose local laws, including those concerning environmental protection. Local self-government in Poland has been functioning since 1990 in the gminas. The reforms in 1999 introduced the two other levels of self-government and reduced the central government's administrative presence at the sub-national level.
The reforms decentralised the competencies and finances to 308 democratically elected self-governments at the poviat level (county level) and to the authorities of 65 municipal gminas, which were granted poviat rights.

14Compliance Costing for approximation of EU environmental legislation in the CEEC, EU DGEnlargementa
The reforms have reduced the number of existing voivodships (regional level) from 49 to 16.
For comparison Denmark is governed by the Danish Parliament, "Folketinget", which has 179 members. The 14 County Councils and 275 Municipalities are largely independent, each with their own administration and financial budget.
Denmark's membership of the European Economic Community was decided in 1972 by referendum.